What It Is
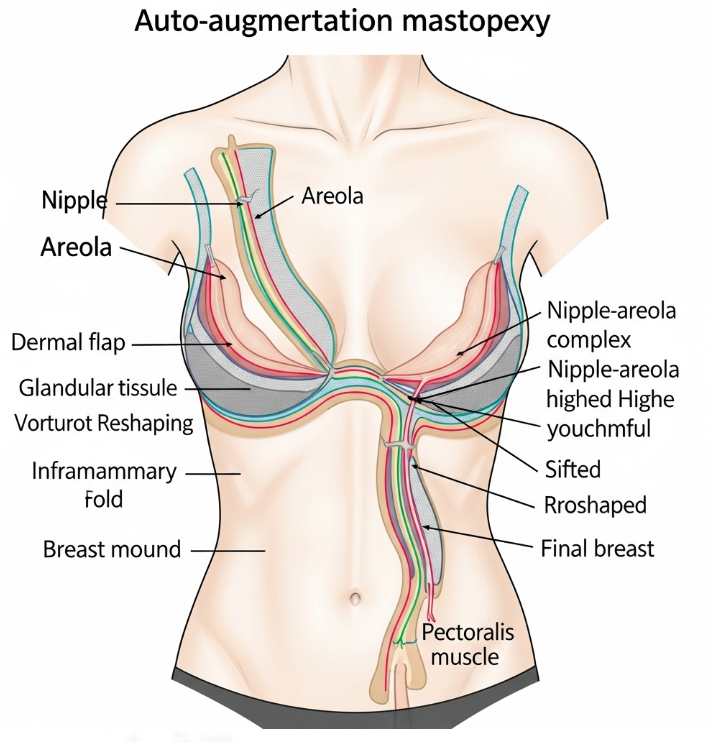
Auto-augmentation mastopexy is a specialized breast lift procedure that uses the patient’s own breast tissue to enhance fullness and shape while lifting sagging breasts. Unlike traditional mastopexy, which only removes excess skin and lifts the tissue, this technique reshapes and repositions lower breast tissue into the upper pole to provide natural volume and projection.
In Korea, surgeons often combine auto-augmentation mastopexy with advanced scar-minimizing techniques and 3D surgical planning, making it an ideal option for women who want a lift with added fullness but without implants.
Why It’s Done
Patients undergo auto-augmentation mastopexy because:
- They want to correct sagging (ptosis) while also restoring lost upper breast fullness.
- They prefer natural enhancement without implants.
- They want to improve breast symmetry and firmness.
- They seek long-lasting results after pregnancy, breastfeeding, weight loss, or aging.
Good candidates include:
- Women with moderate sagging and adequate breast tissue.
- Patients who do not want implants but still want fuller, lifted breasts.
- Individuals in good overall health with realistic expectations.
Alternatives
- Traditional mastopexy: Lifts the breasts but does not restore upper pole fullness.
- Mastopexy with implants: Provides both lift and added volume but involves foreign material.
- Fat transfer augmentation: Uses liposuctioned fat for subtle volume increase, sometimes combined with a lift.
- Supportive bras or non-surgical tightening: Temporary solutions with no structural lift.
Preparation
Before auto-augmentation mastopexy in Korea, patients will:
- Have a consultation with measurements and 3D simulations.
- Undergo imaging if required (mammogram or ultrasound).
- Stop smoking and alcohol 2–4 weeks before surgery.
- Avoid blood-thinning medications and certain supplements.
- Prepare for recovery and follow-up care.
How It’s Done
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is used.
- Incisions: Depend on the degree of sagging (vertical “lollipop” or anchor pattern for more severe cases).
- Tissue reshaping: Lower breast tissue is mobilized, folded, and secured higher within the breast to create upper pole fullness.
- Skin tightening: Excess skin is removed, and the nipple-areola complex is repositioned.
- Closure: Sutures are placed carefully to minimize visible scars.
- Duration: 2–4 hours depending on technique and complexity.
Recovery
- First week: Swelling, bruising, and mild discomfort are common; a support bra is worn continuously.
- Stitches: Usually dissolvable or removed within 7–14 days.
- Return to activities: Light activities in 5–7 days; avoid strenuous exercise for 4–6 weeks.
- Final results: Breasts appear lifted, firmer, and naturally fuller within 2–3 months, with scars fading over 6–12 months.
Possible Complications
- Visible scarring (though minimized with advanced Korean techniques).
- Asymmetry between breasts.
- Temporary or permanent changes in nipple sensation.
- Recurrence of sagging over time.
- Rare risks: wound healing problems, infection, or tissue irregularities.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Korean surgeons use 3D imaging, breast analysis, and physical evaluation to assess sagging severity and tissue availability for auto-augmentation.
Medical Treatments
- Supportive bras or tightening treatments for very mild sagging (limited benefit).
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Auto-augmentation mastopexy for patients wanting lift + natural volume.
- Traditional mastopexy if volume restoration is not needed.
- Mastopexy with implants or fat grafting for patients seeking greater fullness.
Rehabilitation and Support
- Scar management with silicone gels, sheets, or fractional laser.
- Long-term follow-up to ensure stability of lifted tissue.
- Lifestyle guidance to maintain results, including weight management and supportive bras.
- International patients benefit from Korea’s breast surgery expertise, natural-shaping techniques, and multilingual aftercare support.