What It Is
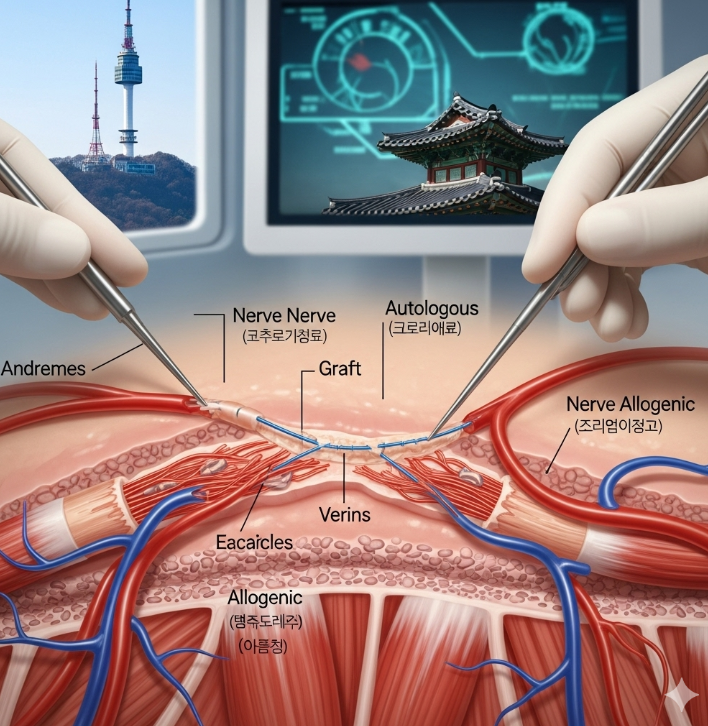
Nerve repair with grafting is a microsurgical procedure used when a nerve is injured and the damaged segment is too long to be repaired by direct end-to-end suturing. In these cases, a nerve graft is used to bridge the gap. The most common donor is the sural nerve (from the leg), though other sensory nerves may also be harvested.
The graft acts as a scaffold that guides regenerating nerve fibers across the gap, restoring function and sensation over time. In Korea, nerve graft surgeries are performed in advanced microsurgical centers, often combined with intraoperative nerve monitoring, high-powered microscopes, and regenerative therapies for better outcomes.
Why It’s Done
Patients undergo nerve repair with grafts because:
- They have suffered a traumatic nerve injury with a significant gap.
- Tumor resection or scar removal required removal of a nerve segment.
- They have functional deficits such as paralysis, weakness, or sensory loss.
- They want to restore hand, arm, facial, or lower limb function after nerve damage.
Good candidates include:
- Patients with nerve injuries less than 12–18 months old (after which muscles may not respond well).
- Those in good health able to undergo microsurgery.
- Patients motivated for long rehabilitation as recovery is gradual.
Alternatives
- Direct nerve repair (end-to-end suturing) if the gap is small.
- Nerve transfer (rerouting a nearby functional nerve) if grafting is not possible.
- Tendon or muscle transfers in severe or chronic injuries.
- Nerve conduits (synthetic or biological tubes) in small gaps instead of autologous grafts.
Preparation
Before nerve graft surgery in Korea, patients will:
- Undergo neurological examination, electromyography (EMG), and nerve conduction studies.
- Have imaging such as MRI neurography to assess injury extent.
- Stop smoking and alcohol at least 4 weeks before surgery.
- Avoid medications that increase bleeding.
- Prepare for rehabilitation and possible staged procedures.
How It’s Done
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is used.
- Exploration: The injured nerve is exposed, and damaged tissue is removed.
- Graft harvest: A donor nerve (often the sural nerve from the leg) is harvested.
- Graft placement: The graft is sutured microscopically to bridge the nerve gap.
- Closure: Wound is sutured, and limb is immobilized to protect the repair.
- Duration: 3–6 hours depending on complexity.
Recovery
- First weeks: Immobilization with a splint or cast; pain and swelling controlled with medication.
- Rehabilitation: Begins after a few weeks, focusing on maintaining joint flexibility and stimulating muscle activity.
- Nerve regeneration: Nerves grow slowly—about 1 mm per day. Functional recovery may take 6–18 months.
- Final results: Many patients regain significant movement and sensation, though recovery may not be complete.
Possible Complications
- Incomplete recovery of function or sensation.
- Donor site numbness (commonly in the outer foot or leg if sural nerve is harvested).
- Scar formation or delayed healing.
- Infection or graft failure (rare).
- Neuropathic pain during regeneration.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Korean surgeons use EMG, nerve conduction studies, MRI neurography, and intraoperative nerve stimulation to plan precise repair.
Medical Treatments
- Pain management with medications or nerve blocks.
- Physical therapy to prevent muscle wasting while waiting for nerve recovery.
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Autologous nerve grafts (sural nerve most common).
- Processed nerve allografts in some specialized centers.
- Nerve conduits for smaller gaps.
- Combination with nerve transfers for better functional recovery.
Rehabilitation and Support
- Long-term physiotherapy and occupational therapy to retrain muscles and movement.
- Electrical stimulation to encourage nerve growth.
- Scar care and pain management if needed.
- International patients benefit from Korea’s microsurgical expertise, advanced imaging, and structured rehabilitation programs.