What It Is
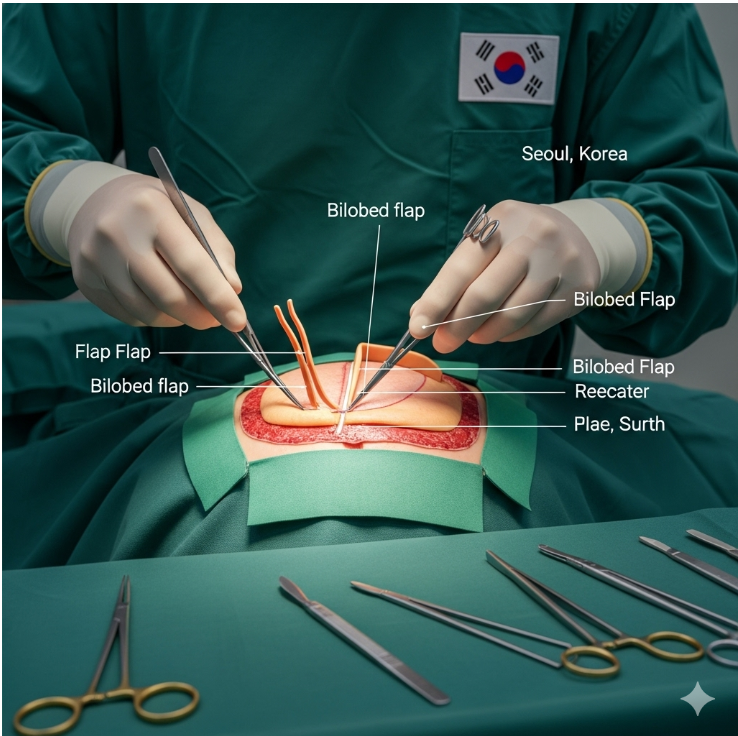
A bilobed flap is a reconstructive surgical technique used to repair skin defects, most commonly on the nose. It involves creating two connected flaps of nearby skin, which are rotated in sequence to cover the defect. This design allows the surgeon to redistribute tension, minimize distortion, and use skin with similar color and texture for a natural-looking repair.
In Korea, bilobed flap surgery is widely performed in plastic surgery and dermatologic surgery centers, often after skin cancer removal (especially basal cell carcinoma) or trauma to the nose.
Why It’s Done
Patients may undergo bilobed flap reconstruction for:
- Nasal defects after removal of skin cancer or benign lesions.
- Post-traumatic injuries where local tissue is missing.
- Cosmetic refinement when other closure methods would create visible distortion.
- Functional reconstruction, ensuring proper nasal shape and airway support.
This flap is especially useful for small- to medium-sized defects of the lower third of the nose, where skin is tight and direct closure is not possible.
Alternatives
Depending on defect size and location, alternatives to bilobed flap include:
- Primary closure: Directly stitching the wound (for very small defects).
- Skin grafts: Transferring skin from another area, though the texture and color may not match as well.
- Other local flaps (W-plasty, Z-plasty, or paramedian forehead flap): Used for larger or more complex nasal defects.
- Prosthetics: In rare cases, artificial replacements may be considered if surgery is not possible.
Preparation
Before undergoing bilobed flap surgery, patients usually complete:
- Consultation: Detailed examination by a plastic or dermatologic surgeon to assess defect size and location.
- Medical evaluation: Blood tests and health review.
- Oncologic clearance: If the defect is from skin cancer removal, ensuring clear surgical margins.
- Lifestyle adjustments: Avoiding smoking and alcohol for 2–4 weeks before surgery.
- Medication review: Pausing blood thinners if needed to reduce bleeding risk.
How It’s Done
Bilobed flap reconstruction is typically performed under local anesthesia with sedation for smaller defects, or under general anesthesia for larger, complex cases. Steps include:
- Flap design: The surgeon marks two adjoining flaps shaped like lobes, usually next to the defect.
- Flap elevation: The flaps are carefully lifted while preserving their blood supply.
- Rotation and transfer: The first flap covers the primary defect, and the second lobe fills the donor site created by the first flap’s rotation.
- Closure: Both donor and defect sites are sutured, creating a smooth, tension-free repair.
The procedure usually takes 1–2 hours.
Recovery
Recovery after bilobed flap surgery is usually straightforward:
- First week: Mild swelling, redness, and bruising are common. Sutures are typically removed within 5–7 days.
- Activity: Light daily activities can be resumed quickly, but patients should avoid strenuous exercise for 2 weeks.
- Scar healing: The scar blends into natural skin creases and improves over several months.
- Final results: Natural contour and color match are usually visible within weeks, with full refinement over 6–12 months.
Possible Complications
While safe and reliable, bilobed flap surgery carries some risks, including:
- Infection or bleeding.
- Flap necrosis (rare, due to poor blood supply).
- Scar widening or irregularity.
- Skin color mismatch (usually minimal with this technique).
- Distortion of nasal structures if not performed carefully.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Detailed facial examination to assess skin laxity, scar location, and cosmetic outcome goals.
- Use of dermoscopy or pathology reports when performed after skin cancer removal.
Medical Treatments
- Local or systemic antibiotics to prevent infection.
- Pain control and topical scar-care products.
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Standard bilobed flap: Most commonly used for small- to medium-sized nasal defects.
- Modified bilobed flap: Adjusted flap angles to reduce scarring or improve skin tension.
- Combination reconstruction: Bilobed flap with cartilage grafting if nasal support is also needed.
Rehabilitation and Support
- Scar management with silicone sheets, creams, or fractional laser therapy.
- Long-term follow-up to monitor healing and cosmetic outcomes.
- International patient services, including translation, care coordination, and virtual check-ups.