What It Is
Lymphedema liposuction, also called suction-assisted lipectomy, is a surgical procedure designed to treat advanced lymphedema. In early lymphedema, swelling is caused mostly by trapped lymphatic fluid, but over time fat and fibrotic tissue build up. Liposuction removes this excess tissue to reduce limb size, improve mobility, and restore quality of life.
In Korea, this procedure is performed in specialized reconstructive and microsurgery centers, often as part of a comprehensive lymphedema care program.
Why It’s Done
Lymphedema liposuction is usually considered when:
- Conservative treatments such as compression and manual drainage are no longer effective
- The limb has developed chronic swelling with fatty and fibrotic tissue
- Patients experience pain, heaviness, or frequent skin infections
- There is a major size difference between affected and unaffected limbs
The goal is not only cosmetic improvement but also better function and comfort.
Alternatives
Depending on the stage of lymphedema, other treatments may be recommended:
- Conservative therapy (CDT): Compression garments, manual lymphatic drainage, exercise
- Lymphovenous bypass (LVB): Microsurgery connecting lymphatic vessels to veins (best for early stages)
- Vascularized lymph node transfer (VLNT): Transplanting healthy lymph nodes to restore drainage
- Combination therapies: Microsurgery plus liposuction for complex cases
Liposuction is best for advanced, fat-dominant lymphedema.
Preparation
Preparation before surgery includes:
- Consultation: With a lymphedema specialist and surgeon
- Imaging: Indocyanine green (ICG) lymphography or lymphoscintigraphy to evaluate lymphatic function
- Health check: Blood tests and general medical evaluation
- Compression training: Patients are instructed on lifelong garment use after surgery
- Lifestyle adjustments: Avoid smoking and alcohol to promote healing
How It’s Done
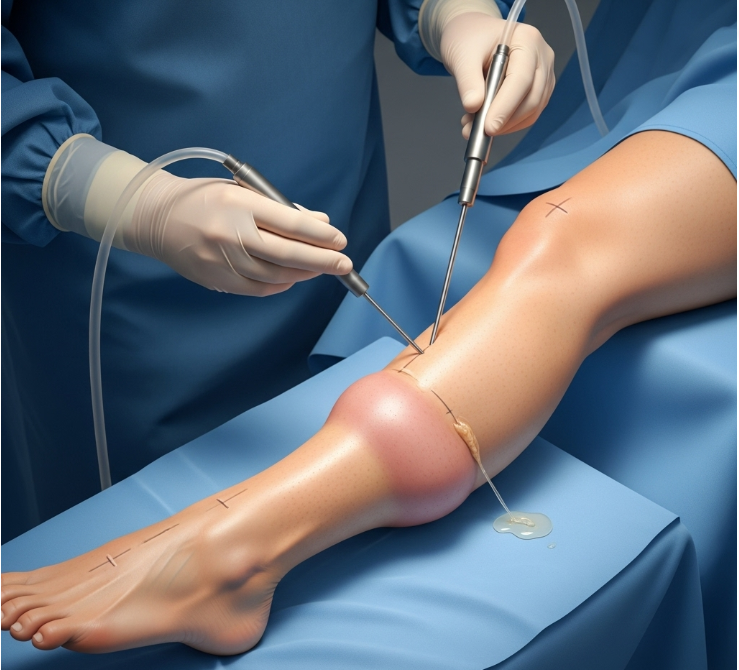
Lymphedema liposuction is performed under general anesthesia and usually takes 3–4 hours.
Steps include:
- Mapping swollen areas for precise fat removal
- Injecting tumescent fluid to reduce bleeding and loosen fibrotic tissue
- Using fine cannulas to suction out fat and fibrotic tissue
- Reshaping the limb to match the opposite side
- Applying compression bandages immediately after surgery
Recovery
Recovery is straightforward but requires strict adherence to compression therapy:
- Hospital stay: Usually 1–3 days
- First weeks: Swelling and bruising are common; compression garments must be worn at all times
- Activity: Walking is encouraged quickly, but heavy activity should be avoided initially
- Follow-ups: Regular visits to check healing and adjust garment fitting
- Long-term: Lifelong compression garments are necessary to maintain results
Possible Complications
While generally safe, risks include:
- Infection or bleeding
- Contour irregularities
- Fluid accumulation (seroma)
- Temporary numbness or discomfort
- Recurrence of swelling if compression therapy is not maintained
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Imaging tests (ICG lymphography, lymphoscintigraphy)
- Limb volume measurement compared to the unaffected side
- Multidisciplinary team evaluation
Medical Treatments
- Compression garments, custom-fitted in specialized Korean centers
- Antibiotics and pain relief after surgery
- Physiotherapy and skin care education
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Liposuction-only approach: For advanced, fat-heavy lymphedema
- Combined surgery: Liposuction with LVB or VLNT for mixed cases
- High-definition liposuction techniques: Used to refine contour and minimize trauma
Rehabilitation and Support
- Ongoing physiotherapy and manual drainage
- Scar management if needed at liposuction sites
- International patient care services including interpreters, hospital coordination, and telemedicine follow-up