What it is
➝ Condyloma acuminata (genital warts) are benign growths caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), most often HPV types 6 and 11.
➝ They appear as flesh-colored, raised, or cauliflower-like lesions on the genital, perianal, or oral mucosa.
➝ While not cancerous, they are highly contagious through sexual contact and can cause discomfort, itching, bleeding, and psychosocial distress.
➝ Treatment aims to remove visible lesions, reduce symptoms, and prevent recurrence, although HPV may persist in the skin.
Why it’s done
→ To eliminate visible and symptomatic warts that cause discomfort or embarrassment.
→ To reduce transmission of HPV to sexual partners.
→ To minimize recurrence and complications, as untreated lesions may enlarge or spread.
→ To improve psychological well-being, as genital warts often cause significant anxiety and stigma.
→ In Korea, treatment is widely available in dermatology, urology, gynecology, and sexual health clinics with a range of modern options.
Alternatives / Treatment Modalities
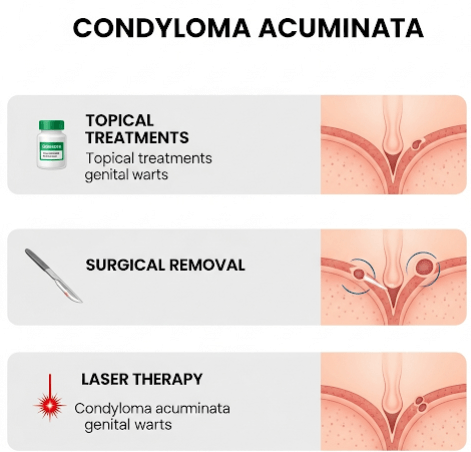
→ Topical patient-applied therapies:
- Imiquimod 5% cream: Immune response modifier applied 3 times per week for up to 16 weeks.
- Podophyllotoxin (0.5% solution or gel): Antimitotic agent applied by the patient in cycles.
- Sinecatechins (15% ointment): Green tea extract with antiviral and immunomodulating effects, used 3 times daily.
→ Clinician-administered treatments:
- Cryotherapy (liquid nitrogen): Freezing the wart tissue, repeated every 1–2 weeks until clearance.
- Electrocautery: Burning off lesions under local anesthesia.
- Laser therapy (CO₂ laser): Precise vaporization of warts, useful for resistant or large lesions.
- Surgical excision: Physical removal, often for bulky or keratinized warts.
- Trichloroacetic acid (TCA): Caustic agent applied directly to warts weekly.
→ Adjunctive / preventive strategies:
- HPV vaccination (Gardasil 9): Prevents infection from HPV types that cause genital warts and certain cancers.
- Barrier methods (condoms): Reduce, but do not completely eliminate, transmission risk.
- Partner evaluation and counseling: To address transmission and reinfection risk.
Preparation
→ Clinical diagnosis is usually sufficient; biopsy is performed if lesions are atypical or unresponsive to treatment.
→ Patients are advised to avoid shaving or scratching lesions to reduce autoinoculation.
→ Sexual partners may also be examined and counseled.
→ In Korea, many clinics include HPV testing and cervical cancer screening for women as part of comprehensive care.
How it’s Done
→ Small, uncomplicated warts: Often treated with cryotherapy or topical agents.
→ Multiple or resistant lesions: Treated with a combination of methods such as laser or electrocautery plus topical maintenance.
→ Bulky or keratinized warts: Excision or laser therapy under local anesthesia.
→ Follow-up care: Most patients require several treatment sessions (every 1–3 weeks) until clearance.
→ In Korean clinics, combination therapy (e.g., cryotherapy + imiquimod) is common to lower recurrence rates.
Recovery
→ Most warts resolve within 4–12 weeks of treatment, depending on method and immune status.
→ Cryotherapy and TCA may cause temporary blistering, scabbing, or mild pain.
→ Laser and electrocautery have longer healing times but lower recurrence rates for stubborn lesions.
→ Psychological relief is significant once lesions are cleared, though patients must be counseled about recurrence risk.
Complications
→ Recurrence is common, with rates up to 30–50% within the first 6 months.
→ Local side effects: Pain, redness, swelling, or scarring depending on treatment.
→ Transmission risk: HPV may persist even after visible warts are cleared.
→ Emotional distress: Anxiety about recurrence or partner transmission.
Treatment Options in Korea
→ Korean dermatology and urology clinics provide a wide range of wart treatments, with access to advanced CO₂ laser therapy and electrocautery equipment.
→ Cryotherapy is the most commonly used first-line treatment due to its effectiveness and simplicity.
→ Imiquimod and podophyllotoxin are available for patient-applied home therapy, often used after clinic-based treatments.
→ Many hospitals use combination regimens (laser removal followed by topical imiquimod) to lower recurrence.
→ Preventive HPV vaccination is strongly encouraged, and many Korean clinics integrate this into genital wart management programs.
→ With Korea’s comprehensive approach, patients benefit from medical, surgical, and preventive strategies, along with strong emphasis on education and counseling to reduce recurrence and transmission.