What it is
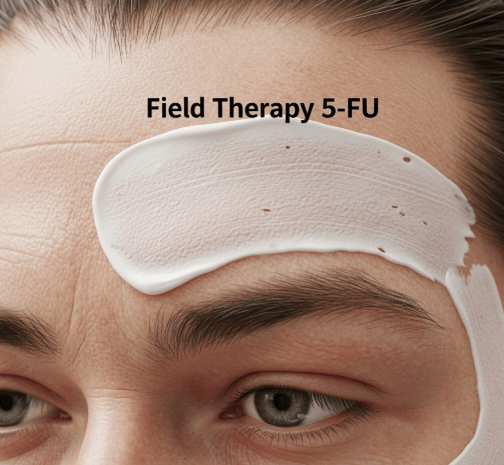
→ Field therapy with 5-FU (5-fluorouracil) is a topical dermatological treatment used to target areas of skin that have developed actinic keratoses (precancerous lesions caused by chronic sun exposure) and other forms of actinic damage.
→ Instead of treating a single lesion, field therapy addresses an entire “field” of sun-damaged skin (such as the face, scalp, forearms, or chest), where both visible and hidden (subclinical) lesions may exist.
→ 5-FU is a chemotherapeutic cream that works by selectively destroying abnormal, sun-damaged skin cells while sparing most normal skin.
→ The goal is to clear existing precancerous lesions, reduce the risk of progression to skin cancer, and rejuvenate the skin’s surface.
Why it’s done
→ Field therapy with 5-FU is performed to:
- Treat multiple actinic keratoses across a large sun-exposed area.
- Target both visible and invisible lesions, preventing future cancers.
- Reduce the risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
- Improve cosmetic appearance, as treatment often leaves skin smoother and clearer after healing.
- Provide a non-surgical option for patients who have widespread sun damage.
→ It is especially useful for individuals with fair skin, a history of long-term sun exposure, or repeated episodes of actinic keratosis.
Alternatives
→ Alternatives to 5-FU field therapy include:
- Imiquimod cream → stimulates the immune system to attack abnormal cells.
- Diclofenac gel → anti-inflammatory topical therapy, milder but slower-acting.
- Ingenol mebutate → previously used but less common due to side effect concerns.
- Photodynamic therapy (PDT) → light-based treatment that destroys damaged cells with a photosensitizing agent.
- Cryotherapy → liquid nitrogen freezing, usually for isolated lesions, not field-wide areas.
- Laser resurfacing or chemical peels → cosmetic options that also reduce precancerous lesions.
→ Dermatologists may combine these therapies with or alternate them after 5-FU treatment for optimal results.
Preparation
→ Preparing for 5-FU field therapy involves:
- Dermatology consultation → to confirm diagnosis and select the treatment area.
- Avoid sun exposure → skin should not be sunburned or freshly tanned before therapy.
- Stop irritating skincare → discontinue harsh exfoliants or retinoids 3–5 days before starting.
- Plan downtime → treatment often causes redness and peeling, so patients may wish to schedule around work or social events.
- Baseline photos → dermatologists may record images to track progress.
- Moisturizers and sunscreens ready → patients should prepare post-treatment skincare in advance.
How it’s Done
→ The therapy typically follows this process:
- Application → 5-FU cream is applied directly to the affected area once or twice daily, as prescribed.
- Duration → treatment usually lasts 2–4 weeks for facial skin and longer (up to 6–8 weeks) for thicker skin on arms or scalp.
- Reaction phase → within a few days, the treated area becomes red, inflamed, and may blister or peel. This indicates the drug is working on damaged cells.
- Completion → treatment continues until most lesions are destroyed and the dermatologist decides to stop.
- Healing phase → after discontinuation, the skin gradually heals, leaving smoother, healthier skin.
→ Some patients may receive sequential or combination treatments (such as cryotherapy or PDT) after the 5-FU cycle for enhanced clearance.
Recovery
→ Recovery involves a healing period after the treatment cycle:
- Redness, swelling, crusting, and peeling usually peak during treatment.
- Discomfort can be managed with soothing ointments, cool compresses, and mild pain relief if needed.
- Healing phase typically takes 2–4 weeks after treatment stops.
- Skin improvements (smoother texture, clearer tone) appear gradually as healing continues.
- Sun protection is critical during recovery to prevent further damage.
→ Most patients fully recover within 1–2 months, depending on the size of the treatment field.
Complications
→ Common temporary side effects include:
- Redness, irritation, and itching.
- Crusting, scaling, or blistering in the treated area.
- Swelling or discomfort.
- Photosensitivity requiring strict sun protection.
→ Rare but possible complications include:
- Infection if the skin barrier is broken.
- Allergic reactions to the cream.
- Persistent pigmentation changes (lighter or darker spots).
- Scarring (rare if used under medical supervision).
→ Despite these risks, 5-FU is considered highly effective and safe when monitored by a dermatologist.
Treatment options in Korea
→ Korea offers advanced dermatology care, and field therapy with 5-FU is widely practiced for sun-damaged skin and actinic keratoses.
- University hospitals and clinics such as Asan Medical Center, Samsung Medical Center, and Seoul National University Hospital frequently prescribe 5-FU therapy.
- Customized protocols → Korean dermatologists often combine 5-FU with other treatments such as photodynamic therapy, cryotherapy, or laser resurfacing for better results.
- Patient education → Korean clinics emphasize strict sunscreen use and preventive strategies during and after therapy.
- Follow-up programs → patients undergo scheduled monitoring to ensure complete healing and detect recurrence.
- Integration with aesthetics → clinics may include cosmetic dermatology treatments (like chemical peels or skin rejuvenation) alongside field therapy to improve both medical outcomes and appearance.
- Medical tourism services → English-speaking staff and international patient programs make these treatments accessible to visitors seeking advanced care.
→ With cutting-edge dermatology, combination treatment strategies, and strong preventive culture, Korea is an excellent place for managing actinic damage with 5-FU field therapy.