What It Is
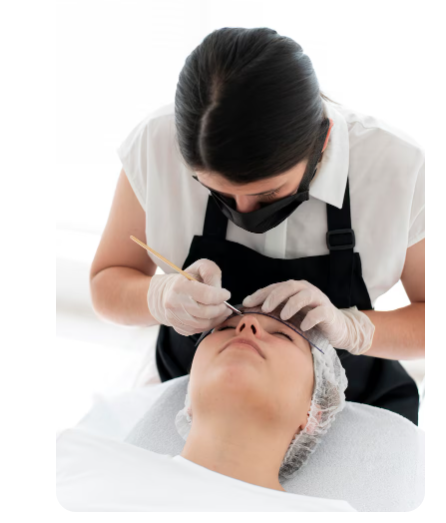
An eyebrow transplant is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that restores or enhances eyebrow density by transplanting hair follicles from a donor site (usually the scalp) to the brow area. The transplanted hairs grow naturally, allowing trimming, shaping, and styling just like normal eyebrows.
In Korea, eyebrow transplants are performed with advanced FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) techniques, ensuring minimal scarring and high graft survival rates. Korean surgeons place special emphasis on aesthetic design, creating eyebrows that complement each patient’s unique facial structure.
Why It’s Done
Cosmetic Purposes:
- Restores thin or sparse eyebrows caused by genetics, aging, or over-plucking
- Enhances facial expression and symmetry
- Provides permanent results compared to makeup, microblading, or tattoos
Corrective Purposes:
- Treats eyebrow loss from trauma, burns, or surgery scars
- Corrects congenital conditions such as eyebrow hypoplasia
- Provides natural restoration for patients with alopecia-related brow loss
Patient Considerations:
- Suitable for men and women seeking permanent, natural-looking eyebrows
- Best for healthy, non-smoking individuals with sufficient donor hair
- Common among international patients seeking refined and natural eyebrow artistry in Korea
Alternatives
- Microblading or Eyebrow Tattoos: Semi-permanent cosmetic solutions; fade over time
- Eyebrow Makeup: Temporary, requires daily application
- Topical Treatments: Serums or minoxidil may improve growth slightly but are limited in effect
- Prosthetic Brows: Stick-on or glued brows, used for medical conditions (not permanent)
Preparation
Before an eyebrow transplant in Korea, patients undergo:
- Consultation: Facial analysis and eyebrow design planning
- Donor Site Evaluation: Usually the back of the scalp (matches natural hair texture best)
- Medical Review: Health screening to rule out contraindications
- Pre-Surgery Instructions: Avoid smoking, alcohol, and blood-thinning medications
- Hair Length Consideration: Donor area may need trimming for follicle extraction
How It’s Done
Type: Minimally invasive surgical procedure
Duration: 2–4 hours depending on graft numbers
Procedure Steps:
- Local anesthesia applied to donor and recipient areas
- Hair follicles harvested from donor site using FUE technique
- Recipient sites are created in the brow region at precise angles and directions
- Follicles are transplanted individually to mimic natural eyebrow growth patterns
- Final shaping is checked for symmetry and design balance
Hospitalization: Outpatient procedure; patients return home the same day
Recovery
- First Week: Mild redness, swelling, and scabbing in the eyebrow area
- Shedding Phase: Transplanted hairs fall out within 2–4 weeks (normal process)
- New Growth: Begins at 3–4 months; thickens gradually over 6–9 months
- Final Results: Fully visible after 9–12 months, with permanent eyebrow density
- Maintenance: Transplanted hairs grow like scalp hair, requiring occasional trimming
Possible Complications
- Temporary redness, swelling, or itching
- Folliculitis (minor infection of transplanted follicles, treatable with medication)
- Uneven growth or density requiring touch-up procedures
- Visible scarring at donor site (rare with modern FUE techniques)
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Korean clinics focus on:
- Eyebrow Mapping and Design for facial harmony
- Donor Hair Analysis to match texture, thickness, and curl pattern
- 3D Imaging (in some clinics) to preview results
Medical Treatments
For mild thinning:
- Eyebrow serums or topical minoxidil for stimulating hair growth
- Makeup or microblading for temporary cosmetic enhancement
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- FUE Eyebrow Transplant: Standard technique using follicular unit extraction
- Dense Packing Technique: For patients desiring thick, bold brows
- Revision Eyebrow Surgery: Corrects poorly done prior transplants or tattoo scars
- Hybrid Approaches: Combination of transplant and micropigmentation for optimal results
Rehabilitation and Support
- Post-op follow-ups to monitor graft survival
- Scar management and donor site care
- International patient services: translation, travel support, recovery accommodations, and discreet care