What It Is
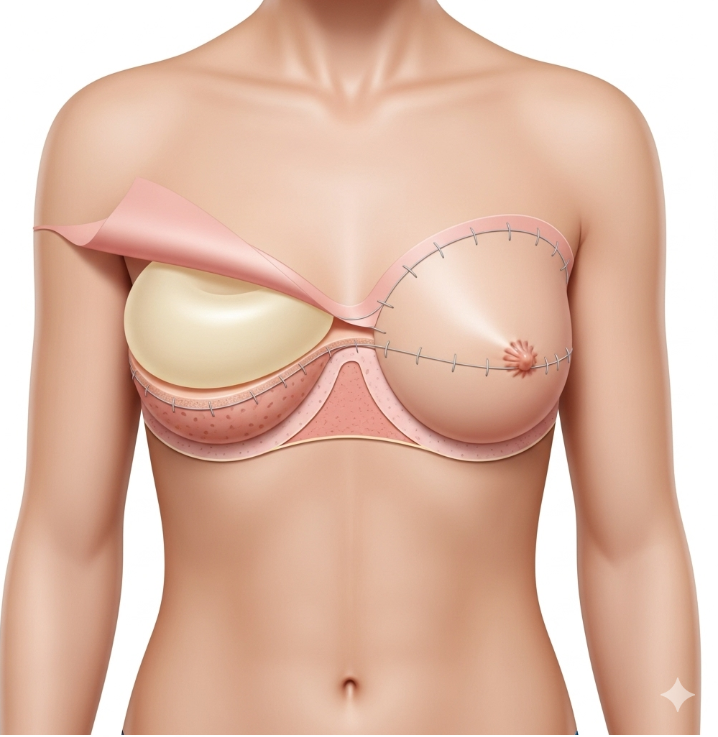
Prepectoral implant reconstruction is a modern breast reconstruction technique where the implant is placed above the chest muscle (pectoralis major), directly beneath the skin and mastectomy flap, rather than under the muscle.
This method avoids muscle dissection and uses acellular dermal matrix (ADM) or mesh to support and cover the implant, ensuring natural contour and reduced complications. In Korea, this approach is increasingly popular because surgeons combine it with 3D surgical planning, advanced implant technology, and refined flap-thickness assessment to provide safe, natural results.
Why It’s Done
Patients undergo prepectoral implant reconstruction because:
- They want a less invasive reconstruction after mastectomy.
- It avoids animation deformity (unnatural implant movement during muscle contraction).
- It results in less pain and faster recovery compared to submuscular placement.
- They want a natural look with stable breast projection.
Good candidates include:
- Women with good skin and soft tissue coverage after mastectomy.
- Patients without severe radiation damage to the chest area.
- Individuals who prefer implant-based reconstruction and want to avoid muscle-related complications.
Alternatives
- Submuscular implant reconstruction: Traditional approach with implant placed under muscle.
- Autologous tissue reconstruction (flaps): Uses patient’s own tissue (e.g., DIEP flap).
- Hybrid reconstruction: Combines implant placement with fat grafting.
- External prosthesis: Non-surgical alternative.
Preparation
Before prepectoral implant reconstruction in Korea, patients will:
- Consult with both a breast surgeon and reconstructive surgeon.
- Undergo imaging and evaluation of skin flap thickness after mastectomy.
- Stop smoking and alcohol 4 weeks before surgery.
- Avoid blood-thinning medications and certain supplements.
- Discuss implant options (size, shape, texture) and use of ADM.
How It’s Done
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is required.
- Implant placement: The implant is positioned above the muscle, directly under the mastectomy skin flap.
- Support material: ADM or mesh is used to fully or partially cover the implant, providing stability and reducing complications.
- Closure: The incisions are carefully sutured to ensure proper healing.
- Duration: 2–4 hours, depending on whether it is immediate or delayed reconstruction.
Recovery
- First week: Less pain compared to submuscular reconstruction, with mild swelling and bruising.
- Hospital stay: 3–5 days in most cases.
- Return to activities: Light activities in 1–2 weeks; avoid heavy lifting for 4–6 weeks.
- Final results: Natural breast shape with stable projection in 2–3 months.
Possible Complications
- Implant visibility or rippling if skin coverage is thin.
- Infection or delayed healing.
- Implant malposition or asymmetry.
- Rare risks: seroma (fluid collection) or implant failure.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Korean surgeons use 3D breast imaging, intraoperative flap-thickness assessment, and MRI if needed to determine candidacy for prepectoral placement.
Medical Treatments
- External prosthesis or fat grafting for patients not choosing implant-based reconstruction.
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Prepectoral implant reconstruction with ADM coverage for best long-term stability.
- Hybrid method combining prepectoral implant placement with fat grafting for natural contour.
- Delayed prepectoral reconstruction for patients who complete cancer treatment first.
- Nipple-areola reconstruction and 3D tattooing for final refinement.
Rehabilitation and Support
- Postoperative scar care with silicone gels or fractional laser.
- Physiotherapy as needed, though less required compared to submuscular techniques.
- Long-term monitoring of implant health with imaging.
- International patients benefit from Korea’s advanced surgical planning, cutting-edge ADM technology, and holistic aftercare programs.