Overview
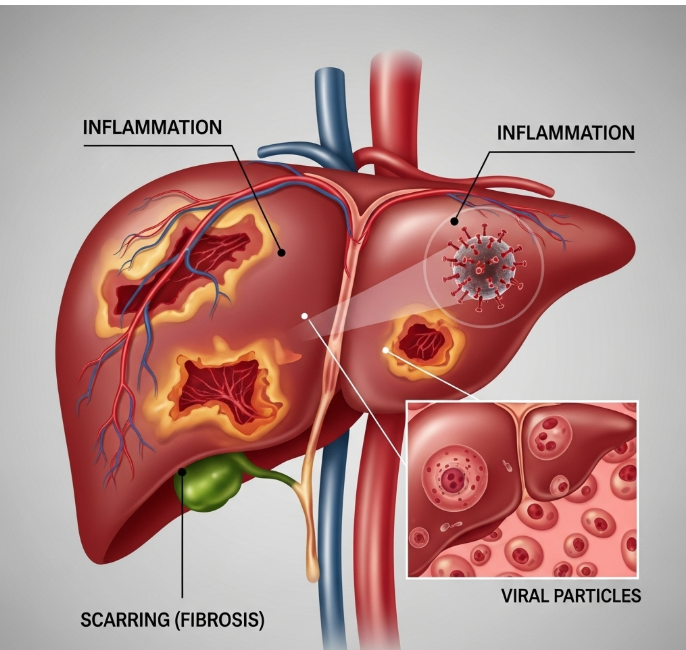
Hepatitis refers to inflammation of the liver caused by viral infections, toxins, alcohol, or autoimmune processes. In Korea, viral hepatitis—particularly hepatitis B and C—remains a significant public health concern. Early diagnosis, vaccination, and antiviral treatment are crucial to prevent chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
What is Hepatitis?
Hepatitis is the inflammation of liver tissue that can affect liver function. It can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term). Common viral causes include hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E, each with different modes of transmission. Hepatitis affects people of all ages, with chronic forms posing long-term health risks.
Symptoms
- Fatigue and general weakness
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes)
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain or discomfort, particularly in the upper right quadrant
- Dark urine and pale stools
- Fever (in some viral types)
Causes
- Viral infections: Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E
- Excessive alcohol consumption leading to alcoholic hepatitis
- Autoimmune hepatitis, where the immune system attacks liver cells
- Medication or toxin-induced hepatitis from certain drugs or chemicals
Risk Factors
- Unprotected sexual activity or multiple partners (hepatitis B and C)
- Intravenous drug use
- Exposure to contaminated food or water (hepatitis A and E)
- Chronic alcohol use
- Family history of liver disease
- Travel to areas with high prevalence of hepatitis A or E
Complications
Untreated hepatitis can lead to:
- Chronic hepatitis and persistent liver inflammation
- Liver fibrosis and cirrhosis
- Liver failure
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer)
- Co-infections with multiple hepatitis viruses
Prevention
- Vaccination against hepatitis A and B (widely available in Korea)
- Safe sex practices and avoiding sharing needles
- Proper hygiene and food safety
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Regular liver function tests for high-risk individuals
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea provides advanced care for hepatitis through specialized hepatology and gastroenterology centers:
- Medications:
- Antiviral therapies for hepatitis B and C to suppress viral replication and achieve remission
- Supportive care for acute hepatitis to manage symptoms
- Monitoring:
- Regular liver function tests, imaging, and fibrosis assessment to monitor disease progression
- Liver transplantation:
- For severe liver failure or end-stage liver disease, available in major hospitals such as Samsung Medical Center, Seoul National University Hospital, and Asan Medical Center
- Lifestyle management:
- Dietary guidance, alcohol abstinence, and weight management to reduce liver stress
- Public health initiatives:
- Nationwide vaccination programs and screening campaigns to prevent viral hepatitis transmission
With early detection, proper treatment, and preventive measures, patients in Korea can manage hepatitis effectively and reduce the risk of severe liver-related complications.