What It Is
Defining Sebaceous Gland Hyperplasia
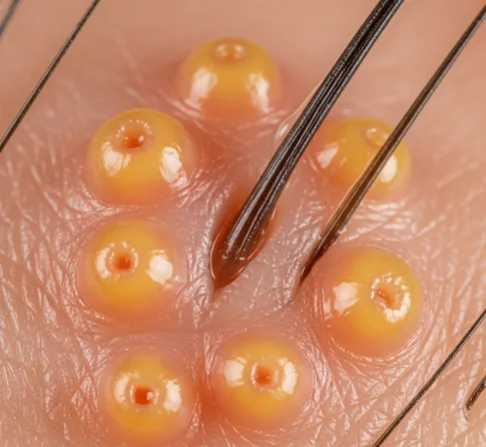
→ Sebaceous gland hyperplasia (SGH) is a common, benign skin condition caused by the overgrowth of sebaceous (oil) glands.
→ It usually appears as small, yellowish or flesh-colored bumps on the skin, often with a central indentation.
→ SGH occurs most frequently on the forehead, cheeks, and nose, but can also appear elsewhere on the face.
→ While not dangerous, SGH is often treated for cosmetic reasons, as the bumps may resemble acne, warts, or even skin cancer lesions.
Key Characteristics
- Small, soft papules (1–5 mm in size)
- Dome-shaped, sometimes with a central pit (umbilication)
- Most common in middle-aged and older adults
- More frequent in people with oily skin, rosacea, or history of sun damage
- Harmless, but may cause cosmetic distress
Why It’s Done
Main Reasons for Treatment
➡ Cosmetic Concerns – Patients often feel self-conscious about facial bumps.
➡ Misdiagnosis Prevention – SGH can resemble basal cell carcinoma; treatment ensures clarity.
➡ Texture Improvement – Smoother skin surface after treatment.
➡ Prevent Enlargement – Lesions can slowly grow larger if untreated.
➡ Emotional Confidence – Treating SGH improves self-image and quality of life.
Alternatives
Non-Medical Options
- Topical Retinoids (Tretinoin, Adapalene) → Help regulate oil glands and may shrink small lesions.
- Chemical Exfoliation → Mild peels (glycolic acid, salicylic acid) can improve appearance, though rarely eliminate bumps.
- Sun Protection → Prevents further sebaceous gland overgrowth and reduces worsening.
Medical Alternatives
→ If direct removal is not preferred, other therapies include:
- Laser Therapy (CO₂ or Erbium:YAG) → Vaporizes bumps with precision.
- Electrosurgery → Burns and removes growths using electric current.
- Cryotherapy → Freezes lesions with liquid nitrogen; less commonly used due to scarring risk.
- Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) → Combines light and photosensitizing agents to shrink sebaceous glands.
- Oral Isotretinoin → Rarely prescribed for extensive cases; reduces gland activity but has systemic side effects.
Preparation
Before Treatment
➡ Dermatology Consultation – A skin doctor examines lesions to confirm SGH and rule out skin cancer.
➡ Dermatoscopy or Biopsy – May be done if diagnosis is uncertain.
➡ Medication Review – Patients should inform doctors about current medications, especially blood thinners.
➡ Skin Cleansing – Area should be clean and makeup-free before treatment.
➡ Expectation Setting – Patients are advised that SGH may recur, and multiple treatments could be needed.
How It’s Done
Common Treatment Methods in Korea
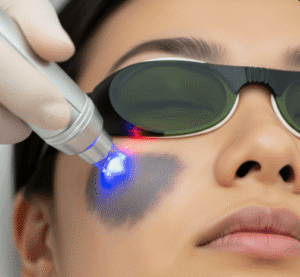
1. Laser Therapy
→ The most popular treatment in Korean dermatology.
- CO₂ Laser or Erbium:YAG Laser precisely vaporizes lesions.
- Provides smooth results with minimal scarring.
- Quick recovery time compared to older surgical methods.
2. Electrosurgery (Electrocautery)
→ A fine electric probe burns and removes SGH lesions.
- Effective for small bumps.
- May leave mild redness that fades over weeks.
3. Cryotherapy
→ Freezing lesions with liquid nitrogen.
- Not commonly favored in Korea due to higher risk of scarring or pigment change.
4. Photodynamic Therapy (PDT)
→ Involves applying a light-sensitive chemical to the skin, then activating it with laser/light.
- Shrinks oil glands and reduces new SGH formation.
- Often combined with lasers for improved outcomes.
5. Oral or Topical Retinoids
→ Used as preventive maintenance for patients with frequent recurrences.
- Helps regulate sebaceous gland activity.
Treatment Course
- Most treatments are outpatient procedures taking less than 30 minutes.
- Often completed in one session, though multiple visits may be required for widespread SGH.
- Maintenance with skincare and sun protection is crucial to prevent new lesions.
Recovery
Immediate Recovery
- Laser and Electrosurgery → Redness, mild swelling, and small scabs for 3–7 days.
- Cryotherapy → Blistering and crusting possible, healing within 1–2 weeks.
- Photodynamic Therapy → Redness and peeling similar to a mild sunburn for several days.
Long-Term Recovery
→ Skin heals within 1–3 weeks depending on treatment method.
→ Lesions typically do not scar if treated properly.
→ Recurrence is possible, requiring repeat treatments every few years.
→ Ongoing skincare with SPF, moisturizers, and gentle exfoliants helps maintain results.
Complications
Possible Risks
- Pigment Changes → Hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation, more common in darker skin types.
- Scarring → Rare, especially with precise laser therapy.
- Infection → Uncommon, but possible if scabs are picked or aftercare is neglected.
- Recurrence → SGH often reappears over time, even after successful removal.
- Prolonged Redness → May persist for weeks with aggressive treatments.
Treatment Options in Korea
Advanced Dermatology Expertise
Korean dermatology is internationally recognized for combining medical precision with cosmetic excellence, making it an ideal destination for SGH treatment.
Why Korea Excels in SGH Treatment
➡ Laser-first approach – Clinics prioritize CO₂ and erbium lasers for smooth, scar-free results.
➡ Integrated Aesthetic Care – Treatments are often combined with skin rejuvenation therapies like microneedling or chemical peels.
➡ Focus on Recurrence Prevention – Doctors emphasize sun protection, retinoids, and maintenance skincare.
➡ Cutting-edge Facilities – Korea is home to some of the world’s most advanced dermatology clinics.
Popular Uses in Korea
- Cosmetic Removal → Patients seek treatment to restore smooth, youthful skin.
- Anti-Aging Programs → SGH removal is often integrated into anti-aging and skin-brightening regimens.
- Combination Treatments → CO₂ laser + PDT is a common Korean approach for stubborn cases.
- Preventive Dermatology → Patients are educated about sun care and skincare to reduce recurrence.
Patient Experience in Korea
- Procedures are quick, safe, and outpatient-based.
- Clinics emphasize minimal downtime and natural cosmetic results.
- Aftercare kits with healing ointments, sunblock, and skincare guidance are often provided.
- Korean dermatologists combine medical care with aesthetic expertise, ensuring patients achieve both health and beauty goals.
Conclusion
Sebaceous gland hyperplasia treatment in Korea is a safe, advanced, and effective solution for patients seeking cosmetic improvement.
With laser therapy, electrosurgery, photodynamic therapy, and supportive skincare, Korean dermatologists provide excellent results while minimizing scarring and downtime.
Although SGH is harmless, its cosmetic impact can be distressing. Korea’s combination of cutting-edge technology, expert dermatologists, and integrated aesthetic programs makes it one of the best destinations for restoring smooth, blemish-free skin.