What it is
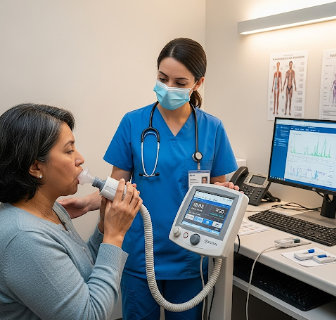
A spirometry test is a non-invasive lung function assessment used to evaluate how well the lungs are working. It measures:
➡ The amount of air a person can inhale and exhale
➡ The speed of airflow during breathing
➡ The capacity of the lungs for oxygen exchange
💡 This test is crucial for diagnosing and monitoring respiratory diseases such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pulmonary fibrosis, and other lung conditions. In Korea, it is widely available at hospitals, pulmonary clinics, and community health centers.
Why it’s done
Doctors in Korea recommend spirometry for:
➤ Diagnosing lung conditions → Detect asthma, COPD, restrictive lung disease
➤ Monitoring disease progression → Track changes in lung function over time
➤ Evaluating treatment effectiveness → Adjust medications and inhalers
➤ Preoperative assessment → Ensure safe anesthesia for surgery
➤ Health screenings → Particularly for smokers, older adults, and those with occupational lung risks
⚠ Early detection via spirometry can prevent complications, hospitalizations, and long-term lung damage.
Alternatives
While spirometry is the standard, alternatives in Korea include:
✔ Peak Flow Measurement → Monitors airflow in asthma patients, less comprehensive than spirometry
✔ Body Plethysmography → Measures total lung volume, used for complex cases
✔ Diffusion Capacity Test (DLCO) → Evaluates oxygen transfer efficiency
✔ Chest Imaging → X-rays or CT scans for structural lung assessment, but do not measure lung function
⚠ None of these alternatives provide the full functional assessment that spirometry offers.
Preparation
Before a spirometry test:
🔹 Avoid smoking for at least 24 hours
🔹 Avoid bronchodilator inhalers (unless directed) 6–12 hours prior
🔹 Wear loose clothing for unrestricted breathing
🔹 Avoid heavy meals before the test
💡 In Korea, patients are often advised to bring prior lung test results, medication lists, and insurance documentation to ensure comprehensive evaluation and proper billing.
How it’s done
➡ Step-by-step procedure in Korea:
- Seated comfortably → Nose clip applied to prevent air escape
- Mouthpiece use → Patient exhales forcefully into a sterile device
- Breathing instructions → Take deep breath, exhale rapidly, repeat several times
- Optional bronchodilator test → Medication inhaled, test repeated to check airway responsiveness
- Result analysis → Digital spirometer provides graphs and numerical values immediately
- Consultation → Doctor explains results and next steps
What Spirometry Measures
✔ FEV1 (Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 second): Volume exhaled in the first second
✔ FVC (Forced Vital Capacity): Total exhaled volume after deep breath
✔ FEV1/FVC ratio: Detects airflow obstruction
✔ PEF (Peak Expiratory Flow): Maximum exhalation speed
💡 These metrics allow physicians to diagnose obstructive or restrictive lung disease accurately.
Effectiveness & Success Rate
✔ Highly reliable: >95% accuracy when performed correctly
✔ Early detection → Prevents progression of chronic lung conditions
✔ Treatment guidance → Helps adjust inhaler doses, monitor recovery, and evaluate rehabilitation outcomes
✔ Monitoring tool → Repeated measurements track disease stability or worsening
Recovery / After the Test
✔ No downtime required; patients resume normal activities immediately
✔ Mild dizziness or shortness of breath may occur temporarily
✔ Some may experience minor coughing during or after the test
✔ Results are typically reviewed with the doctor immediately
Complications / Risks
⚠ Spirometry is generally safe but may cause:
➡ Temporary dizziness or lightheadedness
➡ Mild fatigue from forceful exhalation
➡ Short-term coughing
➡ Rarely, chest discomfort in patients with severe lung or heart disease
💡 In Korea, trained medical staff supervise all tests, ensuring safe administration even for elderly or high-risk patients.
Treatment Options in Korea Based on Results
🔹 Diagnosis → Spirometry identifies asthma, COPD, restrictive lung disease, or fibrosis
🔹 Medical treatments
- Asthma → Inhaled corticosteroids, bronchodilators, allergy management
- COPD → Long-term oxygen therapy, bronchodilator therapy, lifestyle interventions
- Fibrosis → Antifibrotic medication, pulmonary rehabilitation
🔹 Surgical / advanced therapies
- Lung transplant for end-stage disease → available in Seoul Asan Medical Center, Samsung Medical Center
- Bronchoscopy for airway obstruction
🔹 Rehabilitation & Support
- Pulmonary rehab programs (exercise, breathing techniques)
- Smoking cessation clinics and counseling
- Patient education on disease management
Top Hospitals & Clinics in Korea for Spirometry
🏥 Asan Medical Center (Seoul) – Advanced lung function testing
🏥 Samsung Medical Center – Specializes in COPD, asthma, interstitial lung disease
🏥 Seoul National University Hospital – Comprehensive pulmonary care
🏥 Yonsei Severance Hospital – Pulmonary rehab and chronic disease management
🏥 Community Health Screening Centers – Affordable, government-supported lung function tests
Conclusion
The spirometry test in Korea is an essential, safe, and highly effective tool for diagnosing and managing lung disease.
✔ Quick, non-invasive, and repeatable
✔ Crucial for early detection and monitoring of respiratory conditions
✔ Available widely across hospitals, clinics, and screening centers
✔ Supports personalized treatment planning and long-term lung health
By integrating spirometry with Korea’s advanced healthcare system, patients benefit from early detection, effective treatment, and comprehensive respiratory care.