What It Is
Vaginal tightening surgery, also called vaginoplasty or cosmetic vaginal tightening, is a surgical procedure that restores firmness to the vaginal canal and surrounding muscles. It is commonly performed for women who experience vaginal laxity due to childbirth, aging, genetics, or hormonal changes. Unlike non-surgical tightening treatments, this surgery directly repairs and tightens muscles, mucosa, and connective tissues, offering longer-lasting results.
In Korea, vaginal tightening surgery is performed with microsurgical precision, laser-assisted techniques, and advanced suturing methods to achieve natural outcomes and minimize downtime.
Why It’s Done
Patients choose vaginal tightening surgery because:
- Vaginal laxity reduces sexual satisfaction or sensitivity.
- They want to restore confidence and intimate well-being.
- They have difficulty retaining tampons or experience dryness and discomfort.
- It may help improve mild stress urinary incontinence.
Good candidates include:
- Women with vaginal laxity after childbirth or aging.
- Patients in good health with realistic expectations.
- Those who prefer a permanent solution compared to temporary non-surgical devices.
Alternatives
- Laser or radiofrequency vaginal tightening: Non-surgical methods, effective for mild laxity but temporary.
- Pelvic floor exercises (Kegels): Useful for prevention and mild cases but less effective for advanced laxity.
- No intervention: Some women choose lifestyle or hygiene adjustments instead of surgery.
Preparation
Before vaginal tightening surgery in Korea, patients will:
- Undergo a gynecologic examination and consultation.
- Stop smoking and alcohol 2–4 weeks before surgery.
- Avoid blood-thinning medications and supplements.
- Plan for 6–8 weeks of recovery before resuming sexual activity or strenuous exercise.
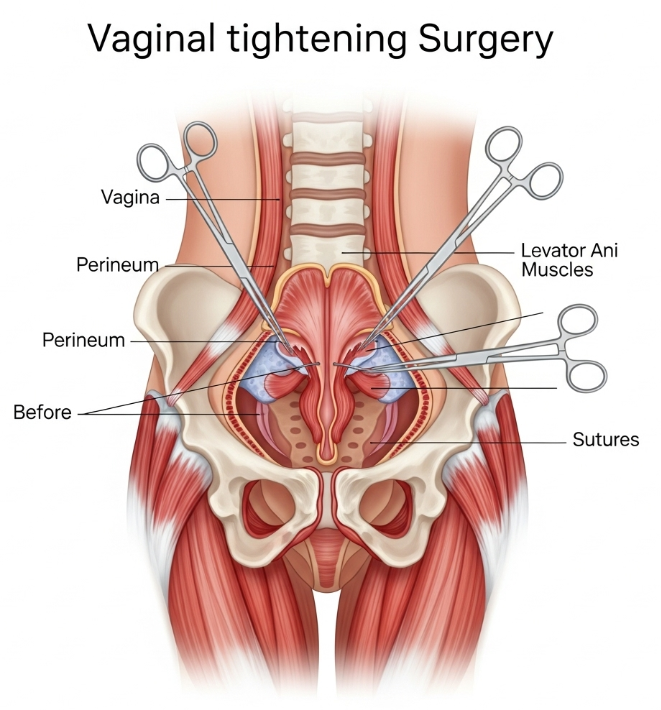
How It’s Done
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia.
- Incision: Inside the vaginal canal, leaving no visible external scars.
- Muscle repair: Weakened vaginal muscles and connective tissues are tightened with sutures.
- Mucosal trimming: Excess tissue may be removed for refinement.
- Closure: Dissolvable sutures are used for natural healing.
- Duration: 1–2 hours, usually outpatient.
Recovery
- First week: Swelling, bruising, and mild soreness are common. Ointments and cold compresses may be prescribed.
- Return to activities: Light duties in 3–5 days; strenuous activities and intercourse avoided for 6–8 weeks.
- Final results: Tighter vaginal canal, improved function, and enhanced comfort achieved in 2–3 months.
Possible Complications
- Prolonged swelling or discomfort.
- Infection or delayed healing.
- Over-tightening, which may cause pain during intercourse.
- Scarring inside the vaginal canal (rare).
- Rare risks: bleeding or anesthesia-related issues.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Korean gynecologic specialists perform pelvic exams, medical history reviews, and patient consultations to assess vaginal laxity and determine the most suitable treatment.
Medical Treatments
- Non-surgical vaginal rejuvenation using laser or radiofrequency energy for patients with mild laxity.
- Pelvic floor therapy for muscle strengthening.
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Vaginal tightening surgery (vaginoplasty) for moderate to severe laxity.
- Laser-assisted vaginoplasty for precision and reduced downtime.
- Combination with perineoplasty or labiaplasty for comprehensive rejuvenation.
Rehabilitation and Support
- Hygiene guidance and topical medications during recovery.
- Scar care with advanced techniques to minimize internal scarring.
- Long-term follow-up visits to monitor healing and satisfaction.
- International patients benefit from Korea’s advanced gynecologic surgical methods, discreet medical care, and comprehensive aftercare programs.