Hydroquinone Protocol in Korea refers to the dermatologist-guided use of hydroquinone, one of the most powerful skin-lightening agents, for treating pigmentation disorders such as melasma, freckles, age spots, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), and sun damage. Hydroquinone works by inhibiting tyrosinase, the key enzyme involved in melanin production, thereby reducing excess pigmentation.
In Korea, hydroquinone is not commonly available as an over-the-counter product because of its potency. Instead, it is used under strict medical supervision in dermatology clinics or prescribed in regulated strengths, often as part of a short-term, cyclical protocol. Korean dermatologists frequently combine hydroquinone with lasers, peels, and K-beauty skincare regimens, ensuring both safety and effectiveness.
What It Is
Hydroquinone is a depigmenting agent considered the gold standard for pigmentation management worldwide. It is available in strengths ranging from 2% (cosmetic) to 4–10% (medical use).
In Korea, hydroquinone is typically used in:
- Prescription creams (4–5% concentration).
- Combination formulas with retinoids, steroids, or Vitamin C.
- Dermatology protocols paired with laser or peel treatments.
Because Asian skin is more prone to rebound pigmentation and irritation, Korean dermatologists apply hydroquinone in a carefully controlled, time-limited regimen rather than continuous use.
Why It’s Done
Hydroquinone protocols are widely used in Korea to:
- Treat melasma → One of the most stubborn pigmentation disorders.
- Fade PIH (post-acne dark spots) → Especially common in young adults.
- Remove freckles and sun spots → For cosmetic skin brightening.
- Maintain results after laser therapy → Prevents pigment from redeveloping.
- Achieve brighter, even-toned skin → In line with K-beauty ideals of radiant skin.
Because it is powerful but potentially irritating, hydroquinone is always prescribed with caution in Korea.
Alternatives
If hydroquinone is not suitable, Korean clinics often recommend alternatives:
- Arbutin → A natural derivative of hydroquinone, gentler but less potent.
- Niacinamide → Reduces melanin transfer between cells.
- Tranexamic acid → Popular in Korea for melasma control.
- Vitamin C serums → Antioxidant brightening.
- Kojic acid, licorice extract, and glutathione → Used in K-beauty products.
- Laser toning or Pico lasers → For stubborn pigmentation.
- Chemical peels → Glycolic or lactic acid peels for exfoliation.
Preparation
Preparation before starting a hydroquinone protocol in Korea includes:
- Consultation → Dermatologists assess pigmentation type, skin sensitivity, and history of PIH.
- Skin conditioning → Patients may be advised to use gentle moisturizers and sunscreen for 1–2 weeks before starting.
- Patch test → A small area is tested to check for irritation.
- Avoidance of irritants → Patients stop retinoids, strong acids, or exfoliants before use.
How It’s Done
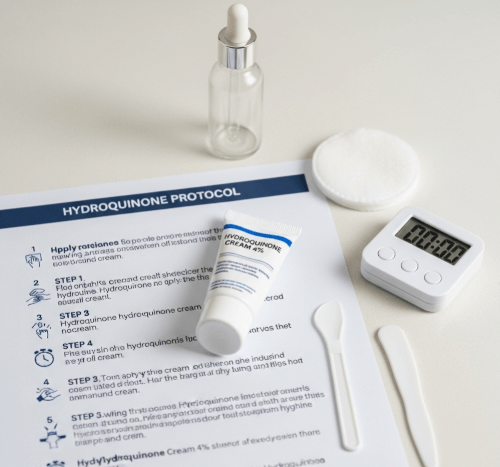
A typical hydroquinone protocol in Korea involves short-term, cyclical application under dermatologist supervision:
- Application phase (8–12 weeks)
- Hydroquinone cream (usually 4%) applied once daily at night on affected areas.
- Sunscreen and antioxidants used in the daytime.
- In resistant cases, a triple combination cream may be prescribed (hydroquinone + retinoid + mild steroid).
- Rest phase (4–8 weeks)
- Hydroquinone is discontinued to prevent side effects.
- Maintenance with niacinamide, arbutin, or Vitamin C serums.
- Repetition phase
- The cycle may be repeated if pigmentation persists, but dermatologists rarely allow hydroquinone use longer than 3–4 months at a time.
- Clinic-based integration
- Many Korean dermatologists combine hydroquinone use with low-fluence laser toning, Pico lasers, or chemical peels to accelerate results.
Recovery
Recovery and monitoring are crucial parts of the hydroquinone protocol:
- First 2 weeks → Mild redness, dryness, or peeling may occur.
- 4–8 weeks → Pigmentation begins to lighten noticeably.
- After 12 weeks → Results peak; hydroquinone is discontinued to prevent side effects.
- Maintenance → Patients switch to gentler brightening agents and continue strict sun protection.
Korean dermatologists emphasize hydration and barrier repair to minimize irritation.
Complications
While hydroquinone is highly effective, potential side effects include:
- Skin irritation → Redness, peeling, stinging.
- Rebound pigmentation → If overused or stopped abruptly without sunscreen.
- Exogenous ochronosis → A rare condition causing bluish-black skin, seen with unsupervised long-term use.
- Allergic contact dermatitis → Rare but possible.
Korean clinics prevent complications by:
- Using low concentrations (4%).
- Applying time-limited protocols.
- Providing rest periods and maintenance regimens.
- Enforcing daily SPF 50+ sunscreen use.
Treatment Options
Korean clinics integrate hydroquinone into broader pigmentation treatment programs:
- Melasma management protocols → Hydroquinone with tranexamic acid and Q-switched laser toning.
- PIH prevention and correction → Hydroquinone cycles after acne or laser treatments.
- Brightening packages → Hydroquinone with Vitamin C infusion and whitening facials.
- Combination therapies → Hydroquinone plus Pico lasers or chemical peels.
- Maintenance programs → Switching to arbutin, niacinamide, or glutathione once hydroquinone is paused.
Clinics in Seoul, particularly in Gangnam, often offer multi-session pigmentation care packages where hydroquinone is part of a larger protocol.
Conclusion
Hydroquinone Protocol in Korea is considered the gold standard for pigmentation treatment, but it is always applied with caution and precision. By limiting usage to short-term cycles under medical supervision, Korean dermatologists maximize results while minimizing risks.
Supported by laser therapies, K-beauty brightening agents, and strict sun protection, Korea’s approach ensures safe, natural-looking, and long-lasting results. For patients struggling with melasma, freckles, PIH, or sun spots, the hydroquinone protocol in Korea provides one of the most effective and scientifically proven solutions available worldwide.