What It Is
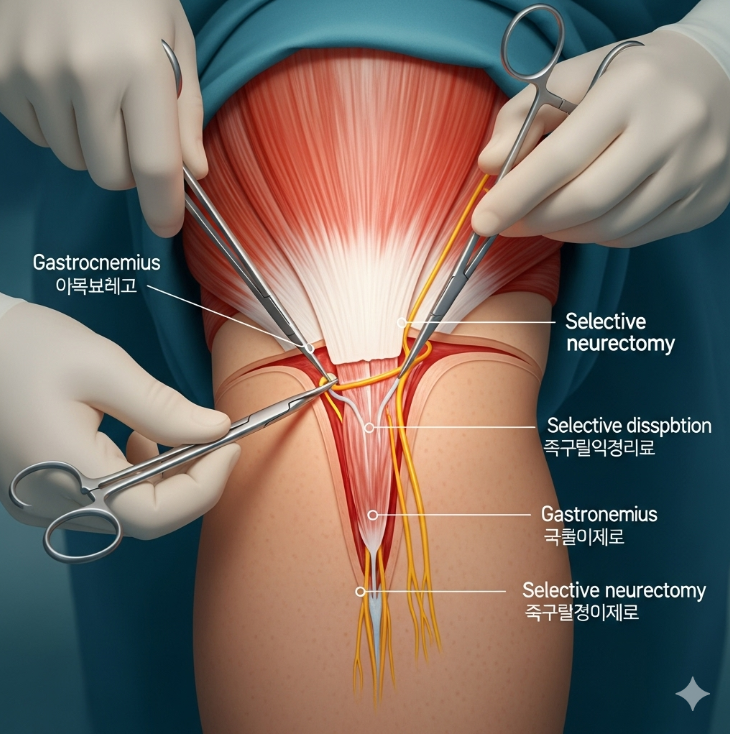
Selective neurectomy for calf reduction is a surgical procedure that reduces calf size by partially cutting or removing specific nerves that stimulate the calf muscles, primarily the gastrocnemius. By limiting muscle activity, the muscle gradually decreases in size, resulting in slimmer calves.
In Korea, this is considered an advanced cosmetic procedure, performed in specialized plastic surgery clinics. It is especially popular among patients who desire a slimmer, more feminine leg contour when bulky calves are due to muscle rather than fat.
Why It’s Done
Patients choose selective neurectomy for several reasons:
- To achieve slimmer, more proportionate calves.
- To correct naturally large or muscular calves caused by genetics.
- To improve confidence when wearing skirts, dresses, or slim-fitting pants.
- To refine leg contour when fat-based calf reduction (via liposuction) is not suitable.
It is especially recommended when calf bulk is muscle-dominant rather than fat-dominant.
Alternatives
Before considering selective neurectomy, patients may explore:
- Botox (botulinum toxin) injections: Temporarily reduce calf muscle bulk by relaxing muscle activity. Results last 4–6 months.
- Calf liposuction: Suitable when fat, not muscle, is the main cause of calf enlargement.
- Radiofrequency or ultrasound treatments: Non-surgical approaches to contour mild calf fullness.
- Lifestyle changes: Exercise and diet may slim the legs overall but cannot selectively shrink calf muscles.
Preparation
Preparation for selective neurectomy involves:
- Consultation: Careful evaluation by a surgeon to confirm muscle-dominant calves.
- Medical assessment: Blood tests, imaging, and sometimes nerve studies.
- Lifestyle adjustments: Stopping smoking and alcohol for at least 2–4 weeks prior.
- Medication review: Discontinuing blood thinners or supplements that increase bleeding risk.
- Recovery planning: Arranging for 1–2 weeks of reduced activity after surgery.
How It’s Done
Selective neurectomy is performed under general or local anesthesia with sedation, depending on the extent of the procedure. Typical steps include:
- A small incision is made behind the knee.
- The nerves that stimulate the calf muscles (often branches of the tibial nerve) are carefully identified.
- Select nerves are partially cut or removed to reduce muscle activity.
- The incision is closed with fine sutures, leaving a discreet scar hidden in natural folds.
The surgery usually takes 1–2 hours and is often done as a day procedure.
Recovery
Recovery after calf reduction via neurectomy is generally manageable:
- First week: Swelling, bruising, and mild discomfort around the calves are common. Compression bandages may be applied.
- Mobility: Walking is possible within a day or two, but strenuous activity should be avoided for 4–6 weeks.
- Follow-up care: Regular check-ups are scheduled to monitor healing and nerve response.
- Results: Calf slimming develops gradually over 3–6 months as the muscle reduces in size. Final results may take up to a year.
Possible Complications
As with any surgery, selective neurectomy carries risks, including:
- Infection or bleeding at the incision site.
- Numbness or changes in sensation in the calf or foot.
- Muscle weakness (over-reduction).
- Asymmetry between calves.
- Scarring, though usually minimal and hidden.
- Rare but serious nerve-related complications affecting calf strength or mobility.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Thorough consultation and examination to confirm muscle-based calf hypertrophy.
- Sometimes nerve conduction studies to map muscle activity.
Medical Treatments
- Pre- and post-operative medications for pain control and infection prevention.
- Use of compression stockings or bandages for faster recovery.
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Selective neurectomy: Standard procedure for long-term calf muscle reduction.
- Partial neurectomy: Limited approach for subtle contouring.
- Combination procedures: Neurectomy with Botox or liposuction for tailored results.
Rehabilitation and Support
- Physical therapy to support calf function and gait.
- Scar care treatments such as silicone gels or laser therapy.
- International patient support, including translators, hospital coordinators, and virtual follow-up care.