What It Is
Cleft palate repair, also known as palatoplasty, is a surgical procedure to correct a congenital split or gap in the roof of the mouth (palate). This condition occurs when the tissues of the palate fail to fuse during fetal development. A cleft palate may occur alone or with a cleft lip.
The surgery reconstructs the muscles and tissues of the soft and hard palate, closing the gap to restore proper speech, feeding, and swallowing functions. In Korea, cleft palate repair is performed by highly specialized pediatric plastic surgeons using advanced microsurgical techniques and speech-focused methods, ensuring functional restoration and minimal scarring.
Why It’s Done
Patients undergo cleft palate repair because:
- A cleft palate interferes with feeding, swallowing, and speech development.
- Children are at risk of ear infections and hearing loss due to poor eustachian tube function.
- The condition can cause nasal-sounding speech and language delays.
- Early surgical repair supports normal growth, development, and social confidence.
Good candidates include:
- Infants aged 9–18 months, when tissues are strong enough but before significant speech development begins.
- Children needing revision surgeries to improve speech or correct fistulas.
- Adults with untreated cleft palates seeking functional and cosmetic repair.
Alternatives
- Speech therapy alone: Helpful but not a substitute for surgery.
- Prosthetic obturators: Temporary devices that close the gap, used before surgery or when surgery is delayed.
- Secondary surgeries: May be performed later for speech or nasal function improvements.
Preparation
Before cleft palate repair in Korea, patients (or their parents) will:
- Have a consultation with a multidisciplinary cleft team (plastic surgeon, pediatrician, speech therapist, ENT).
- Undergo blood tests and anesthesia clearance.
- Use special feeding techniques or devices until surgery.
- Discuss the possibility of staged surgeries as the child grows.
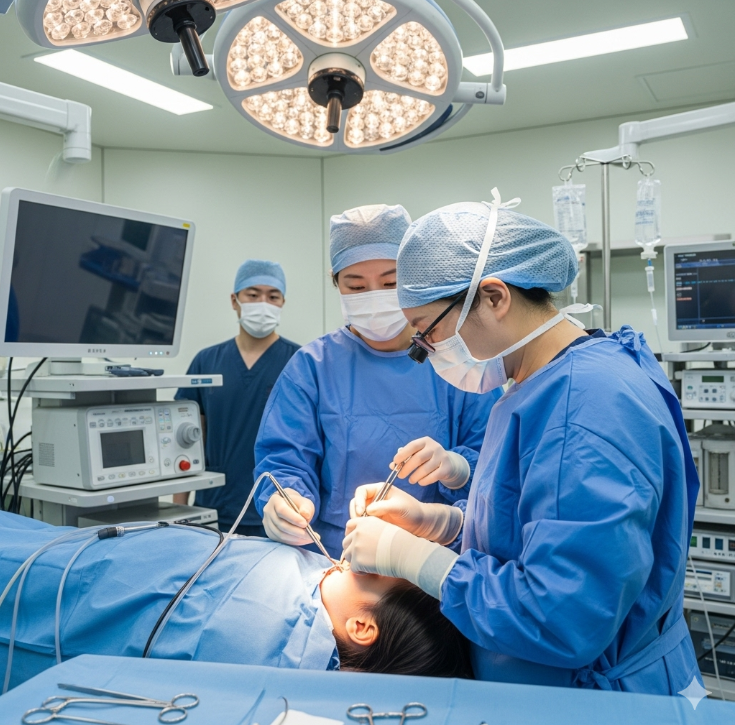
How It’s Done
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is required.
- Incisions: Made along the edges of the cleft inside the mouth.
- Reconstruction: The surgeon repositions and sutures the muscles of the soft palate, lengthens the palate if needed, and closes the cleft with tissue flaps.
- Closure: Dissolvable stitches are used inside the mouth.
- Duration: 2–4 hours depending on complexity.
Recovery
- First week: Swelling, mild pain, and feeding difficulties are common. Infants are fed with a spoon or syringe instead of a bottle.
- Hospital stay: Usually 3–7 days.
- Diet: Soft or liquid diet is recommended for several weeks.
- Speech therapy: Begins as the child grows, often necessary for proper language development.
- Final results: Significant improvement in feeding and speech, with scars hidden inside the mouth.
Possible Complications
- Fistula (small hole in the palate) requiring revision surgery.
- Persistent nasal-sounding speech.
- Scarring or shortening of the palate.
- Rare risks: wound breakdown, infection, or bleeding.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Korean cleft teams use physical exams, imaging, and speech evaluations to assess cleft severity and plan individualized treatment.
Medical Treatments
- Feeding support with specialized bottles or devices until surgery.
- Speech therapy to support language development after surgery.
- ENT management for ear infections or hearing loss.
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Primary palatoplasty at 9–18 months.
- Furlow double-opposing Z-plasty for lengthening the palate and improving speech.
- Secondary palatoplasty for fistula closure or velopharyngeal insufficiency (VPI).
- Combined procedures with cleft lip repair or orthognathic surgery as the child grows.
Rehabilitation and Support
- Long-term speech therapy to ensure clear articulation.
- Regular follow-ups with orthodontists, ENT specialists, and psychologists.
- Scar management if necessary, though scars are typically hidden.
- International patients benefit from Korea’s multidisciplinary cleft centers, speech-focused surgical techniques, and multilingual aftercare support.