What It Is
Polydactyly correction is a surgical procedure to treat polydactyly, a congenital condition where a child is born with extra fingers or toes. The additional digit may be fully formed with bone and joints, or it may be small and rudimentary, connected only by soft tissue.
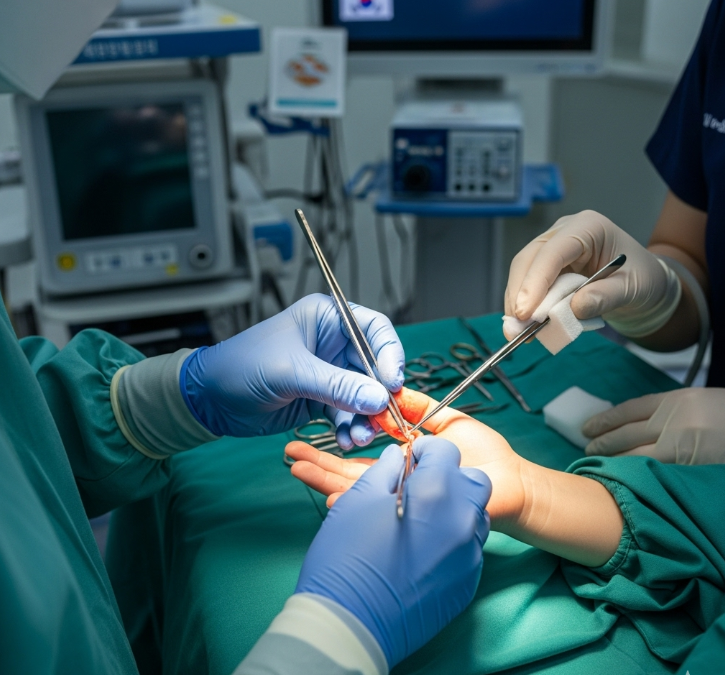
The surgery involves removing the extra digit and reconstructing the hand or foot for proper function and appearance. In Korea, pediatric plastic and orthopedic surgeons use microsurgical and reconstructive techniques to ensure precise correction, natural shape, and minimal scarring.
Why It’s Done
Patients undergo polydactyly correction because:
- The extra digit interferes with hand or foot function (grip, walking, fine motor skills).
- It affects cosmetic appearance, causing self-consciousness.
- Early removal prevents joint deformity, abnormal bone growth, or misalignment.
- Parents wish to provide their child with normal hand or foot development.
Good candidates include:
- Infants and children, typically between 6–12 months, when surgery offers the best outcome.
- Adults with untreated polydactyly seeking functional or cosmetic improvement.
- Patients in good health without uncontrolled medical conditions.
Alternatives
- Observation: In very small or soft-tissue-only cases, monitoring may be considered until the right age for surgery.
- Ligation (tying off): Sometimes used in newborns for tiny, soft-tissue-only digits, but less precise than surgery.
- Prosthetics or adaptive devices: Rarely used, only if surgery is not possible.
Preparation
Before undergoing polydactyly correction in Korea, patients will:
- Have a clinical evaluation and imaging (X-rays) to check if bones, joints, or tendons are involved.
- Undergo general medical clearance, especially for infants.
- Parents will discuss the timing and type of surgery with the surgeon.
- Prepare for possible need for physiotherapy if reconstruction is complex.
How It’s Done
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia in children; adults may have general or regional anesthesia.
- Incision: A careful cut is made around the extra digit.
- Excision: The surgeon removes the extra digit, including bones, joints, or tendons if present.
- Reconstruction: Tendons, ligaments, and skin are repaired to create a natural finger or toe contour.
- Closure: The incision is sutured with fine stitches to minimize scarring.
- Duration: 1–2 hours depending on complexity.
Recovery
- First week: Mild swelling and discomfort are common. The hand or foot is dressed and protected.
- Stitches: Usually removed in 1–2 weeks, unless dissolvable sutures are used.
- Therapy: Hand or foot physiotherapy may be recommended to optimize function.
- Return to activities: Infants recover quickly; older children may return to normal use in 2–3 weeks.
- Final results: Natural-looking hand or foot with improved function and minimal scarring.
Possible Complications
- Scarring or asymmetry at the surgical site.
- Stiffness or weakness in the corrected digit.
- Rare recurrence of deformity if growth plates are involved.
- Rare risks: infection, nerve injury, or delayed healing.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Korean specialists use clinical exams and imaging (X-rays or CT scans) to classify the type of polydactyly (preaxial, postaxial, or central) and plan precise surgery.
Medical Treatments
- No medical therapy can correct polydactyly; only surgery provides permanent treatment.
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Simple excision for soft-tissue-only extra digits.
- Complex reconstruction when bones, tendons, or joints are involved.
- Microsurgical techniques in Korea ensure precise tendon and ligament repair.
- Advanced scar management methods are used to achieve natural cosmetic results.
Rehabilitation and Support
- Regular follow-up to monitor growth and hand/foot development.
- Scar management with silicone sheets, massage, or laser if needed.
- Physiotherapy for children requiring fine motor skill improvement.
- International patients benefit from Korea’s pediatric reconstructive surgery expertise, multidisciplinary teams, and multilingual aftercare programs.