What it is
Radiotherapy (also called radiation therapy) is a medical treatment that uses high-energy radiation (such as X-rays, gamma rays, or proton beams) to destroy or control cancer cells. It can be used alone or in combination with surgery, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy.
➡ Key points about radiotherapy:
- ☑ It targets cancer cells while sparing surrounding healthy tissues as much as possible
- ☑ Used for both curative (aim to cure) and palliative (symptom-relieving) purposes
- ☑ In Korea, radiotherapy is performed with cutting-edge equipment such as IMRT, stereotactic radiotherapy, and proton therapy
💡 Important fact: Korea is a global leader in precision oncology, offering advanced radiotherapy centers with highly trained oncologists and radiation specialists.
Why it’s done
Radiotherapy is used to:
➤ Treat cancer directly by shrinking or eliminating tumors
➤ Prevent recurrence after surgery by destroying residual cancer cells
➤ Control symptoms (such as pain, bleeding, or obstruction) in advanced cancer cases
➤ Assist surgical procedures by shrinking large tumors before removal
🎯 Cancers commonly treated with radiotherapy in Korea:
- Breast cancer
- Prostate cancer
- Lung cancer
- Brain tumors
- Head and neck cancers
- Cervical and uterine cancers
- Liver and pancreatic cancers
Alternatives
Radiotherapy may be combined with or replaced by other treatments depending on the case.
✔ Surgery → Removal of tumors when operable
✔ Chemotherapy → Drugs to kill or slow cancer cell growth
✔ Immunotherapy → Boosting the body’s natural defenses
✔ Targeted therapy → Attacking specific cancer cell pathways
✔ Palliative care → Focused on comfort and quality of life in advanced cases
Note: Radiotherapy is often part of a multimodal treatment plan rather than a stand-alone option.
Preparation
Before starting radiotherapy, patients go through careful planning and assessments.
🔹 Medical preparation:
- Comprehensive medical history and physical examination
- Imaging tests (CT, MRI, PET-CT) to map tumor location
- Blood tests to assess general health
- Simulation session where patients are positioned for treatment and immobilization devices are created
🔹 Lifestyle preparation:
- Maintain healthy nutrition and hydration
- Discuss current medications with oncologist (some may interfere with therapy)
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol
- Psychological readiness through counseling or support groups
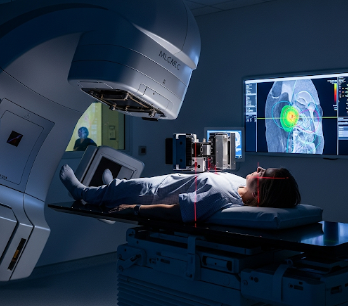
How it’s done
Radiotherapy is delivered in highly specialized settings under strict precision.
➡ Step-by-step process:
- Consultation
- Patient meets radiation oncologist to discuss treatment plan and expected outcomes.
- Simulation and planning
- Imaging scans are used to map the tumor in 3D
- Custom molds or masks are made to keep the body still during therapy
- Treatment delivery
- Patient lies on a treatment table
- Radiation machine (linear accelerator or proton beam) directs radiation precisely to the tumor site
- Each session typically lasts 10–30 minutes
- Schedule
- Usually given 5 days a week for several weeks (varies depending on cancer type and stage)
- Follow-up
- Regular monitoring with imaging and blood tests to assess effectiveness
- Adjustments to treatment plan as needed
💡 Tip: Radiotherapy is painless during delivery, though side effects may appear later.
Recovery / Expected Outcomes
Recovery depends on the type of cancer, overall health, and treatment goals.
🔹 Short-term outcomes:
- Tumor shrinkage or stabilization
- Symptom relief (less pain, improved breathing, reduced bleeding)
- Better chances of successful surgery if given pre-operatively
🔹 Long-term outcomes:
- Increased survival rates for many cancers
- Reduced recurrence risks when combined with surgery or chemotherapy
- Improved quality of life in both curative and palliative settings
🔹 Patient empowerment:
- Patients regain control over symptoms
- Integration of rehabilitation and psychological support ensures better long-term coping
Complications / Considerations
While radiotherapy is generally safe, it may cause side effects depending on the treatment area.
⚠ Common short-term side effects:
- Fatigue
- Skin irritation (redness, peeling, sensitivity)
- Loss of appetite
- Hair loss (only in treated area)
⚠ Long-term side effects:
- Fibrosis (tissue stiffness)
- Secondary cancers (rare but possible)
- Hormonal changes if glands are affected (e.g., thyroid, ovaries, testes)
⚠ Special considerations:
- Pregnant women are usually not recommended for radiotherapy
- Patients with implanted medical devices (e.g., pacemakers) may need special planning
Mitigation: Advanced techniques like IMRT, VMAT, stereotactic radiosurgery, and proton therapy reduce complications by sparing healthy tissues.
Treatment Options in Korea
🏥 Top hospitals and centers offering radiotherapy in Korea:
- National Cancer Center (NCC), Goyang → Comprehensive cancer radiotherapy programs
- Samsung Medical Center, Seoul → Proton therapy and cutting-edge imaging integration
- Asan Medical Center, Seoul → Specialized in head, neck, and liver cancer treatments
- Seoul National University Hospital (SNUH) → IMRT, Gamma Knife radiosurgery, and clinical trials
💰 Cost and Insurance:
- Covered by Korea’s National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) for most cancers
- Private insurance may cover newer therapies like proton therapy
- Costs vary depending on duration, type of radiotherapy, and hospital
🔹 Additional services:
- Psycho-oncology support for emotional well-being
- Nutritional therapy for patients during treatment
- Rehabilitation programs for long-term recovery
Conclusion
Radiotherapy in Korea combines medical expertise, modern technology, and personalized care to provide safe and effective cancer treatment.
Patients benefit from:
- High precision treatments with IMRT, stereotactic therapy, and proton beams
- Integration with surgery and chemotherapy for improved survival
- Supportive care systems to reduce side effects and enhance recovery
- National insurance coverage, making advanced treatments more accessible
With its state-of-the-art hospitals, skilled oncologists, and comprehensive cancer centers, Korea is one of the leading destinations in Asia for radiotherapy.