What it is
Curettage and electrodesiccation in Korea is a dermatological surgical technique used to treat certain skin cancers and precancerous lesions such as basal cell carcinoma (BCC), squamous cell carcinoma in situ, and actinic keratosis.
The procedure combines two steps:
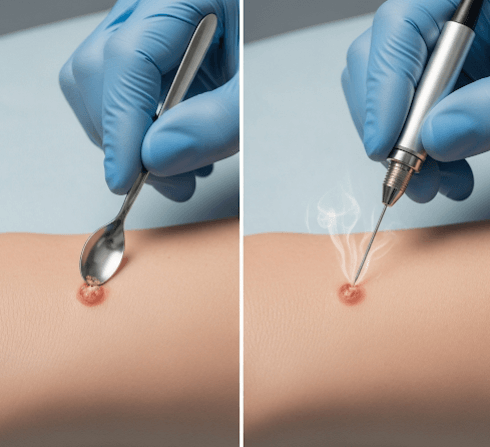
- Curettage → The lesion is scraped away using a curette (a sharp, spoon-shaped surgical instrument).
- Electrodesiccation → An electric current is applied to the tissue to destroy residual cancer cells and control bleeding.
→ This process may be repeated 2–3 times in the same session to ensure complete removal.
• In Korea, curettage and electrodesiccation is typically performed in dermatology and skin cancer clinics, especially for small, low-risk lesions on the trunk or extremities.
• It is valued for its efficiency, affordability, and effectiveness, though not usually chosen for areas requiring high cosmetic precision (e.g., the face).
Why it’s done
Patients in Korea undergo curettage and electrodesiccation for:
→ Treatment of non-melanoma skin cancers → Especially superficial or nodular BCC and SCC in situ.
→ Actinic keratosis management → As an alternative to cryotherapy.
→ Quick outpatient removal → Often completed in a single visit.
→ Minimal equipment needs → Less invasive than excision or Mohs surgery.
→ Functional convenience → Used when cosmetic outcome is less critical.
Alternatives
Other treatments for similar lesions include:
• Cryosurgery → Freezing precancerous or cancerous cells with liquid nitrogen.
• Mohs micrographic surgery → Gold standard for high-risk or facial skin cancers.
• Excisional surgery → Complete removal with suturing, useful for suspicious melanomas.
• Topical treatments → Imiquimod or 5-fluorouracil for superficial cancers.
• Photodynamic therapy (PDT) → Light-based destruction of cancerous cells.
→ Curettage and electrodesiccation is chosen for superficial, low-risk lesions where speed and efficiency are priorities.
Preparation
Before undergoing curettage and electrodesiccation in Korea, preparation includes:
- Dermatology consultation → To confirm lesion type (via biopsy if needed).
- Medical history review → Checks for pacemakers (important with electrical devices), bleeding disorders, or allergies.
- Local anesthesia planning → Injection of lidocaine around the lesion.
- Patient education → Clear explanation of procedure, healing process, and cosmetic expectations.
→ Korean dermatologists often use digital dermoscopy to confirm lesion margins before treatment.
How it’s done
Curettage and electrodesiccation in Korea is performed in dermatology clinics as an outpatient procedure:
- Local anesthesia → Numbs the treatment area.
- Curettage → The lesion is scraped away using a curette.
- Electrodesiccation → A fine-tipped electrode applies electric current to destroy residual cells and seal blood vessels.
- Repetition → The curettage–desiccation cycle is repeated 2–3 times.
- Dressing → The wound is covered with ointment and a sterile dressing.
→ The entire procedure usually takes 15–30 minutes.
Recovery
Recovery after curettage and electrodesiccation is straightforward:
• Healing time → Typically 2–4 weeks, depending on lesion size and depth.
• Scab formation → A crust forms and falls off naturally as the wound heals.
• Scar outcome → Usually a flat, hypopigmented (lighter) scar.
• Aftercare → Patients apply ointment, keep the site clean, and avoid picking scabs.
• Sun protection → Required to reduce pigmentation changes.
→ Most patients return to daily activities immediately.
Complication
Possible risks include:
- Scarring → Often lighter or atrophic scars at the treatment site.
- Pigment changes → Hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation may occur.
- Recurrence → Slightly higher risk compared to Mohs surgery.
- Infection → Rare with proper wound care.
- Delayed healing → More likely in larger or deeper lesions.
→ Korean dermatologists minimize risks by careful selection of lesions suitable for this procedure.
Treatment option in Korea
Korea provides advanced curettage and electrodesiccation treatments for skin lesions:
→ Dermatology hospitals → Equipped with modern electrosurgical units for precise tissue control.
→ Skilled dermatologists → Experienced in balancing complete lesion removal with minimal tissue damage.
• Combination care → May be paired with cryosurgery, topical creams, or laser therapy for enhanced outcomes.
• Scar management → Korean clinics often add fractional laser or silicone gel therapy post-treatment to reduce scar visibility.
• Medical tourism → Korea is increasingly chosen for its affordable, efficient, and cosmetically conscious skin cancer treatments.
→ With its precision, efficiency, and integration of scar management, curettage and electrodesiccation in Korea remains an effective option for selected low-risk skin cancers and actinic keratoses.