What It Is
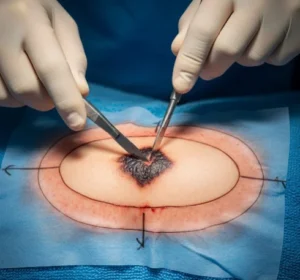
Nasal fracture closed reduction is a non-invasive surgical procedure to correct a broken nose by manually realigning displaced nasal bones without making external incisions. Nasal fractures are the most common type of facial fracture, usually caused by accidents, falls, or sports injuries.
The procedure restores nasal shape, airway function, and facial symmetry. In Korea, closed reduction is often performed under local or general anesthesia with precise imaging and minimally invasive tools, ensuring accurate correction and fast recovery.
Why It’s Done
Patients undergo nasal fracture closed reduction because:
- Their nose is visibly crooked, flattened, or displaced after trauma.
- They experience nasal obstruction or difficulty breathing.
- The fracture causes pain, swelling, or deformity.
- They want to prevent permanent nasal deformity or functional issues.
Good candidates include:
- Patients with recent nasal fractures (ideally within 1–2 weeks of injury).
- Individuals with mild to moderate displacement.
- Patients who prefer a minimally invasive correction without open surgery.
Alternatives
- Observation: For non-displaced or minor fractures.
- Open reduction with internal fixation (ORIF): Used for severe fractures or when closed reduction fails.
- Septorhinoplasty: Considered later for combined functional and cosmetic correction.
Preparation
Before nasal fracture closed reduction in Korea, patients will:
- Have a clinical exam and imaging (X-ray or CT scan) to confirm fracture type.
- Stop smoking and alcohol at least 1–2 weeks before surgery.
- Avoid blood-thinning medications and supplements.
- Undergo general health assessment to decide on local vs general anesthesia.
How It’s Done
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia is used.
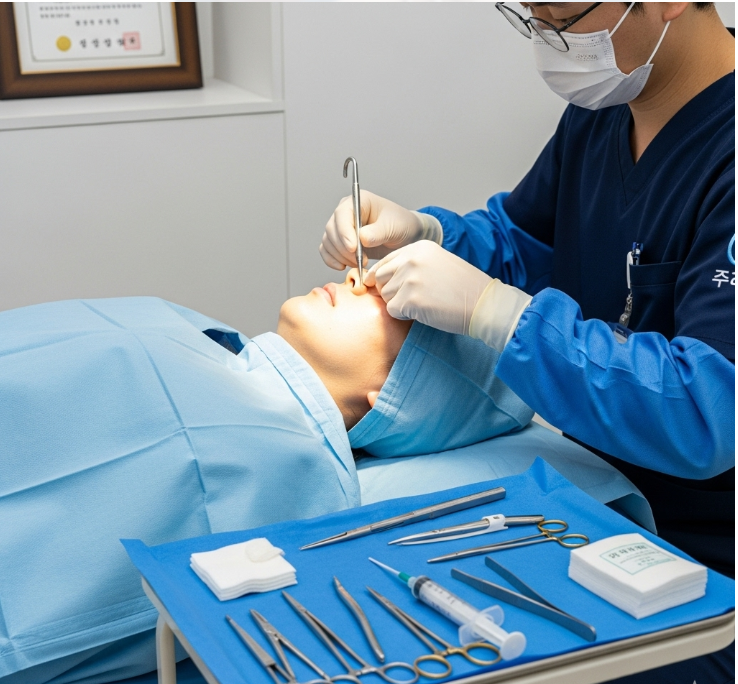
- Manual reduction: The surgeon uses instruments to realign nasal bones and cartilage into their proper position.
- Stabilization: An external nasal splint is applied to hold the bones in place while they heal.
- Duration: 30–60 minutes, usually outpatient.
Recovery
- First week: Swelling, bruising, and mild discomfort are expected. Ice packs and pain medication help.
- Splint: Worn for 5–7 days to support healing.
- Return to activities: Light daily activities after 2–3 days; avoid contact sports for at least 6 weeks.
- Final results: Nasal shape and breathing typically restored within 2–4 weeks.
Possible Complications
- Incomplete correction or residual deformity.
- Persistent nasal obstruction if the septum is also fractured.
- Nosebleeds or swelling.
- Rare risks: infection or need for revision surgery.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Korean ENT and plastic surgeons use clinical assessment, nasal endoscopy, and CT scans to evaluate fractures and plan treatment.
Medical Treatments
- Pain medication, ice, and decongestants for minor nasal injuries.
- Observation for non-displaced fractures.
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Closed reduction for recent, mild to moderate fractures.
- Open reduction or septorhinoplasty if deformity persists or septum is involved.
- Combination surgery for functional and cosmetic restoration.
Rehabilitation and Support
- Follow-up visits to check bone alignment and breathing function.
- Scar management is not needed as there are no external incisions.
- Long-term cosmetic refinements, if desired, can be performed with rhinoplasty.
- International patients benefit from Korea’s specialized facial trauma centers, minimally invasive techniques, and multilingual aftercare services.