What it is
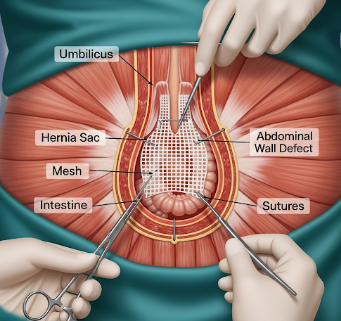
Umbilical hernia repair is a surgical procedure to correct an umbilical hernia, where part of the intestine or fatty tissue protrudes through the abdominal wall near the belly button.
➡ Key facts:
- ✔ Common in infants, children, and adults, more frequent in adults with obesity or increased abdominal pressure
- ✔ Can be open surgery or laparoscopic, depending on hernia size and patient health
- ✔ Performed in hospitals, surgical centers, and specialized hernia clinics in Korea
- ✔ Goals: restore abdominal wall integrity, prevent complications, and relieve discomfort
💡 Umbilical hernia repair is a routine, safe, and effective procedure that prevents hernia complications and improves quality of life.
Why it’s done
Umbilical hernia repair is indicated for:
➤ Pain or discomfort → Especially during bending, coughing, or lifting
➤ Bulging at the navel → Protrusion that does not reduce naturally
➤ Complications prevention → Risk of incarceration (trapped hernia) or strangulation (cut-off blood supply)
➤ Cosmetic concerns → Hernia may affect appearance, especially in adults
➤ Enlarging hernia → Progressive size increase over time
⚠ Untreated hernias can lead to serious complications requiring emergency surgery.
Alternatives / Complementary Measures
Other approaches include:
✔ Observation → Small, asymptomatic hernias in infants may close naturally
✔ Lifestyle modifications → Weight management, avoiding heavy lifting
✔ Hernia belts or trusses → Temporary support; not a permanent solution
✔ Minimally invasive techniques → Laparoscopic repair with quicker recovery
⚠ Surgical repair is recommended for adults or symptomatic hernias, as non-surgical measures cannot fully resolve the defect.
Preparation
Before umbilical hernia repair in Korea:
🔹 Medical evaluation → Blood tests, imaging (ultrasound or CT scan)
🔹 Medication review → Stop blood thinners or anticoagulants as instructed
🔹 Fasting → Usually 6–8 hours prior to surgery
🔹 Consent and counseling → Discuss procedure, risks, anesthesia type, and recovery
🔹 Comorbidity management → Control diabetes, hypertension, or other conditions
💡 Korean hospitals provide preoperative instructions and multidisciplinary evaluation to ensure safe surgery.
How it’s done
➡ Step-by-step procedure:
- Anesthesia → General or regional anesthesia
- Incision → Small cut at the base of the belly button
- Hernia sac management → Herniated tissue is returned to the abdominal cavity
- Defect closure → Sutures or synthetic mesh used to reinforce the abdominal wall
- Skin closure → Incision closed with absorbable sutures or skin adhesive
- Post-op monitoring → Patient observed for bleeding, infection, and vital signs
💡 Laparoscopic repair involves small incisions, insertion of a camera and instruments, and mesh placement, offering shorter recovery and less scarring.
Effectiveness & Success Rate
✔ High success rate → >95% of patients have full recovery without recurrence
✔ Symptom relief → Eliminates bulging and discomfort
✔ Durable repair → Mesh reinforcement reduces recurrence risk
✔ Minimally invasive option → Faster recovery, smaller scars, and shorter hospital stay
💡 Korean surgeons use modern surgical techniques, high-quality mesh, and strict sterile protocols to ensure excellent outcomes.
Recovery / Expected Outcomes
✔ Hospital stay → Usually 1–2 days for open repair; same-day discharge possible for laparoscopic surgery
✔ Pain management → Mild to moderate discomfort managed with analgesics
✔ Activity → Light activity within a few days; heavy lifting avoided for 4–6 weeks
✔ Incision care → Keep area clean and dry; monitor for signs of infection
✔ Follow-up → Routine post-op check-ups to assess healing and recurrence
💡 Most patients return to normal activities within 2–4 weeks, with improved comfort and appearance.
Complications / Risks
⚠ Umbilical hernia repair is generally safe, but possible complications include:
➡ Immediate risks:
- Bleeding or hematoma
- Infection at incision site
- Reaction to anesthesia
➡ Intermediate risks:
- Seroma (fluid accumulation)
- Pain or swelling around the belly button
- Mesh-related complications (rare)
➡ Long-term risks:
- Recurrence of hernia
- Scarring or cosmetic changes
- Chronic discomfort (rare)
💡 Korean hospitals follow strict surgical and post-op care protocols to minimize complications.
Treatment Options in Korea (Post-Operative Care)
🔹 Pain and swelling management → Analgesics, cold compress, and rest
🔹 Wound care → Keep incision clean, dry, and monitor for infection
🔹 Activity guidance → Gradually increase activity; avoid heavy lifting
🔹 Dietary advice → High-fiber diet to prevent constipation and strain
🔹 Follow-up imaging → If needed, to ensure repair integrity
💡 Korean hospitals emphasize patient education and structured follow-up for safe recovery and reduced recurrence risk.
Top Hospitals & Clinics in Korea for Umbilical Hernia Repair
🏥 Seoul National University Hospital (SNUH) – Advanced hernia surgery and postoperative care
🏥 Asan Medical Center (Seoul) – High-volume minimally invasive hernia procedures
🏥 Samsung Medical Center (Seoul) – Expertise in laparoscopic and open repair
🏥 Yonsei Severance Hospital – Pediatric and adult hernia repair services
🏥 Regional tertiary hospitals – Access to experienced surgeons and modern surgical techniques
Conclusion
Umbilical hernia repair in Korea is a safe, effective, and commonly performed surgical procedure that corrects abdominal wall defects and prevents complications.
✔ Restores normal abdominal structure and function
✔ Reduces pain, bulging, and risk of serious complications
✔ Offers minimally invasive options for faster recovery and better cosmetic outcomes
✔ Korean hospitals ensure advanced surgical techniques, high-quality care, and comprehensive post-operative support
By combining expert surgical teams, modern mesh technology, and structured post-operative follow-up, Korea ensures patients recover safely and regain comfort and mobility.