What it is
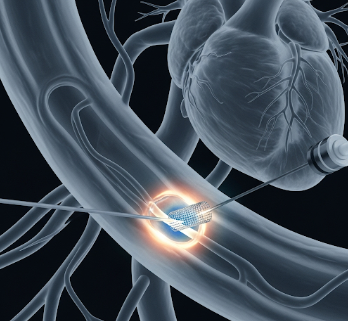
Stent insertion is a minimally invasive procedure in which a small mesh tube (stent) is placed inside a blood vessel or other hollow structure to keep it open and ensure proper blood flow.
➡ Key facts about stents:
- ✔ Commonly used in coronary arteries to treat blocked or narrowed arteries.
- ✔ Can also be used in peripheral arteries, bile ducts, ureters, and other tubular organs.
- ✔ Types of stents:
- Bare-metal stents (BMS) → Provide structural support
- Drug-eluting stents (DES) → Release medication to prevent re-narrowing
- Biodegradable stents → Gradually dissolve after vessel healing
- ✔ In Korea, stent insertion is performed in major cardiac and vascular centers with advanced imaging technology.
💡 Stent insertion helps restore blood flow, relieve symptoms, and prevent life-threatening complications like heart attacks or organ ischemia.
Why it’s done
Doctors recommend stent insertion for:
➤ Coronary artery disease → Chest pain (angina), blocked arteries
➤ Heart attack (myocardial infarction) → Emergency restoration of blood flow
➤ Peripheral artery disease → Blockages in leg or arm arteries
➤ Other organ blockages → Bile ducts (jaundice), ureters (urinary obstruction)
➤ Prevent future complications → Reduce risk of heart attack, stroke, or organ damage
⚠ Without timely stent placement, severe blockages can lead to heart failure, organ damage, or death.
Alternatives
Depending on the condition, alternatives include:
✔ Medication therapy → Antiplatelets, statins, or blood thinners
✔ Balloon angioplasty alone → Temporarily opens artery without a stent
✔ Bypass surgery → Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) for severe blockages
✔ Lifestyle modification → Diet, exercise, smoking cessation, especially in mild cases
⚠ Stent insertion is often preferred for immediate relief and minimally invasive treatment.
Preparation
Before stent insertion in Korea:
🔹 Medical evaluation → Blood tests, ECG, echocardiogram, coronary angiography
🔹 Medication management → Stop certain blood thinners or adjust dosages
🔹 Fasting → Usually 6–8 hours before the procedure
🔹 Allergy check → Especially for contrast dye used in imaging
🔹 Consent and counseling → Risks, procedure details, and recovery explained
💡 Korean hospitals provide preoperative cardiac education and ensure patients understand post-procedure medication adherence.
How it’s done
➡ Step-by-step stent insertion process in Korea:
- Anesthesia → Local anesthesia at the insertion site (wrist or groin)
- Access → Small catheter inserted into artery
- Imaging guidance → Contrast dye and X-ray (angiography) used to locate blockage
- Balloon angioplasty → Inflates to widen the narrowed artery
- Stent placement → Mesh tube deployed to keep artery open
- Final imaging → Ensures proper stent placement and blood flow
- Closure and monitoring → Catheter removed, puncture site closed, patient observed
💡 The procedure usually lasts 30–90 minutes, depending on complexity.
Effectiveness & Success Rate
✔ High success rates in Korea:
- Coronary stents: >95% success in opening blocked arteries
- Peripheral stents: 90–95% initial success
✔ Symptom relief → Chest pain and shortness of breath improve immediately in most patients
✔ Long-term outcomes → Drug-eluting stents reduce re-narrowing risk to <10%
⚠ Proper post-procedure care is critical for maintaining stent patency.
Recovery / Expected Outcomes
✔ Hospital stay → Usually 1–3 days for elective cases; emergency cases may vary
✔ Activity resumption → Light activity the next day; avoid heavy lifting for 1–2 weeks
✔ Medications → Dual antiplatelet therapy (aspirin + clopidogrel) for 6–12 months
✔ Follow-up → ECG, stress tests, and periodic angiography if needed
💡 Most patients experience immediate symptom relief and return to normal daily activities within a few days.
Complications / Risks
⚠ While generally safe, stent insertion carries risks:
➡ Procedure-related complications:
- Bleeding or hematoma at the insertion site
- Allergic reaction to contrast dye
- Artery dissection or perforation
➡ Post-procedure risks:
- Blood clot formation in stent (stent thrombosis)
- Re-narrowing (restenosis)
- Heart attack or stroke (rare)
💡 In Korea, advanced imaging, skilled cardiologists, and strict post-procedure monitoring minimize these risks.
Treatment Options in Korea (Post-Stent Care)
🔹 Medications → Long-term antiplatelet therapy, statins, beta-blockers
🔹 Lifestyle modification → Heart-healthy diet, exercise, smoking cessation
🔹 Follow-up tests → ECG, echocardiogram, stress tests, or angiography
🔹 Reintervention if needed → Repeat angioplasty or stent replacement for restenosis
🔹 Specialist support → Cardiologists, dietitians, rehabilitation teams
💡 Korean hospitals provide comprehensive post-stent programs, including cardiac rehabilitation and patient education for medication adherence.
Top Hospitals & Clinics in Korea for Stent Insertion
🏥 Asan Medical Center (Seoul) – Leading cardiovascular center
🏥 Samsung Medical Center (Seoul) – Advanced interventional cardiology programs
🏥 Seoul National University Hospital (SNUH) – Specialized in complex coronary and peripheral interventions
🏥 Yonsei Severance Hospital – Offers complete cardiac rehabilitation
🏥 CHA Bundang Medical Center – High-volume stent insertion with minimally invasive techniques
Conclusion
Stent insertion in Korea is a safe, effective, and minimally invasive procedure for treating blocked arteries and restoring blood flow.
✔ High success rates with immediate symptom relief
✔ Wide availability in advanced cardiac centers
✔ Minimizes need for open surgery and supports rapid recovery
✔ Post-procedure care, medication adherence, and lifestyle modification are essential for long-term outcomes
By offering state-of-the-art interventional cardiology services, Korea ensures patients benefit from effective, life-saving stent procedures with excellent recovery and follow-up care.