What It Is
Defining Urticaria
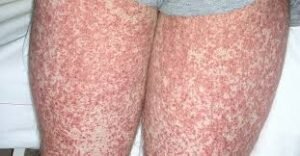
→ Urticaria, also known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by itchy, raised welts that can appear anywhere on the body.
→ Welts may be red, pink, or skin-colored and often change size and shape rapidly.
→ Episodes can last from a few hours to several weeks, and in chronic cases, longer than 6 weeks.
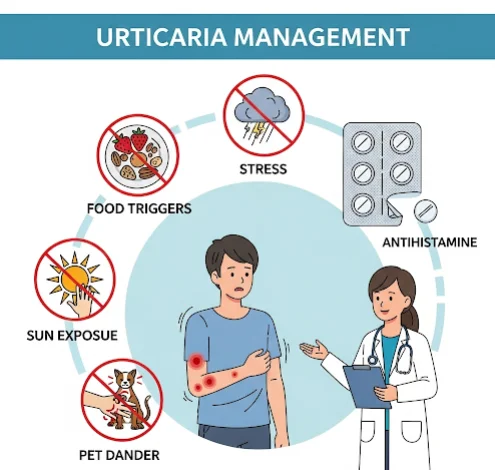
→ Triggers include allergies, infections, medications, stress, autoimmune reactions, and physical stimuli (heat, cold, pressure).
→ In Korea, urticaria is managed with structured treatment plans, combining allergy testing, modern antihistamines, and advanced biologic therapies for resistant cases.
Key Characteristics
- Sudden itchy welts that appear and fade within hours
- Angioedema (swelling of lips, eyelids, hands, or feet) may accompany hives
- Acute urticaria → Lasts less than 6 weeks, often allergy-related
- Chronic urticaria → Persists beyond 6 weeks, often without identifiable cause
- Commonly worsens at night or after stress
Why It’s Done
Main Reasons for Management
➡ Relief from Severe Itching – Urticaria can be extremely uncomfortable and disrupt daily life.
➡ Preventing Angioedema Complications – Swelling in the throat can rarely cause breathing difficulties.
➡ Identifying Triggers – Allergy testing helps pinpoint and avoid causes.
➡ Improving Quality of Life – Reduces embarrassment and discomfort from visible welts.
➡ Controlling Chronic Cases – Structured care prevents frequent relapses.
Alternatives
Non-Medical Options
- Avoidance of Triggers → Identifying and avoiding allergens, heat, or pressure stimuli.
- Stress Management → Yoga, relaxation techniques, or counseling for stress-induced hives.
- Cool Compresses → Provide temporary relief from itching and redness.
- Loose Clothing → Reduces irritation in pressure-related urticaria.
Medical Alternatives
→ Standard protocols involve stepwise treatment:
- Non-sedating Antihistamines → First-line therapy for all types of urticaria.
- Increased Antihistamine Dosing → If symptoms persist, dose may be increased up to 4x the standard.
- Short-term Corticosteroids → For severe flares, but not long-term use.
- Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists → Montelukast sometimes added for refractory cases.
- Biologic Therapy (Omalizumab) → Advanced therapy for chronic spontaneous urticaria resistant to antihistamines.
- Immunosuppressants (Cyclosporine, Methotrexate) → Used rarely in severe cases.
Preparation
Before Treatment
➡ Dermatology or Allergy Consultation – Confirm diagnosis and exclude similar conditions (eczema, drug eruption).
➡ Patient History – Review of medications, food intake, infections, and stress levels.
➡ Allergy Testing – Skin prick tests or blood IgE levels for suspected triggers.
➡ Blood Tests – To check autoimmune or thyroid associations in chronic urticaria.
➡ Patient Counseling – Explanation that chronic urticaria is often idiopathic (no clear cause) but manageable with structured care.
