Advanced dermatologic management for tattoo-related skin allergies
What it is
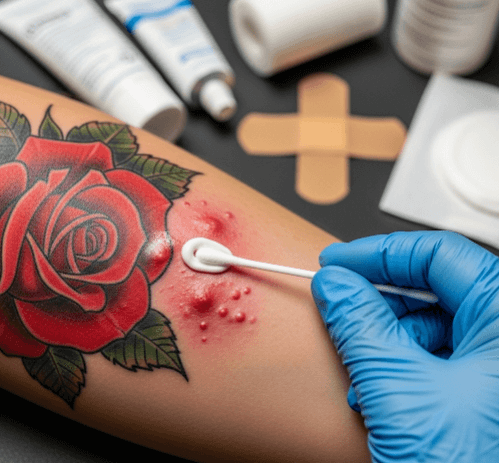
An allergic tattoo pigment reaction happens when the immune system identifies certain components of tattoo ink as harmful and triggers an inflammatory response. This is most common with red, yellow, green, and blue pigments, which often contain metals, azo dyes, or preservatives.
Reactions may appear soon after tattooing or even months to years later, and can look like:
- Itching, redness, and swelling localized to the tattoo
- Raised or scaly patches, mimicking eczema or psoriasis
- Blistering or nodules, as the skin reacts strongly to the pigment
- Chronic irritation, where the tattooed area never fully settles
In Korea, allergic tattoo pigment reaction care is highly specialized, focusing not only on reducing inflammation but also on restoring skin health and appearance through dermatology and cosmetic treatments.
Why it’s done
Treating allergic tattoo pigment reactions is important for both health and aesthetics.
✔ Symptom relief – Persistent itching, burning, or pain can affect quality of life.
✔ Preventing complications – Ongoing inflammation may lead to infections, scarring, or chronic dermatitis.
✔ Cosmetic correction – Reactions often distort the tattoo, causing uneven appearance.
✔ Emotional well-being – Tattoos are personal; allergic changes may cause stress and embarrassment.
✔ Skin protection – Continuous inflammation weakens skin and may increase sensitivity to other allergens.
Alternatives
There are several management and corrective options for tattoo pigment reactions.
→ Topical treatments:
- Corticosteroid creams reduce inflammation
- Antihistamine creams control itching
→ Systemic medications:
- Oral antihistamines relieve allergy symptoms
- Short steroid courses may be used in severe cases
→ Laser removal:
- Q-switched or picosecond lasers break down allergenic pigments
- Especially effective for red or multi-colored tattoos
→ Surgical excision:
- Cutting out the tattooed area, used for small, stubborn reactions
→ Observation:
- For mild cases, doctors may choose careful monitoring without intervention
In Korea, laser methods combined with post-laser skin repair therapies are the most common and effective solutions.
Preparation
Before treatment begins, proper preparation ensures the best outcome.
➤ Clinical evaluation – A dermatologist inspects the tattoo to confirm allergy and rule out infection.
➤ Patch testing – Identifies specific allergens within the pigment.
➤ Medical history – Includes prior allergic responses, skin healing capacity, or chronic conditions.
➤ Treatment planning – Options such as laser removal, topical care, or excision are explained to the patient.
➤ Skin care instructions – Patients are advised to avoid scratching, harsh creams, or sun exposure before therapy.
How it’s done
Management depends on the type and severity of the reaction.
➔ Topical and systemic therapy:
- Steroid creams calm localized inflammation
- Oral antihistamines reduce itching and allergic spread
- Moisturizing ointments restore skin barrier
➔ Laser therapy:
- Q-switched Nd:YAG or picosecond lasers deliver targeted pulses to fragment pigment particles
- The body’s immune system clears pigment fragments naturally
- Requires multiple sessions at 4–8 week intervals
➔ Surgical excision:
- Reserved for small areas with severe reactions
- Performed under local anesthesia, followed by stitches or skin grafts if needed
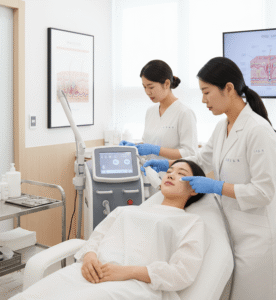
➔ Post-treatment cosmetic care:
- In Korea, clinics often include LED light therapy, scar prevention creams, and skin rejuvenation treatments for optimal healing
Recovery
Recovery time varies by treatment choice.
→ Topical or oral therapy: Symptoms ease within days to weeks but may recur if pigment remains.
→ Laser treatment: Temporary redness, swelling, or scabbing lasts 1–2 weeks; pigment fades gradually across months.
→ Surgery: Healing takes 2–3 weeks, with scarring possible if not carefully managed.
→ Cosmetic results: Korean dermatologists often follow up with pigment correction or scar care lasers to ensure natural skin appearance.
Complications
Potential risks include:
✔ Temporary irritation from topical steroids or antihistamines
✔ Laser side effects such as blistering or crusting
✔ Pigmentation changes – hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation
✔ Scarring – rare, but possible with excision or aggressive healing response
✔ Recurrence – if pigment fragments remain in the skin
Korea’s advanced dermatology practices reduce risks through modern laser systems, gentle aftercare, and aesthetic follow-up treatments.
Treatment options in Korea
Korea is a global leader in pigment and allergy management, making it one of the best places for tattoo-related allergic care.
➤ Advanced laser technology – Q-switched and picosecond lasers, specifically calibrated for pigment removal.
➤ Dermatology-cosmetic integration – Medical management is combined with aesthetic procedures to restore natural skin texture and tone.
➤ Scar prevention protocols – Clinics use silicone gels, regenerative ointments, and microneedling as needed.
➤ Comprehensive testing – Many clinics test tattoo inks for allergen content to personalize treatment.
➤ Medical tourism services – International patients benefit from bilingual consultations and tailored treatment schedules.
➤ Ongoing research – Korean dermatologists publish global studies on pigment reactions, ensuring evidence-based treatments.
Patients who seek allergic tattoo pigment reaction care in Korea receive world-class treatment, superior cosmetic results, and advanced aftercare, making it one of the safest and most effective destinations for this condition.