What it is
→ Ingrown hair treatment refers to medical and cosmetic methods used to manage and prevent hairs that curl back or grow sideways into the skin instead of emerging normally.
→ Ingrown hairs typically cause red bumps, inflammation, pain, and sometimes infection, most commonly in areas subject to shaving, waxing, or friction — such as the face, underarms, bikini line, legs, and neck.
→ Treatments range from home care and topical therapies to medical dermatology procedures designed to release trapped hairs, reduce inflammation, and prevent recurrence.
→ In Korea, ingrown hair treatments are advanced, often combining dermatology care, skincare innovation, and aesthetic procedures to restore smooth, healthy skin.
Why it’s done
→ Ingrown hair treatment is performed to:
- Relieve pain, itching, and irritation.
- Reduce redness, swelling, and infection risk.
- Improve skin appearance, since ingrown hairs may leave dark marks (post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation).
- Prevent scarring or keloid formation from chronic inflammation.
- Restore confidence and comfort, especially in visible or intimate areas.
→ It is especially important for:
- People with curly or coarse hair, more prone to ingrown hairs.
- Patients with sensitive skin irritated by shaving or waxing.
- Individuals undergoing frequent grooming (beard, bikini line, legs).
- Those with a history of folliculitis or hyperpigmentation.
Alternatives
→ Alternatives to formal ingrown hair treatment include:
- Warm compresses → to soften skin and encourage trapped hairs to emerge.
- Exfoliation → gentle scrubs or chemical exfoliants (salicylic acid, glycolic acid) to free hairs.
- Topical soothing creams → aloe vera or hydrocortisone for mild inflammation.
- Over-the-counter antiseptic creams → prevent infection.
→ While useful for mild cases, professional treatments are needed for recurrent, painful, or infected ingrown hairs.
Preparation
→ Before seeking ingrown hair treatment, patients should:
- Stop aggressive shaving or waxing in the affected area.
- Avoid picking or squeezing ingrown hairs, which worsens inflammation and risks scarring.
- Keep skin clean → wash gently with a mild cleanser.
- Note history of outbreaks → frequency, triggers, and past treatments.
- Disclose skin conditions (eczema, keloids, pigmentation issues) to the dermatologist.
→ In Korean clinics, patients often undergo skin analysis and dermoscopy to assess the depth and severity of ingrown hairs.
How it’s Done
→ Ingrown hair treatment typically includes:
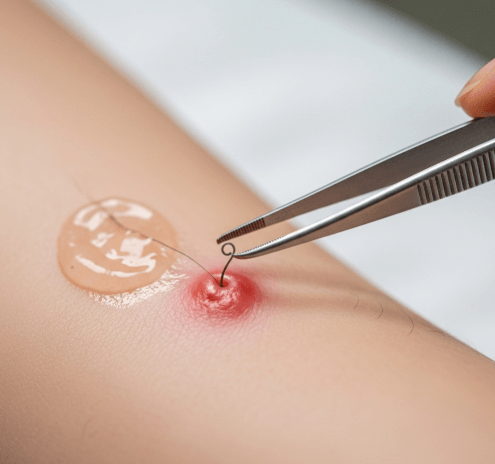
- Professional extraction
- Dermatologists may gently release ingrown hairs with sterile tools.
- This is done carefully to avoid scarring.
- Topical therapy
- Exfoliating agents → salicylic acid, glycolic acid, or retinoids to prevent follicle blockage.
- Anti-inflammatory creams → hydrocortisone or prescription steroid creams.
- Antibiotic creams → for infected ingrown hairs.
- Oral medications (if severe)
- Oral antibiotics → for widespread infected folliculitis.
- Oral retinoids (isotretinoin) → in chronic, severe cases with scarring.
- Laser hair removal (LHR)
- One of the most effective long-term solutions.
- Lasers destroy hair follicles, drastically reducing the chance of future ingrown hairs.
- Especially recommended for beard areas, bikini line, and legs.
- Chemical peels or microdermabrasion
- Used to smooth skin texture and reduce post-inflammatory dark spots.
- LED light therapy
- Reduces inflammation and speeds healing.
→ Sessions vary depending on severity — from a single extraction visit to ongoing treatment plans for chronic cases.
Recovery
→ Recovery after ingrown hair treatment depends on the method used:
- Professional extraction → mild redness for 1–2 days, resolves quickly.
- Topical therapy → ongoing use clears bumps within 1–2 weeks.
- Laser hair removal → gradual reduction in ingrown hairs over multiple sessions.
- Chemical peels or exfoliants → mild peeling for 3–5 days, smoother skin afterward.
→ Patients should:
- Avoid shaving or waxing the treated area for several days.
- Use fragrance-free moisturizers to keep skin hydrated.
- Apply sunscreen daily to prevent pigmentation of healing spots.
- Refrain from scratching or picking at treated skin.
Complications
→ If untreated or mismanaged, ingrown hairs can lead to:
- Chronic folliculitis (recurring infections).
- Hyperpigmentation → dark spots after inflammation.
- Scarring or keloids in severe cases.
- Abscess formation requiring drainage.
→ Professional treatment minimizes these risks and improves both skin health and appearance.
Treatment options in Korea
→ Korea offers some of the most advanced options for ingrown hair treatment:
- Dermatology-led programs → combining extraction, topical therapies, and preventive care.
- Laser hair removal → widely used as a permanent solution, with specialized devices for sensitive areas.
- Cosmetic add-ons → clinics often combine ingrown hair care with skin whitening, brightening, or scar-reduction treatments for an even skin tone.
- Advanced skincare products → medical-grade exfoliating toners, serums, and calming creams are prescribed as part of aftercare.
- High hygiene standards → strict sterilization ensures safe extraction and treatment.
- Medical tourism → English-speaking staff and tailored recovery plans make Korean clinics attractive for international patients.
→ With cutting-edge technology, medical expertise, and an aesthetic focus, Korea is one of the best destinations for effective and long-term ingrown hair treatment.