What It Is
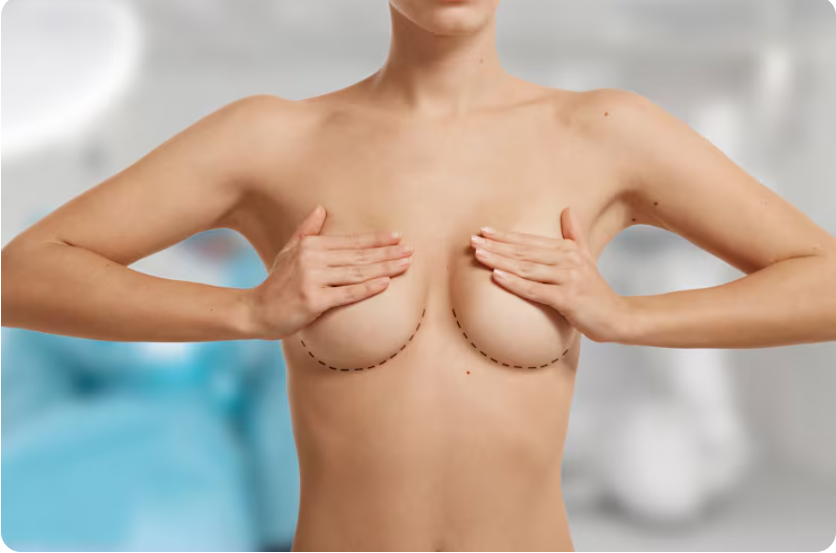
Breast reduction, also called reduction mammaplasty, is a surgical procedure to reduce the size and weight of overly large breasts by removing excess breast tissue, fat, and skin. The surgery reshapes the breasts to a smaller, lighter, and more proportionate size, while also lifting them for improved contour.
In Korea, breast reduction is performed not only for cosmetic enhancement but also for medical relief of back, neck, and shoulder pain, postural issues, and skin irritation. Korean surgeons specialize in advanced techniques that provide balanced aesthetics, minimal scarring, and improved function.
Why It’s Done
Patients undergo breast reduction because:
- Large breasts cause chronic pain in the neck, shoulders, or back.
- They experience skin irritation, rashes, or bra strap grooving.
- Breast size interferes with physical activity and daily comfort.
- They want to improve aesthetic proportions and self-confidence.
Good candidates include:
- Women with symptomatic macromastia (overly large breasts).
- Patients in good health who can undergo surgery.
- Those with realistic expectations about scars and results.
Alternatives
- Liposuction alone: May help in selected cases with fatty, non-ptotic breasts.
- Weight loss: Can reduce breast size but does not address excess skin or sagging.
- Supportive bras and physiotherapy: Provide symptom relief but no permanent reduction.
Preparation
Before breast reduction in Korea, patients will:
- Undergo consultation with breast measurements and imaging if necessary.
- Stop smoking and alcohol 2–4 weeks before surgery.
- Avoid blood-thinning medications and certain supplements.
- Discuss incision patterns and expected breast size with the surgeon.
- Plan for recovery and time off from strenuous activity.
How It’s Done
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is used.
- Incisions: Technique depends on breast size and amount of tissue removed:
- Vertical (lollipop) for moderate reductions.
- Anchor (inverted-T) for larger reductions and significant sagging.
- Tissue removal: Excess glandular tissue, fat, and skin are excised.
- Reshaping: Remaining tissue is lifted and contoured for a natural shape.
- Nipple repositioning: The nipple-areola complex is moved higher for proportional results.
- Closure: Sutures are placed, and dressings applied.
- Duration: 3–5 hours, usually inpatient.
Recovery
- First week: Swelling, bruising, and mild pain are common; support bras are required.
- Hospital stay: 1–2 days depending on the case.
- Return to activities: Light duties in 1–2 weeks; avoid strenuous exercise for 4–6 weeks.
- Final results: Breasts appear smaller, lighter, and lifted within 2–3 months, with scars fading over 12–18 months.
Possible Complications
- Visible scarring, although minimized with Korean techniques.
- Temporary or permanent changes in nipple sensation.
- Asymmetry between breasts.
- Infection, hematoma, or delayed healing.
- Rare risks: fat necrosis, nipple loss, or need for revision.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Korean surgeons use clinical evaluation, imaging, and 3D planning to assess the degree of reduction required and select the best surgical technique.
Medical Treatments
- Support bras, posture therapy, and pain management for symptom relief in mild cases.
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Vertical breast reduction for moderate hypertrophy.
- Anchor-pattern reduction for severe hypertrophy with sagging.
- Liposuction-assisted reduction for selected fatty breasts with minimal sagging.
- Simultaneous lift (mastopexy) for improved contour.
Rehabilitation and Support
- Scar care with silicone gels, massage, or fractional laser.
- Postoperative physiotherapy or posture correction if needed.
- Long-term follow-up to monitor breast shape and size.
- International patients benefit from Korea’s functional-aesthetic approach, advanced scar-minimizing methods, and comprehensive aftercare support.