What It Is
Breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure to restore the shape, size, and symmetry of the breast after mastectomy, lumpectomy, trauma, or congenital absence. It can be performed using implants, autologous tissue (flaps), or a combination of both.
In Korea, breast reconstruction is performed by highly skilled plastic and reconstructive surgeons using state-of-the-art microsurgical techniques, advanced implant options, and 3D surgical planning to provide natural-looking results and support patient recovery both physically and emotionally.
Why It’s Done
Patients undergo breast reconstruction because:
- They want to restore breast appearance after mastectomy or lumpectomy.
- Reconstruction can help with body image, self-esteem, and emotional healing.
- It improves clothing fit and balance in posture.
- Some patients choose it for symmetry after partial breast removal or congenital absence.
Good candidates include:
- Women who have undergone or plan to undergo mastectomy or lumpectomy.
- Patients with stable health and realistic expectations.
- Those seeking immediate or delayed reconstruction depending on their cancer treatment plan.
Alternatives
- External prostheses or padded bras: Non-surgical solutions for breast shape restoration.
- No reconstruction: Some women choose to remain flat after mastectomy.
- Fat grafting alone: Suitable for partial reconstruction or volume correction.
Preparation
Before breast reconstruction in Korea, patients will:
- Consult with both a breast surgeon and a reconstructive plastic surgeon.
- Undergo imaging and blood tests to plan the procedure.
- Discuss reconstruction options (implant-based, autologous flap, or hybrid).
- Stop smoking and alcohol 4 weeks before surgery.
- Avoid blood-thinning medications and certain supplements.
How It’s Done
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is required.
- Timing: Can be immediate (at the time of mastectomy) or delayed.
- Techniques:
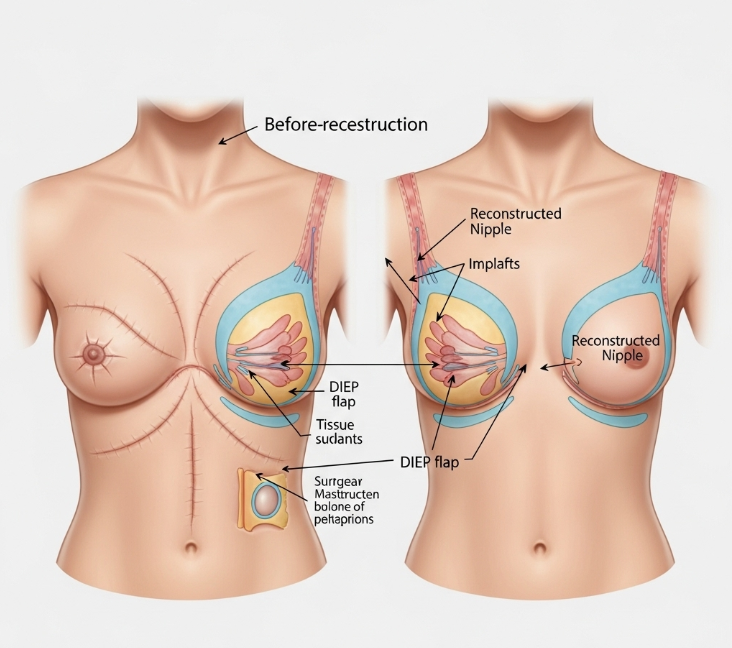
- Implant-based reconstruction: Uses tissue expanders followed by permanent implants.
- Autologous reconstruction (flap): Uses patient’s own tissue (e.g., DIEP flap, TRAM flap, latissimus dorsi flap).
- Hybrid reconstruction: Combines implant with fat grafting for softness and contour.
- Duration: 3–8 hours depending on method.
Recovery
- First week: Swelling, bruising, and soreness are common; drains may be placed.
- Hospital stay: 3–7 days, depending on technique.
- Return to activities: Light duties in 2–3 weeks; avoid strenuous exercise for 6–8 weeks.
- Final results: Breasts appear natural within 3–6 months, with scars maturing over 12–18 months.
Possible Complications
- Infection or wound healing problems.
- Implant-related complications (capsular contracture, rupture).
- Flap-related risks such as partial loss or fat necrosis.
- Asymmetry or irregularities requiring revision surgery.
- Rare risks: blood clots or anesthesia-related complications.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Korean surgeons use 3D breast imaging, MRI, and virtual planning software to design individualized reconstruction strategies.
Medical Treatments
- External prosthetics or compression garments for patients not choosing surgery.
- Fat grafting alone for mild corrections.
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Implant-based reconstruction with modern silicone implants.
- Autologous tissue flaps (DIEP, TRAM, latissimus dorsi, or gluteal flaps).
- Hybrid reconstruction combining implants with fat transfer.
- Nipple-areola reconstruction and 3D medical tattooing for final aesthetic refinement.
Rehabilitation and Support
- Postoperative physiotherapy to restore arm and chest mobility.
- Scar care with silicone sheets, microneedling, or fractional laser.
- Psychological support and counseling as part of holistic care.
- International patients benefit from Korea’s multidisciplinary breast cancer and reconstructive centers, advanced microsurgery, and dedicated aftercare programs.