What it is
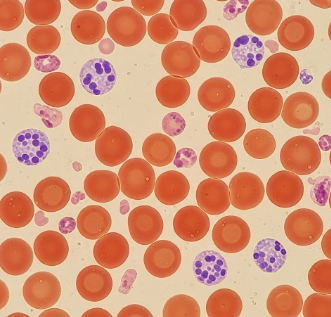
A red blood cell count (RBC count) is a common blood test that measures the number of red blood cells (erythrocytes) in your blood. RBCs are responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues and returning carbon dioxide back to the lungs for exhalation.
➡ Key points:
- ✔ Part of a complete blood count (CBC)
- ✔ Helps evaluate overall health and detect medical conditions
- ✔ Used to diagnose anemia, dehydration, bleeding disorders, and bone marrow diseases
💡 In Korea, RBC counts are widely available at hospitals, health screening centers, and private clinics. They are often included in routine check-ups and specialized diagnostic packages, thanks to Korea’s strong focus on preventive healthcare.
Why it’s done
Doctors recommend an RBC count to:
➤ Assess general health
- As part of a routine physical examination or health screening
➤ Diagnose conditions
- Detect anemia (low RBC count)
- Identify polycythemia (high RBC count)
- Evaluate causes of fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, or dizziness
➤ Monitor existing conditions
- Track blood disorders like thalassemia or sickle cell anemia
- Check progress in bone marrow diseases or chronic kidney disease
- Evaluate response to chemotherapy, radiation, or medications
Alternatives
While RBC count is simple and valuable, other tests may provide additional details:
✔ Hemoglobin test → Measures oxygen-carrying protein in RBCs
✔ Hematocrit (HCT) test → Measures proportion of RBCs in blood
✔ Reticulocyte count → Evaluates new RBC production
✔ Iron studies (serum iron, ferritin, TIBC) → For anemia diagnosis
✔ Bone marrow biopsy → If abnormal production is suspected
⚠ Typically, RBC count is performed as part of a CBC, which offers a more complete picture.
Preparation
Minimal preparation is needed for an RBC count.
🔹 Before the test:
- No special fasting required unless combined with other tests
- Inform doctor of medications or supplements (e.g., iron pills, erythropoietin, chemotherapy drugs)
- Hydration is recommended since dehydration can artificially raise RBC count
How it’s done
➡ Step-by-step process in Korea:
- Sample collection
- Blood is drawn from a vein (usually arm)
- Done in outpatient clinics, diagnostic labs, or hospitals
- Processing
- Sample sent to the lab for analysis using an automated hematology analyzer
- Duration
- Blood draw: just a few minutes
- Results: often available within hours in Korean hospitals
- Patient experience
- Mild discomfort at needle site
- No restrictions afterward
Normal Results
🔹 Reference ranges (may vary by lab):
- Men: 4.7 – 6.1 million cells/µL
- Women: 4.2 – 5.4 million cells/µL
- Children: 4.1 – 5.5 million cells/µL
- Newborns: 4.8 – 7.1 million cells/µL
Abnormal Results – What they mean
⚠ Low RBC count (Anemia) may indicate:
→ Iron deficiency anemia
→ Vitamin B12 or folate deficiency
→ Chronic diseases (kidney disease, cancer, infection)
→ Bone marrow disorders
→ Blood loss (trauma, ulcers, heavy menstruation)
⚠ High RBC count (Polycythemia) may indicate:
→ Polycythemia vera (bone marrow disorder)
→ Dehydration
→ Lung disease (COPD, pulmonary fibrosis)
→ Heart disease (congenital heart defect)
→ Living at high altitudes (body makes more RBCs to compensate)
Recovery / Expected Outcomes
✔ Recovery is immediate after a blood draw
✔ Normal RBC count means healthy oxygen transport
✔ Abnormal results usually require further tests (iron studies, hemoglobin electrophoresis, imaging, bone marrow exam)
✔ In Korea, results are quickly discussed with patients, often alongside other CBC findings
Complications / Considerations
An RBC count itself is very safe.
⚠ Risks from blood draw include:
- Mild bruising at puncture site
- Slight dizziness
- Rare infection
⚠ Considerations:
- Pregnancy lowers RBC count naturally
- Altitude and smoking may raise RBC count
- Dehydration can make RBC appear falsely elevated
Treatment Options in Korea (When abnormalities are found)
🔹 Diagnosis
- Comprehensive blood tests (CBC, iron panel, vitamin levels)
- Bone marrow biopsy if blood cancers suspected
- Imaging (ultrasound, CT, MRI) if organ-related causes
🔹 Medical treatments
- Iron supplements or injections for iron deficiency
- Vitamin B12 or folic acid therapy
- Medications for bone marrow stimulation
- Erythropoietin therapy for chronic kidney disease
🔹 Surgical or advanced therapies
- Blood transfusions for severe anemia
- Bone marrow transplant for aplastic anemia or leukemia
- Phlebotomy (controlled blood removal) for polycythemia vera
🔹 Rehabilitation and support
- Nutritional counseling (iron-rich diet, folate, B12)
- Lifestyle changes (quit smoking, hydration, exercise)
- Ongoing monitoring with Korea’s advanced electronic health records
Top Hospitals or Clinics in Korea for RBC Count Testing
- Seoul National University Hospital (SNUH) – Advanced hematology & oncology labs
- Asan Medical Center, Seoul – Specialized in blood disorders and transfusion services
- Samsung Medical Center – Automated labs with rapid turnaround
- Korea University Anam Hospital – Strong hematology department for rare blood diseases
Conclusion
The red blood cell count test in Korea is a quick, affordable, and highly accurate diagnostic tool that plays a central role in monitoring blood health, diagnosing anemia, and detecting blood-related diseases.
✔ Widely available in all hospitals and clinics
✔ Integrated into routine check-ups and health screening packages
✔ Helps in early detection of anemia, polycythemia, and chronic illnesses
✔ Supported by Korea’s advanced laboratory systems and expert hematologists
With Korea’s emphasis on preventive medicine, RBC count testing is not just a routine check—it is a gateway to identifying and treating blood-related conditions early.