What It Is
Dupuytren’s contracture fasciectomy is a surgical treatment for Dupuytren’s disease, a condition where abnormal thickening of the palmar fascia (connective tissue in the hand) causes the fingers to bend inward toward the palm. Over time, the affected fingers cannot straighten fully, leading to difficulty with daily activities.
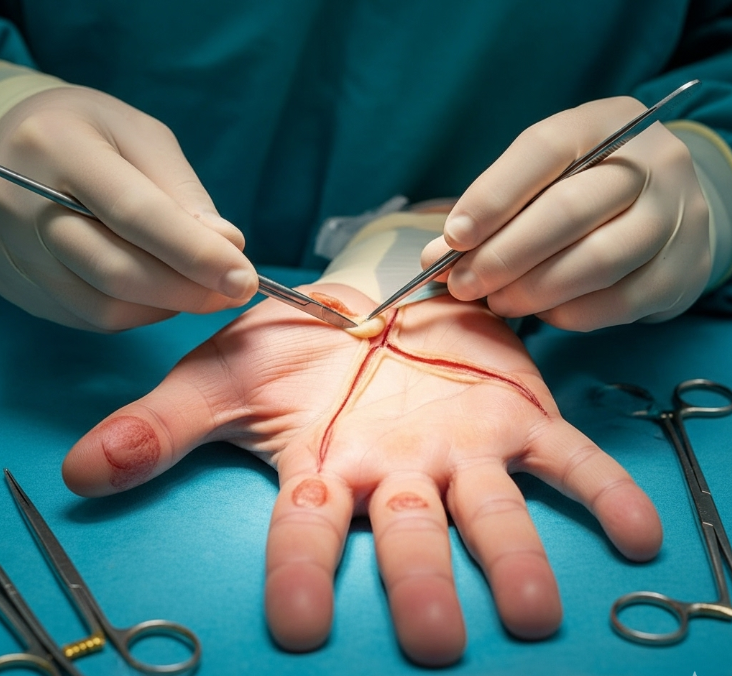
A fasciectomy involves removing the diseased fascia to release the contracted fingers and restore mobility. In Korea, surgeons use both traditional open techniques and minimally invasive methods, often supported by microsurgical precision and advanced rehabilitation programs.
Why It’s Done
Patients undergo fasciectomy because:
- Their fingers are permanently bent and interfere with normal hand function.
- They struggle with activities such as writing, typing, or gripping objects.
- The contracture causes discomfort or progresses despite non-surgical treatment.
- They want to improve both function and appearance of the hand.
Good candidates include:
- Patients with moderate to severe Dupuytren’s contracture.
- Individuals with good overall health.
- People whose contracture prevents full hand use.
Alternatives
- Needle aponeurotomy (percutaneous fasciotomy): A less invasive procedure using a needle to divide cords.
- Collagenase injections: An enzyme is injected to dissolve the cords; effective for mild to moderate cases.
- Physical therapy and splinting: Useful for very early stages but not curative.
Preparation
Before undergoing fasciectomy in Korea, patients will:
- Have a consultation with a hand surgeon, including physical examination and functional tests.
- Undergo imaging (ultrasound or MRI) if needed to assess severity.
- Stop smoking and alcohol 2–4 weeks prior to surgery.
- Avoid blood-thinning medications and certain supplements.
- Plan for postoperative therapy and possible downtime from work.
How It’s Done
- Anesthesia: Regional block or general anesthesia.
- Incision: The surgeon makes small zig-zag (Bruner-type) incisions in the palm and fingers for better access and to prevent scarring.
- Excision: The diseased fascia is removed while preserving nerves, tendons, and blood vessels.
- Closure: The wound is closed with sutures, sometimes using skin grafts if extensive removal is required.
- Duration: 1–2 hours, usually as an outpatient or short hospital stay.
Recovery
- First week: Swelling, bruising, and mild pain are common. The hand is dressed and sometimes splinted.
- Stitches: Removed after 10–14 days.
- Physiotherapy: Begins early to restore mobility, prevent stiffness, and strengthen grip.
- Return to work: Light activities after 2–3 weeks; full recovery in 6–12 weeks.
- Results: Fingers can usually straighten much more, improving both function and appearance.
Possible Complications
- Recurrence of Dupuytren’s contracture over time.
- Nerve or tendon injury (rare with experienced surgeons).
- Scarring or stiffness of the fingers.
- Wound healing issues or infection.
- Temporary numbness or tingling in the fingers.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Korean specialists diagnose Dupuytren’s disease through physical examination, functional assessment, and imaging if needed. Severity is staged based on finger contracture angle.
Medical Treatments
- Collagenase injections to dissolve cords (effective in select cases).
- Needle aponeurotomy as a minimally invasive option.
- Splints and therapy for early disease.
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Limited fasciectomy for moderate cases.
- Extended fasciectomy or dermofasciectomy for severe or recurrent cases.
- Microsurgical precision in Korea ensures nerve and tendon protection.
- Combination with skin grafts if large tissue removal is needed.
Rehabilitation and Support
- Early and structured hand physiotherapy to restore mobility.
- Splinting programs to maintain finger extension.
- Scar management with silicone sheets or laser if necessary.
- International patients benefit from Korea’s advanced hand surgery centers, rapid recovery programs, and multilingual aftercare services