A Comprehensive Guide to Skin and Care Treatment
➤ What it is
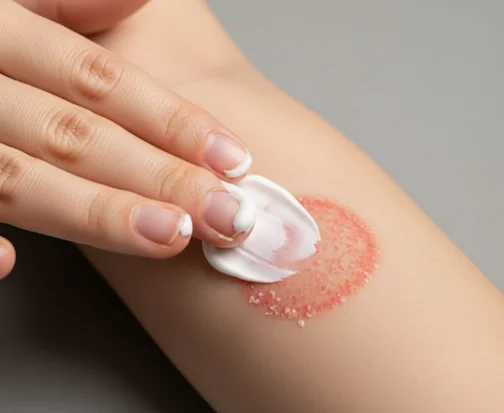
Tinea corporis, commonly called ringworm of the body, is a superficial fungal infection caused by dermatophytes, usually Trichophyton species. Despite its name, it has nothing to do with worms.
Clinical features include:
- Red, circular, ring-shaped patches,
- Raised, scaly borders with central clearing,
- Itching and discomfort,
- Spread on arms, legs, trunk, or face (excluding scalp, groin, and feet, which have their own terms like tinea capitis, cruris, or pedis).
In Korea, tinea corporis is treated through a combination of antifungal medications, topical care, and preventive skincare practices, with an emphasis on early detection and recurrence prevention.
➤ Why it’s done
Patients seek treatment for tinea corporis because:
- Symptom relief → itching, redness, and scaling can be uncomfortable.
- Prevent spread → untreated infection may spread to other body areas or to close contacts.
- Cosmetic improvement → visible red patches affect self-confidence.
- Avoid chronic recurrence → dermatophyte infections are known to return without proper management.
- Korean clinical perspective → clear, even-toned skin is culturally important, so rapid and effective treatment is emphasized.
➤ Alternatives
Multiple treatment options exist, depending on severity:
Topical Antifungals (First-Line for Mild Cases)
- Azoles: clotrimazole, ketoconazole, econazole.
- Allylamines: terbinafine, naftifine, butenafine.
- Ciclopirox or tolnaftate creams.
Systemic Antifungals (For Widespread, Severe, or Resistant Infections)
- Oral terbinafine, itraconazole, or fluconazole.
- Typically prescribed for 2–4 weeks under medical supervision.
Adjunctive Care
- Medicated antifungal powders for moisture-prone areas.
- Gentle exfoliation to remove scaling.
- Barrier creams for irritated skin.
Korean Dermatology Practices
- Medicated washes with antifungal ingredients (ketoconazole, zinc pyrithione).
- LED blue light therapy in some clinics for adjunctive antifungal effects.
- K-beauty barrier-repair creams integrated into post-treatment routines.
➤ Preparation
Preparation before treatment ensures effectiveness:
- Medical Evaluation
- Dermatologist examines lesions visually.
- May scrape skin for KOH (potassium hydroxide) exam to confirm fungal elements.
- In Korea, digital dermoscopy or UV imaging may be used to detect fungal spread.
- Pre-Treatment Guidelines
- Avoid steroid creams → they worsen fungal infections (“tinea incognito”).
- Do not cover lesions with heavy ointments before consultation.
- Keep affected skin clean and dry.
- Patient Education
- Inform about recurrence risks and importance of full treatment course.
➤ How it’s Done
Tinea corporis treatment in Korea follows a structured approach:
1. Topical Antifungal Therapy
- First-line for localized cases.
- Applied twice daily for 2–4 weeks.
- Commonly used: terbinafine, clotrimazole, ketoconazole.
- Korean clinics may provide prescription-strength medicated creams.
2. Oral Antifungal Therapy
- Used when:
- Lesions are widespread,
- Recurrent or resistant cases,
- Immunocompromised patients.
- Oral terbinafine, itraconazole, or fluconazole prescribed.
- Liver function monitored during systemic therapy.
3. Supportive Skincare
- Gentle cleansers with antifungal actives.
- Barrier creams with ceramides to reduce irritation.
- Lightweight, non-oily moisturizers to avoid yeast/fungal growth.
4. Preventive Measures
- Keep skin dry and well-ventilated.
- Avoid tight clothing that traps sweat.
- Wash clothes, towels, and bedding frequently.
5. Korean Dermatology Enhancements
- LED therapy (blue light) to reduce fungal load and soothe inflammation.
- Hydration facials to restore barrier after antifungal therapy.
- Customized K-beauty skincare regimens for long-term skin health.
➤ Recovery
Recovery depends on treatment type and extent of infection:
- Mild cases with topical antifungals → improve within 2 weeks, full resolution in 4 weeks.
- Systemic antifungals → significant improvement within 1–2 weeks, but full course must be completed.
- Pigmentation changes → may remain temporarily after clearance, especially in darker skin tones.
Aftercare Instructions:
- Continue antifungal creams for at least 1 week after visible clearance.
- Avoid scratching to reduce secondary infections.
- Maintain hygiene and dryness in affected areas.
- Use antifungal body wash weekly during humid seasons for prevention.
Korean Recovery Practices:
- Barrier-repair ampoules with centella and hyaluronic acid.
- Brightening serums (niacinamide, vitamin C) to reduce post-inflammatory marks.
- Routine follow-ups to prevent recurrence during summer months.
➤ Complications
If left untreated or improperly managed, tinea corporis may lead to:
- Chronic recurrence.
- Tinea incognito (misuse of steroid creams masks symptoms but worsens infection).
- Secondary bacterial infections from scratching.
- Emotional distress due to cosmetic appearance.
Treatment-related complications may include:
- Skin dryness or irritation from antifungal creams.
- Liver toxicity (rare) from oral antifungals.
Korean dermatology reduces risks by:
- Avoiding steroid-antifungal combination creams.
- Monitoring patients on systemic therapy.
- Incorporating soothing skincare alongside antifungal treatments.
➤ Treatment Options in Korea
Korea is known for comprehensive fungal skin management, with an emphasis on both medical clearance and cosmetic recovery.
Why Korea excels:
- Cutting-edge diagnostic tools → dermoscopy, Wood’s lamp, digital imaging.
- Holistic care → antifungal therapy + skincare for barrier repair.
- Integration with K-beauty science → pigmentation correction, hydration regimens.
- Focus on prevention → education on hygiene and long-term maintenance.
Unique Korean Practices:
- Customized antifungal skincare regimens → combining prescription and cosmeceuticals.
- LED therapy sessions to support antifungal clearance.
- Pigment-balancing facials after recovery.
- Medical tourism programs → skin infection management for international patients.
✨ Final Thoughts
Tinea Corporis Treatment in Korea offers a holistic, patient-centered approach to fungal skin infections. With topical and systemic antifungals, supported by barrier-repair skincare, LED therapy, and preventive regimens, Korean dermatologists ensure effective clearance and reduced recurrence.
By blending medical dermatology with K-beauty skincare practices, Korea has become a global leader in fungal infection management, helping patients restore both skin health and cosmetic confidence.