What It Is
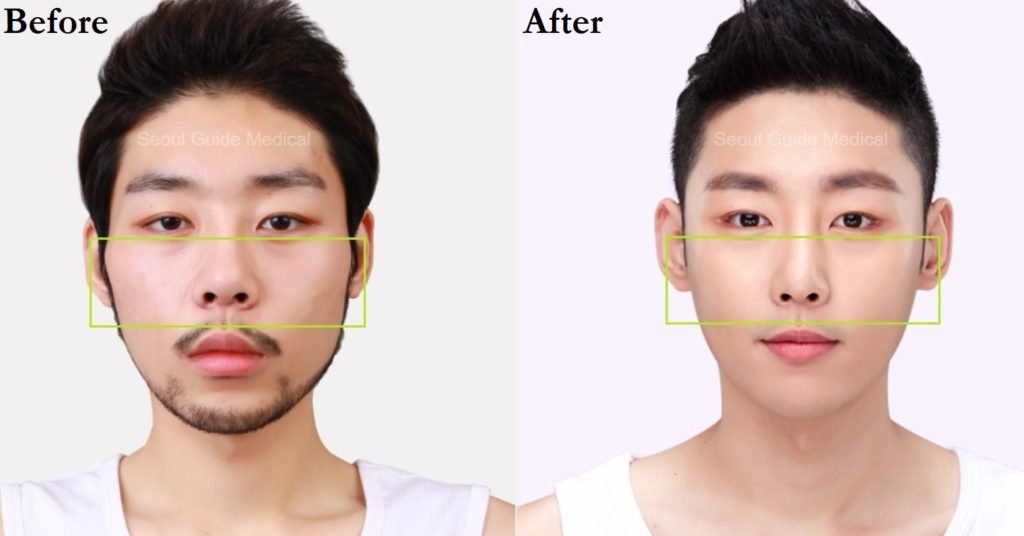
Zygomatic arch reduction is a facial contouring surgery designed to reshape and slim the cheekbone (zygoma) area. The procedure involves reducing the prominence of the zygomatic arch, which extends laterally from the cheekbone, creating a softer and more balanced facial appearance. This treatment is particularly popular in Korea, where facial aesthetics often emphasize V-line contouring and harmony between the forehead, cheeks, and jawline.
Why It’s Done
Patients choose zygomatic arch reduction for both cosmetic and functional reasons.
- Cosmetic goals include creating a slimmer, softer, and more balanced facial contour.
- Functional reasons may include correction of asymmetric cheekbones due to trauma or congenital differences.
It is especially sought after by patients with broad or protruding cheekbones that make the face look wider or more angular than desired.
Alternatives
There are both surgical and non-surgical alternatives:
- Non-surgical: Dermal fillers or fat grafting can create balance by augmenting other facial areas but cannot reduce cheekbone width.
- Surgical: Cheek shaving or malar reduction surgery are alternatives, depending on bone structure and aesthetic goals.
Preparation
Patients undergo comprehensive consultation with 3D facial imaging to design a personalized plan. Preparation includes:
- Stopping smoking and alcohol before surgery.
- Avoiding blood-thinning medications (aspirin, ibuprofen, etc.).
- Completing blood tests and facial imaging scans.
- Fasting if general anesthesia will be used.
How It’s Done
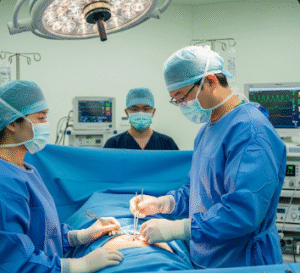
- The procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
- Small incisions are made inside the mouth and near the hairline, leaving no visible scars.
- The zygomatic arch is carefully shaved, cut, or repositioned inward to achieve a slimmer look.
- Titanium plates or screws may be used to stabilize repositioned bones.
- Surgery typically lasts 1–2 hours, and patients usually stay one night in the hospital.
Recovery
- Initial swelling and bruising last 1–2 weeks.
- Patients should follow a soft food diet for several days.
- Return to work or school is possible within 2–3 weeks, but full healing takes several months.
- Regular follow-up visits ensure proper bone healing and symmetry.
Possible Complications
As with any surgery, risks exist. These include:
- Asymmetry or irregular contour.
- Temporary numbness in the cheek area.
- Infection or bleeding.
- Rarely, damage to facial nerves.
Choosing an experienced Korean surgeon significantly reduces these risks.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
In Korea, diagnosis and treatment planning involve:
- Detailed facial CT scans and 3D imaging.
- Physical examination of cheekbone structure.
- Consultations with plastic surgeons specializing in facial contouring.
Medical Treatments
Non-surgical options are limited, but Korean clinics may use:
- Dermal fillers or fat grafting to balance proportions.
- Botox for jaw slimming (often combined with zygomatic surgery).
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
Korean surgeons are globally recognized for their advanced techniques, such as:
- Minimally invasive incisions to avoid visible scars.
- Precision bone repositioning for natural results.
- Use of fixation devices for long-term stability.
Rehabilitation and Support
- Post-surgical rehabilitation includes swelling management, dietary guidance, and physiotherapy if needed.
- Follow-up appointments track healing progress.
- International patient support programs assist with translation, travel arrangements, and aftercare.
Advantages of Receiving Treatment in Korea:
- Highly skilled surgeons with specialized expertise in Asian facial anatomy.
- State-of-the-art technology, including 3D surgical planning and minimally invasive approaches.
- Competitive pricing compared to Western countries.
- Comprehensive aftercare tailored for international patients.