What It Is
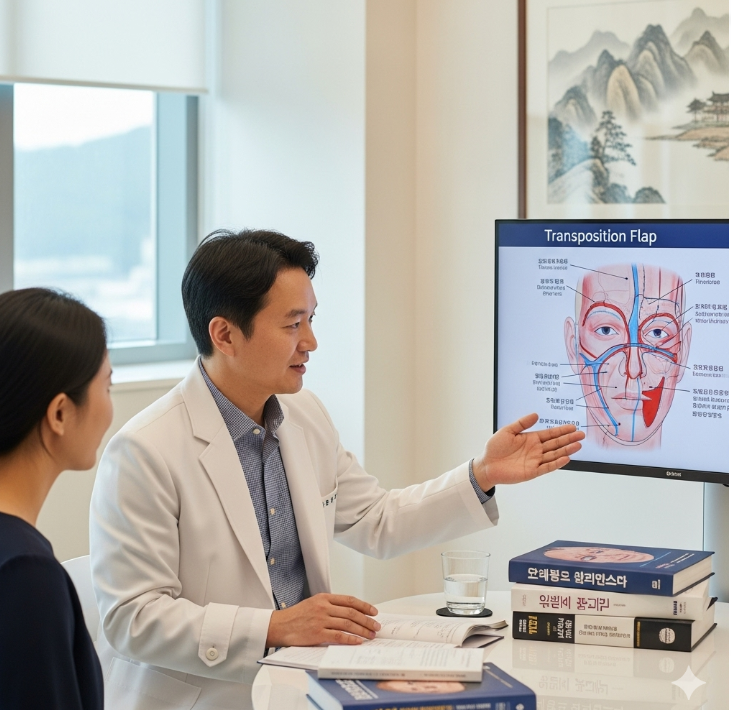
A transposition flap is a reconstructive surgery technique that uses a triangular or rectangular section of nearby skin and soft tissue, which is lifted and moved over an area of intact skin to cover a defect. Unlike advancement or rotation flaps, transposition flaps cross over adjacent tissue to reach the wound, making them ideal for irregularly shaped or awkwardly positioned defects.
Common examples include Z-plasty, bilobed flaps, and rhomboid flaps. This technique is especially useful for repairing defects on the face, nose, eyelids, and around joints, where precise cosmetic and functional restoration is essential.
Why It’s Done
Patients undergo transposition flap surgery because:
- They have wounds or surgical defects that cannot be closed directly.
- They want a natural skin match in color, texture, and thickness.
- The scar or defect is in a highly visible location (e.g., face, nose, neck).
- Functional movement is restricted due to scar contracture.
Good candidates include:
- Patients with small to medium-sized defects in areas with adjacent healthy skin.
- Individuals in good health with realistic expectations.
- Patients requiring both functional restoration and aesthetic improvement.
Alternatives
- Advancement flap: For simple, straight-line defects.
- Rotation flap: For larger, arc-shaped wounds.
- Skin grafts: For large defects, though they may not blend as naturally.
- Free flaps: For very large or complex wounds when local tissue is insufficient.
Preparation
Before undergoing transposition flap surgery in Korea, patients will:
- Have a consultation with a reconstructive surgeon to plan flap design.
- Undergo routine medical evaluation (blood tests, health check).
- Stop smoking and alcohol 2–4 weeks before surgery to ensure good blood supply.
- Avoid blood thinners and certain supplements.
- Discuss expected scar pattern, as flap design usually results in geometric incisions.
How It’s Done
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia depending on defect size and location.
- Flap design: The surgeon marks a flap adjacent to the defect, shaped in a geometric pattern (triangular, rhomboid, or bilobed).
- Tissue elevation: The flap is lifted while preserving its vascular supply.
- Transposition: The flap is rotated or pivoted over nearby intact skin to fill the defect.
- Closure: The donor and recipient sites are sutured carefully for natural blending.
- Duration: 1–3 hours depending on size and complexity.
Recovery
- First week: Swelling, redness, and bruising are common. Stitches are usually removed in 5–10 days.
- Return to activities: Most patients resume light activities within a few days.
- Healing: The flap is monitored closely to ensure proper blood flow.
- Final results: Natural blending with surrounding skin typically achieved within 2–3 months, with scars continuing to improve over time.
Possible Complications
- Partial flap loss if blood supply is compromised.
- Scar irregularities or widening at incision lines.
- Temporary numbness or skin tightness.
- Rare risks: infection, delayed healing, or asymmetry.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Korean surgeons assess scar or wound size, skin elasticity, and location. 3D surgical planning may be used, especially in facial cases, to optimize flap design.
Medical Treatments
For minor scars or defects, laser therapy, microneedling, or resurfacing may be recommended instead of flap surgery.
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Transposition flaps (rhomboid, bilobed, or Z-plasty) for geometric closure.
- Combination with rotation or advancement flaps for complex cases.
- Microsurgical refinements to minimize visible scarring and optimize results.
Rehabilitation and Support
- Regular follow-up visits for scar monitoring and flap survival.
- Scar management therapies (silicone gels, pressure dressings, fractional lasers).
- Physical therapy for flaps near joints to restore mobility.
- Multilingual aftercare services in Korean clinics to support international patients.