What it is
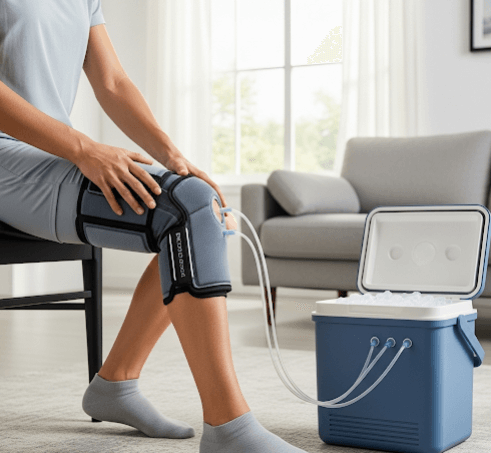
→ Cooling device therapy refers to the use of medical or cosmetic cooling systems during or after dermatological procedures — particularly laser treatments, light-based therapies, injectables, and aesthetic procedures — to protect the skin, minimize discomfort, and prevent complications.
→ Cooling may be delivered in several ways:
- Contact cooling → chilled sapphire or metal tips built into laser handpieces.
- Cryogen spray cooling (CSC) → a short burst of cryogenic fluid sprayed onto skin before each laser pulse.
- Air cooling → continuous cold air streams directed at the skin.
- Post-treatment cooling packs/masks → applied after procedures to soothe inflammation.
→ In Korea, cooling device therapy is a standard component of advanced dermatology and cosmetic treatments, ensuring both safety and patient comfort.
Why it’s done
→ Cooling device therapy is used to:
- Protect the epidermis → prevents burns and pigmentation issues during high-energy treatments.
- Reduce pain and discomfort → improves patient tolerance of lasers and injectables.
- Minimize redness, swelling, and inflammation after procedures.
- Improve recovery → speeds healing and reduces downtime.
- Enhance treatment precision → allows dermatologists to use higher energy safely, improving effectiveness.
→ It is especially important in:
- Laser hair removal (LHR).
- Vascular lasers (pulsed dye, Nd:YAG).
- Pigmentation lasers (Q-switched, Alexandrite).
- Skin resurfacing (CO₂, Er:YAG).
- Injectable procedures (fillers, Botox, PRP).
Alternatives
→ Alternatives to professional cooling device therapy include:
- Ice packs → simple but uneven cooling and less precise.
- Cold compresses → soothing but not strong enough for laser protection.
- Topical numbing creams → reduce pain but do not protect the skin barrier from heat.
- No cooling → increases risk of burns, pigmentation, and discomfort.
→ While useful for minor care, device-based cooling systems are superior in medical and cosmetic treatments.
Preparation
→ Before cooling therapy is used:
- Skin is cleansed → oils, lotions, or makeup are removed for even cooling.
- Medical history is reviewed → conditions like Raynaud’s disease or cold urticaria (cold allergy) may require adjustments.
- Device selection is matched → depending on procedure type (e.g., cryogen spray for lasers, air cooling for injectables).
- Patch testing → sometimes combined with test patch protocols for laser treatments.
→ Korean clinics typically explain the cooling process before procedures to reassure patients.
How it’s Done
→ Cooling device therapy is applied in different ways depending on the procedure:
- During laser procedures
- Contact cooling tips → continuously chill the skin as the laser pulse is delivered.
- Cryogen spray → applied milliseconds before each laser pulse.
- Cold air flow → directed at treatment area throughout session.
- During injectables
- Small cooling probes or cold air devices numb the skin before needle insertion.
- Cooling reduces pain, swelling, and bruising.
- Post-treatment recovery
- Cold masks, gel packs, or cooling sheets are applied to reduce redness and inflammation.
- Cooling is often combined with soothing serums or LED therapy.
→ Duration varies:
- Laser cooling → delivered in real time during every laser pulse.
- Injectable cooling → a few seconds before injection.
- Post-treatment cooling → 10–20 minutes after procedure.
Recovery
→ Cooling therapy itself does not require recovery but enhances recovery after procedures:
- Immediate relief → reduced pain, burning, or stinging sensations.
- 24 hours → less swelling and redness compared to treatments without cooling.
- 1–7 days → smoother, quicker healing process with fewer complications.
→ Patients are advised to:
- Continue gentle at-home cooling with cold compresses if needed.
- Use hydrating creams to support barrier repair.
- Apply sunscreen daily, as cooling does not eliminate photosensitivity.
Complications
→ Cooling device therapy is generally safe, but possible risks include:
- Frostbite or overcooling burns (rare, with excessive cryogen or contact cooling).
- Skin irritation or dryness from prolonged exposure.
- Uneven cooling leading to inconsistent protection in some devices.
- Cold-induced conditions → flare-ups in patients with cold urticaria.
→ These risks are rare in professional Korean clinics, where devices are precisely calibrated and closely monitored.
Treatment options in Korea
→ Korea is internationally recognized for its use of cooling systems in dermatology and cosmetic treatments:
- Integrated cooling in laser devices → most Korean clinics use platforms with sapphire contact cooling, cryogen spray, or dynamic air systems.
- Comfort-first approach → many clinics market “painless laser” sessions thanks to advanced cooling devices.
- Post-treatment cooling facials → soothing masks, cryotherapy facials, and cooling gels are standard recovery add-ons.
- Skin rejuvenation packages → cooling therapy is paired with LED therapy, hydration boosters, or stem-cell serums to accelerate healing.
- Medical tourism services → international patients are offered structured cooling-based aftercare with detailed instructions.
- Advanced safety → Korean dermatologists rely heavily on cooling to prevent pigmentation in Asian and darker skin tones.
→ With cutting-edge devices, patient-focused protocols, and integrated skincare, Korea provides some of the world’s best cooling therapy as part of laser and cosmetic treatments.