What it is
→ A skin screening exam is a thorough evaluation of the skin performed by a dermatologist or healthcare professional to detect signs of skin cancer, precancerous lesions, and other skin abnormalities.
→ The exam includes a head-to-toe visual inspection of moles, freckles, birthmarks, and unusual skin changes.
→ The goal is to identify skin cancers such as melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma at an early stage, when treatment is most effective.
→ A skin screening exam may also detect non-cancerous skin conditions, including chronic sun damage, keratoses, fungal infections, and pigmentary disorders.
Why it’s done
→ The main purpose of a skin screening exam is early detection of skin cancer, which significantly improves survival rates.
→ It is recommended for:
- Individuals with a personal or family history of skin cancer.
- People with fair skin, light hair, and light eyes, who are more prone to sun damage.
- Those with a high number of moles or atypical moles.
- Patients with a history of frequent sunburns or tanning bed use.
- Anyone noticing new or changing skin growths.
→ Beyond cancer detection, the exam also helps with monitoring chronic skin conditions and providing guidance on sun safety, skincare, and lifestyle adjustments.
Alternatives
→ While nothing replaces a professional skin screening exam, some alternatives include:
- Self-examination → regularly checking moles and skin spots at home using mirrors and photographs.
- Mobile apps and AI tools → apps that analyze moles from smartphone photos, though they are not fully reliable.
- Primary care checks → general physicians may do partial inspections before referring to dermatologists.
→ However, only a dermatologist-led exam with dermoscopy offers the most accurate detection.
Preparation
→ Preparing for a skin screening exam involves a few simple steps:
- Remove makeup and nail polish → so the skin and nails can be fully examined.
- Wear loose clothing → to make full-body inspection easier.
- Avoid tanning or heavy sun exposure → in the days before the exam.
- List concerns → prepare notes about any new, changing, or painful spots.
- Bring history records → including photos of past moles, biopsy reports, or family history of melanoma.
- No need to shave body hair → dermatologists are trained to examine skin thoroughly.
How it’s Done
→ A typical skin screening exam includes:
- Visual inspection → dermatologist examines the skin from head to toe, including scalp, nails, between fingers and toes, and hidden areas.
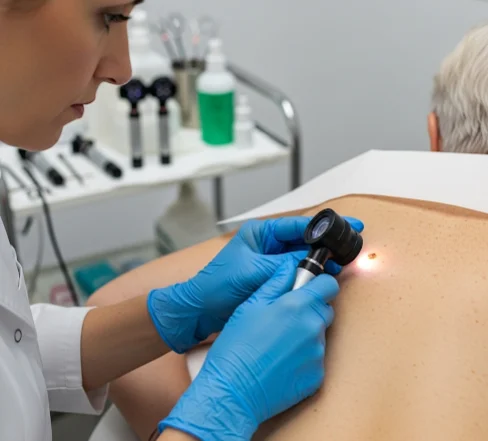
- Dermoscopy → handheld magnification with light to analyze mole structures and pigmentation.
- Photographic mapping → in some clinics, high-resolution body photography records baseline images for comparison over time.
- Suspicious lesion evaluation → if a mole meets the ABCDE rule (Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variation, Diameter >6 mm, Evolving), it may need further testing.
- Biopsy → if needed, a small sample is taken under local anesthesia for histological analysis.
→ The exam usually takes 10–30 minutes, depending on the number of moles and findings.
Recovery
→ The screening exam itself has no downtime. Patients can immediately return to daily activities.
→ If a biopsy is performed:
- Mild soreness or redness may last 1–3 days.
- A small bandage is applied, and aftercare involves cleaning and applying ointment.
- Healing occurs within 1–2 weeks.
→ Patients are advised to monitor skin regularly after the exam and schedule follow-ups as recommended.
Complications
→ The exam itself carries no risks.
→ Biopsy-related risks include:
- Minor pain or discomfort at the site.
- Infection, though rare with proper aftercare.
- Scarring at the biopsy site (usually minimal).
→ The most significant risk comes from not undergoing regular screenings, as skin cancers can progress undetected and become harder to treat.
Treatment options in Korea
→ Korea offers world-class skin screening exams, combining advanced dermatology with preventive care.
- Dermatology hospitals such as Seoul National University Hospital, Asan Medical Center, and Samsung Medical Center provide comprehensive screening programs.
- High-tech dermoscopy and digital mole mapping are widely used for accurate detection and long-term monitoring.
- Preventive culture → Korean clinics emphasize annual screenings, especially for high-risk patients.
- AI-supported analysis → some advanced clinics use artificial intelligence to support mole evaluation.
- Integration with aesthetics → screening exams often include personalized skincare guidance and sun protection regimens.
- Accessibility → private clinics in Seoul, Busan, and Daegu make screenings widely available, catering to both locals and international patients.
→ Korea is also at the forefront of skin cancer research and clinical trials, offering patients access to the latest diagnostic techniques and treatments.