What it is
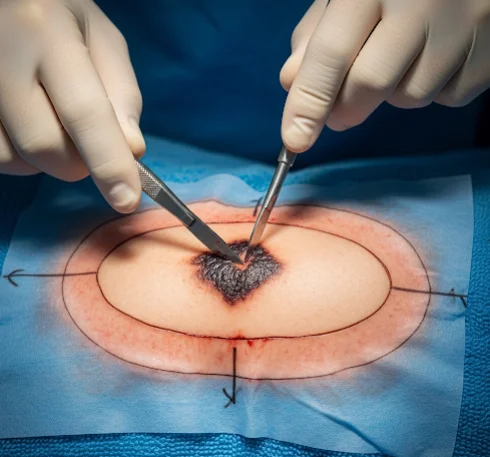
Wide local excision (skin) in Korea is a surgical procedure in which a skin cancer or suspicious lesion is removed along with a margin of healthy surrounding tissue to ensure complete clearance.
This method is primarily used for malignant melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), and certain high-risk basal cell carcinomas (BCC). The “wide” aspect refers to removing not just the visible tumor but also extra healthy tissue around it—the margin size depends on cancer type and stage.
→ In Korea, wide local excisions are performed in dermatology hospitals, plastic surgery clinics, and cancer centers, where the balance between oncologic safety and cosmetic outcomes is prioritized.
• The excised tissue is sent to pathology for confirmation of clear margins.
• Reconstruction techniques (suturing, flaps, or grafts) are often used for aesthetic restoration.
Why it’s done
Patients in Korea undergo wide local excision for:
→ Definitive treatment of melanoma → Ensures all malignant cells are removed.
→ High-risk skin cancers → When smaller biopsies confirm aggressive features.
→ Margin control → Prevents recurrence by taking healthy tissue around the lesion.
→ Oncologic safety → Standard practice in cancer treatment guidelines.
→ Cosmetic-functional preservation → Especially important in Korea for areas like the face, hands, or scalp.
Alternatives
Depending on cancer type and site, alternatives include:
• Mohs micrographic surgery → Preferred for facial and tissue-sparing areas with non-melanoma cancers.
• Simple excision → Smaller removal, not suitable for aggressive cancers.
• Cryosurgery → Freezing technique, mostly for precancerous or superficial lesions.
• Topical therapies → Imiquimod or 5-FU for superficial cancers only.
• Radiation therapy → Option for patients who cannot undergo surgery.
→ Wide local excision is considered essential and standard for melanoma and invasive skin cancers.
Preparation
Before undergoing wide local excision in Korea, patients go through:
- Dermatology-oncology consultation → Review of biopsy results and treatment planning.
- Imaging tests → Sometimes used for deeper or suspicious melanomas.
- Medical history review → Includes bleeding risks, heart conditions, and medications.
- Anesthesia planning → Most cases use local anesthesia; larger excisions may need sedation or general anesthesia.
- Patient education → Explanation of scar, possible reconstruction, and follow-up requirements.
→ In Korea, pre-op planning often includes digital imaging and skin mapping to optimize excision lines.
How it’s done
Wide local excision in Korea is a structured surgical procedure:
- Anesthesia → Local anesthetic injection (or sedation/general anesthesia for larger cases).
- Excision → The tumor is removed with an elliptical incision, including a margin of healthy tissue.
- Typical melanoma margins: 0.5–2 cm, depending on thickness.
- Specimen collection → The removed tissue is labeled and sent to pathology for margin assessment.
- Wound closure → Options include:
- Direct suturing for small excisions.
- Skin flaps for larger or irregular sites.
- Skin grafts for extensive excisions.
- Dressing and aftercare → Sterile bandage and ointment applied.
→ The procedure usually takes 30–90 minutes, depending on lesion size and complexity.
Recovery
Recovery after wide local excision varies by wound size:
• Stitch removal → After 7–14 days.
• Healing time → Small wounds heal in 2–3 weeks; grafts or flaps may take longer.
• Scar outcome → Korea places emphasis on scar minimization with layered suturing and post-op scar care.
• Activity restriction → Patients avoid stretching or pressure on the site.
• Follow-up visits → Pathology results reviewed within 1–2 weeks to confirm clear margins.
→ Long-term follow-up is important for recurrence monitoring, especially in melanoma cases.
Complication
Possible risks include:
- Bleeding or infection → Rare with sterile technique and aftercare.
- Scarring → Often minimized with Korean scar-care protocols (laser, silicone gels, LED therapy).
- Wound healing delays → More common with grafts or large excisions.
- Nerve or vessel damage → Rare but possible in deeper or facial excisions.
- Recurrence → If margins are not completely clear.
→ Risks are minimized in Korea through precision surgery and advanced reconstructive methods.
Treatment option in Korea
Korea provides world-class options for wide local excision of skin cancers:
→ Specialized cancer dermatology centers → Equipped for skin cancer diagnosis, excision, and reconstruction.
→ Plastic surgery integration → Ensures cosmetically refined closure in visible areas.
• Scar management programs → Post-op care often includes fractional CO₂ lasers, V-beam, and topical scar gels.
• Multidisciplinary care → Dermatologists, oncologists, and reconstructive surgeons collaborate for best outcomes.
• Medical tourism → Korea attracts international patients for oncologic safety with aesthetic precision.
→ With its high cure rates, margin-focused techniques, and cosmetic refinement, wide local excision in Korea is a trusted and effective treatment for melanoma and high-risk skin cancers.