What it is
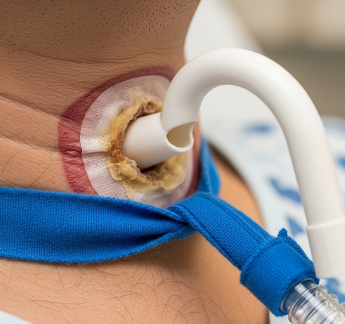
A tracheostomy is a surgical procedure that creates an opening in the front of the neck into the trachea (windpipe) to assist breathing.
➡ Key facts:
- ✔ Provides an alternate airway for patients with blocked upper airways or prolonged ventilation needs
- ✔ Can be temporary or permanent, depending on the underlying condition
- ✔ Performed in operating rooms or intensive care units (ICUs) in Korea
- ✔ Helps in airway management, secretion removal, and long-term ventilation
💡 Tracheostomy is life-saving in emergencies and can also improve comfort for long-term ventilated patients.
Why it’s done
Tracheostomy is indicated for:
➤ Airway obstruction → Tumors, trauma, or congenital anomalies
➤ Prolonged mechanical ventilation → ICU patients needing long-term respiratory support
➤ Neuromuscular disorders → Conditions like ALS, spinal cord injury, or stroke causing breathing difficulty
➤ Secretion management → Chronic lung disease or impaired cough reflex
➤ Emergency airway access → When intubation is not possible
⚠ Delaying a needed tracheostomy can lead to respiratory failure or death.
Alternatives / Complementary Measures
Other approaches include:
✔ Endotracheal intubation → Short-term airway support
✔ Non-invasive ventilation (CPAP/BiPAP) → For mild respiratory insufficiency
✔ Surgical airway alternatives → Cricothyrotomy in emergency settings
✔ Medical management → Bronchodilators, corticosteroids, or suctioning to manage secretions
⚠ Tracheostomy is preferred for long-term airway management or when non-invasive methods fail.
Preparation
Before a tracheostomy in Korea:
🔹 Medical assessment → Blood tests, imaging (CT, X-ray), coagulation profile
🔹 Anesthesia evaluation → General anesthesia usually required
🔹 Consent and counseling → Explain procedure, risks, and post-op care
🔹 Equipment readiness → Suction, ventilator, and emergency resuscitation equipment
🔹 Fasting → Typically 6–8 hours before surgery
💡 Korean hospitals provide detailed preoperative counseling and ICU planning for patients and families.
How it’s done
➡ Step-by-step tracheostomy procedure:
- Positioning → Patient lying on back with neck extended
- Anesthesia → General or local, depending on urgency
- Incision → Horizontal or vertical cut in lower neck
- Tracheal opening → Expose trachea and create stoma
- Tube insertion → Tracheostomy tube inserted into trachea
- Securing tube → Sutures or ties to keep tube in place
- Immediate care → Connect to ventilator if needed, suction secretions, monitor oxygen
💡 In Korea, surgical teams use sterile techniques, precise instruments, and modern tracheostomy tubes for safety and comfort.
Effectiveness & Success Rate
✔ High success rate in providing airway support
✔ Life-saving in emergencies and for patients needing long-term ventilation
✔ Improves quality of life for patients with chronic respiratory insufficiency
✔ Reduces complications compared to prolonged endotracheal intubation (less airway trauma, easier oral care)
💡 Korean hospitals integrate multidisciplinary teams for optimal outcomes, including surgeons, anesthesiologists, nurses, and respiratory therapists.
Recovery / Expected Outcomes
✔ Immediate post-op care → ICU or monitored ward for 24–48 hours
✔ Airway management → Regular suctioning, humidification, and tube care
✔ Communication aids → Speaking valves or writing tools for verbal communication
✔ Physical activity → Gradual mobilization with respiratory support
✔ Long-term outcomes → Tube may be temporary or permanent, depending on underlying condition
💡 Families in Korea are trained in home care for tracheostomy patients when discharge is planned.
Complications / Risks
⚠ Tracheostomy carries surgical and post-operative risks:
➡ Immediate complications:
- Bleeding
- Pneumothorax (air in chest cavity)
- Accidental tube displacement
➡ Intermediate risks:
- Infection at stoma site
- Mucus plugging
- Tracheal injury
➡ Long-term complications:
- Tracheal stenosis or scarring
- Persistent cough or voice changes
- Dependence on ventilator if underlying disease persists
💡 Korean hospitals implement strict infection control, regular monitoring, and patient/family education to minimize risks.
Treatment Options in Korea (Post-Tracheostomy Care)
🔹 ICU and ward monitoring → Oxygen saturation, tube patency, secretion management
🔹 Suctioning and humidification → Maintain airway hygiene
🔹 Speech therapy → Use of speaking valves and alternative communication methods
🔹 Physical therapy → Maintain mobility and prevent complications
🔹 Home care education → Tube cleaning, suctioning, emergency management
💡 Korean healthcare emphasizes multidisciplinary, patient-centered post-op care for safe recovery.
Top Hospitals & Clinics in Korea for Tracheostomy
🏥 Seoul National University Hospital (SNUH) – Advanced airway surgery and ICU care
🏥 Asan Medical Center (Seoul) – Specialized respiratory and critical care units
🏥 Samsung Medical Center (Seoul) – Expertise in emergency and elective tracheostomy
🏥 Yonsei Severance Hospital – Pediatric and adult airway management
🏥 Regional tertiary hospitals – Provide emergency tracheostomy and long-term follow-up
Conclusion
Tracheostomy in Korea is a critical surgical procedure for managing airway obstruction, chronic respiratory failure, or prolonged ventilation.
✔ Provides safe and reliable airway support
✔ Effective in emergency and long-term settings
✔ Minimizes complications of prolonged intubation
✔ Korean hospitals offer advanced surgical techniques, ICU care, and home care education
By integrating expert surgical teams, post-operative monitoring, and family training, Korea ensures patients receive life-saving care and maintain quality of life.