What It Is
Brow ptosis repair is a surgical procedure that corrects drooping of the eyebrows. As skin and soft tissues lose elasticity with age, or due to nerve and muscle weakness, the brows may sag and press down on the upper eyelids. This not only causes a tired or sad appearance but can also obstruct vision if the brows droop significantly.
In Korea, brow ptosis repair is performed by plastic surgeons and oculoplastic specialists who focus on both functional vision improvement and aesthetic rejuvenation.
Why It’s Done
Patients seek brow ptosis repair for:
- Functional reasons: Heavy brows pushing on the upper eyelids, reducing peripheral vision
- Aesthetic reasons: Correcting a tired, angry, or aged appearance
- Asymmetry: When one brow droops more than the other
- Adjunct to eyelid surgery: Often combined with blepharoplasty to optimize results
The procedure helps restore a youthful, open look to the eyes and improves visual comfort.
Alternatives
Depending on the degree of brow droop, alternatives include:
- Non-surgical treatments: Botox injections to elevate the brows temporarily
- Thread lifting: Minimally invasive method for mild cases, though results are temporary
- Upper blepharoplasty only: May help in mild cases if skin excess is the main issue
- Forehead lift / endoscopic brow lift: Broader rejuvenation of the entire forehead and brow area
Surgical brow ptosis repair is most effective for moderate to severe cases or when long-lasting results are desired.
Preparation
Preparation for surgery includes:
- Consultation: Eyelid and brow measurements, vision assessment, and discussion of patient goals
- Medical evaluation: Blood tests and anesthesia clearance
- Lifestyle changes: Avoid smoking and alcohol for 2–4 weeks before surgery
- Medication review: Temporary discontinuation of blood thinners or supplements that increase bleeding risk
- Treatment planning: Deciding whether to combine with eyelid or forehead surgery
How It’s Done
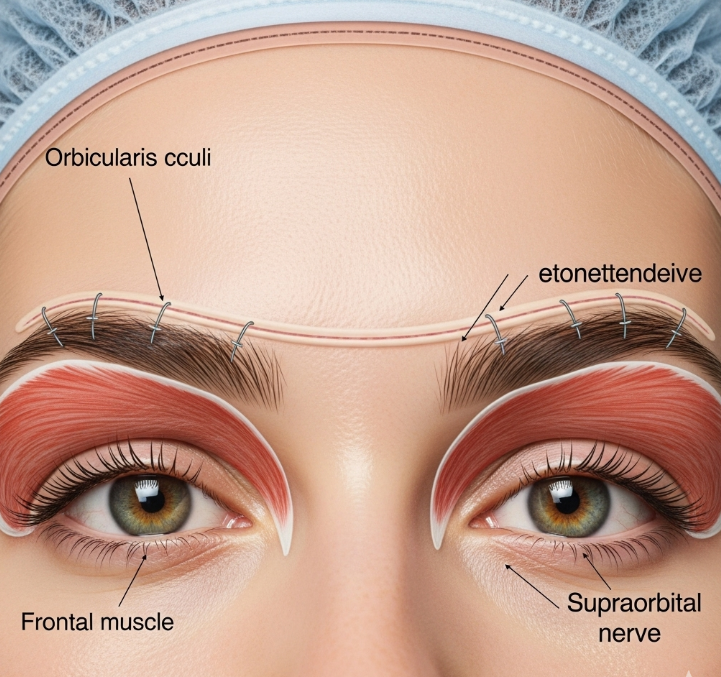
The surgical technique depends on the severity and location of brow droop. Common methods in Korea include:
- Direct brow lift: Incision just above the brow hairs to lift and secure the brow higher
- Transblepharoplasty brow lift: Performed through the same incision as an upper eyelid surgery
- Endoscopic brow lift: Small incisions hidden in the hairline with camera-assisted lifting (for patients needing forehead and brow elevation together)
Surgery is usually done under local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia and lasts 1–2 hours.
Recovery
- First week: Swelling, bruising, and mild tightness in the forehead and brow region
- Stitches removal: Usually within 5–7 days (longer if hairline incisions are used)
- Return to activities: Light daily activities within a few days, but strenuous activity should be avoided for 2–3 weeks
- Final results: Visible within 2–3 weeks, with continued improvement as swelling resolves over several months
Possible Complications
As with any surgery, risks include:
- Infection or bleeding
- Scarring (though incisions are often well hidden)
- Asymmetry between brows
- Temporary numbness of the forehead or scalp
- Overcorrection or undercorrection requiring revision
- Rare hairline changes if an endoscopic approach is used
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Detailed brow position and eyelid function assessment
- Visual field testing if brow droop affects sight
Medical Treatments
- Pain management and antibiotics post-surgery
- Scar care with silicone gel or ointments
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Direct brow lift: Precise correction for significant droop
- Transblepharoplasty brow lift: Subtle lift during eyelid surgery
- Endoscopic brow lift: Minimally invasive option with hidden scars
- Combination procedures: Brow ptosis repair with upper eyelid blepharoplasty for optimal results
Rehabilitation and Support
- Scar management with creams or laser therapy if needed
- Regular follow-up visits to ensure symmetry and healing
- International patient services including interpreters, hospital coordination, and telemedicine follow-ups