What it is
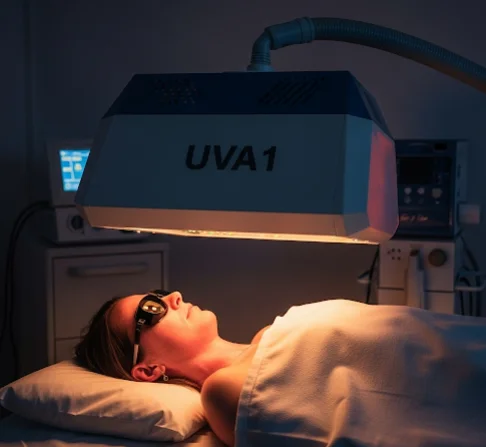
UVA1 phototherapy in Korea is a specialized light-based treatment that uses long-wave ultraviolet A light (340–400 nm) to manage various inflammatory, autoimmune, and sclerosing skin conditions.
Unlike narrowband UVB (NB-UVB), which targets superficial skin, UVA1 penetrates deeper into the dermis, making it effective for diseases involving deeper skin structures such as scleroderma, morphea, atopic dermatitis, and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL).
→ In Korea, UVA1 phototherapy is available in university hospitals, dermatology centers, and advanced phototherapy clinics.
• Considered one of the most advanced phototherapy techniques, especially for chronic or treatment-resistant skin diseases.
• Delivered in low-, medium-, or high-dose regimens depending on the condition.
Why it’s done
Patients in Korea undergo UVA1 phototherapy for:
→ Sclerotic conditions → Localized scleroderma (morphea), systemic sclerosis.
→ Severe eczema / atopic dermatitis → Especially in chronic or lichenified cases.
→ Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL, early stages) → Mycosis fungoides.
→ Lupus tumidus → Certain photosensitive autoimmune diseases.
→ Keloid / hypertrophic scar modulation → By softening collagen tissue.
→ Other inflammatory dermatoses → Granuloma annulare, lichen sclerosus, prurigo nodularis.
→ Chosen when topical steroids, immunosuppressants, or standard NB-UVB are insufficient.
Alternatives
Other phototherapy and systemic options include:
• Narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) → Gold standard for psoriasis, vitiligo, and superficial dermatoses.
• PUVA (Psoralen + UVA) → Uses psoralen photosensitizer with UVA light, but higher side effect risks.
• Excimer laser / excimer light (308 nm) → For localized lesions.
• Systemic immunosuppressants → Methotrexate, cyclosporine, azathioprine.
• Biologic therapies → Dupilumab, JAK inhibitors, or monoclonal antibodies for autoimmune skin disease.
→ UVA1 is chosen when deep dermal involvement makes other options less effective.
Preparation
Before undergoing UVA1 phototherapy in Korea, preparation involves:
- Dermatology consultation → Diagnosis confirmation and severity scoring.
- Baseline photography → To monitor improvement.
- Eye protection → Special UVA-blocking goggles required.
- Skin evaluation → Screening for photosensitivity, lupus, or prior skin cancer.
- Medication review → Some drugs increase photosensitivity (e.g., tetracyclines, thiazides).
→ Korean clinics also measure minimal phototoxic dose (MPD) to tailor safe UVA1 intensity.
How it’s done
UVA1 phototherapy in Korea is performed with large, specialized devices:
- Patient preparation → Protective eyewear and minimal clothing (affected areas exposed).
- Treatment session → Patient stands or lies in a UVA1 chamber.
- Light exposure
- Low dose → 10–20 J/cm².
- Medium dose → 30–50 J/cm².
- High dose → 60–130 J/cm².
- Dose depends on disease severity and tolerance.
- Session duration → Usually 15–30 minutes.
- Treatment frequency → 2–5 sessions per week, for 6–12 weeks.
→ Many Korean centers combine UVA1 with topical steroids, calcineurin inhibitors, or systemic medications for synergy.
Recovery
Recovery during UVA1 therapy is usually smooth:
• No downtime → Patients can continue normal activities after each session.
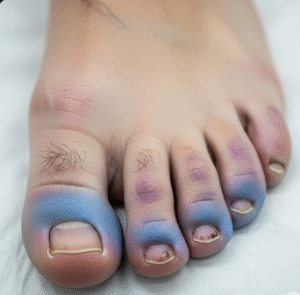
• Mild redness or tanning → Temporary skin darkening may occur.
• Symptom relief → Softening of sclerotic skin and reduction of itching often within 4–8 sessions.
• Maintenance care → Patients often continue with reduced frequency sessions after initial course.
→ Korean dermatologists emphasize daily sunscreen use to prevent rebound pigmentation.
Complication
Possible risks of UVA1 phototherapy include:
- Tanning / hyperpigmentation → Common but usually fades.
- Dryness / itching → Due to repeated exposure.
- Photoaging → Long-term risk with prolonged UVA exposure.
- Carcinogenesis → Theoretical risk (lower than PUVA but higher than NB-UVB).
- Flare of photosensitive diseases → Rare, if not screened properly.
→ In Korea, complications are minimized by precise dosing, strict monitoring, and limited treatment courses.
Treatment option in Korea
Korea provides advanced UVA1 phototherapy programs with world-class safety and efficacy:
→ University hospitals → Equipped with full-body UVA1 cabins for systemic dermatoses.
→ Specialized dermatology centers → Offer medium- and high-dose UVA1 for resistant conditions.
• Combination protocols → UVA1 often paired with NB-UVB, excimer laser, or systemic agents for better outcomes.
• Digital skin monitoring → Clinics use imaging tools to track pigmentation and sclerosis improvement.
• Medical tourism → International patients visit Korea for innovative phototherapy access combined with aesthetic expertise.
→ With its deep-penetrating wavelength, precision dosing, and integration into multimodal treatment plans, UVA1 phototherapy in Korea is a leading solution for complex, chronic, and treatment-resistant skin conditions.