How It’s Done
Urticaria Management Protocol in Korea
1. First-Line: Non-Sedating Antihistamines
→ Medications like cetirizine, loratadine, fexofenadine, or bilastine.
- Taken once daily.
- Safe for long-term use.
- Most patients achieve control at this stage.
2. Step-Up Therapy
→ If standard doses are insufficient:
- Increase dosage up to 4 times daily under medical supervision.
- Combination of different antihistamines may be considered.
3. Adjunctive Therapies
→ For patients not fully controlled:
- Montelukast (leukotriene receptor antagonist)
- Short courses of oral steroids for severe acute episodes
4. Biologic Therapy – Omalizumab
→ Widely used in Korean hospitals for chronic spontaneous urticaria unresponsive to antihistamines.
- Administered by subcutaneous injection every 2–4 weeks.
- Highly effective in reducing or eliminating hives.
5. Immunosuppressants (Last Resort)
→ For severe cases resistant to all therapies:
- Cyclosporine, methotrexate, or mycophenolate
- Require careful monitoring due to potential side effects
6. Lifestyle and Supportive Care
→ Emphasis on trigger avoidance, stress management, and skincare.
- Hypoallergenic cleansers and moisturizers
- Cooling gels or lotions for itch relief
Recovery
Immediate Recovery
- Antihistamines begin working within hours to days, reducing itching and welts.
- Acute urticaria usually resolves within 1–2 weeks with treatment.
- Chronic cases may take longer to stabilize.
Long-Term Recovery
→ Chronic urticaria often requires months to years of management.
→ With regular follow-up and stepwise therapy, most patients achieve long-term remission.
→ Relapses can occur, but Korean clinics provide structured follow-up plans.
Complications
Risks Without Proper Care
- Severe Angioedema → Rare but dangerous if it affects the airway.
- Persistent Itching → Causes sleep disturbance, anxiety, or depression.
- Secondary Skin Infections → Scratching can lead to impetigo or cellulitis.
- Chronic Quality-of-Life Impairment → Ongoing hives can affect social and work life.
Risks With Treatment
- Sedation → With older-generation antihistamines.
- Steroid Side Effects → Long-term use causes weight gain, bone thinning, or high blood pressure.
- Biologic Therapy Risks → Rare allergic reactions to omalizumab injections.
- Immunosuppressant Risks → Require careful monitoring of kidneys, liver, and blood counts.
Treatment Options in Korea
Why Korea Excels in Urticaria Management
➡ Stepwise Guidelines – Korean dermatologists follow international and local urticaria guidelines strictly.
➡ Access to Advanced Therapies – Omalizumab and other biologics are widely available in major hospitals.
➡ Integrated Allergy-Dermatology Clinics – Multidisciplinary care ensures accurate diagnosis and management.
➡ Patient-Centered Programs – Education about triggers, lifestyle modifications, and medication adherence.
Popular Approaches in Korea
- Acute urticaria → Managed with antihistamines and short steroid bursts.
- Chronic spontaneous urticaria → Stepwise antihistamines → omalizumab → immunosuppressants.
- Physical urticaria (cold, pressure, heat) → Managed with both medication and trigger avoidance programs.
Patient Experience in Korea
- Treatment is outpatient-based, with quick access to medications.
- Hospitals provide allergy testing and dermatology consultation in the same visit.
- Patients receive personalized treatment plans with lifestyle advice.
- Follow-ups every few weeks to monitor progress and adjust therapy.
Conclusion
Urticaria management in Korea follows a clear, structured, stepwise protocol that combines modern antihistamines, biologics, and lifestyle strategies.
Through a combination of trigger avoidance, medication escalation, and advanced therapies like omalizumab, Korean dermatology clinics achieve excellent long-term control.
Patients benefit from Korea’s integrated dermatology and allergy services, which ensure both symptom relief and improved quality of life.
For individuals struggling with acute or chronic hives, Korea offers some of the most advanced, reliable, and patient-centered management approaches worldwide.