What It Is
Animation deformity correction is a surgical procedure to treat distortion of the breasts during chest muscle movement, a complication that commonly occurs after submuscular breast implant placement. When the pectoralis muscle contracts, the implant may shift unnaturally, causing the breast to appear deformed or move in an obvious way.
In Korea, surgeons correct animation deformity by using advanced revision techniques such as converting implants to prepectoral placement, reinforcing with acellular dermal matrix (ADM), adjusting muscle coverage, or combining fat grafting for natural softness and contour.
Why It’s Done
Patients undergo animation deformity correction because:
- Their breasts change shape or shift unnaturally when they flex chest muscles.
- They experience discomfort or tightness during physical activity.
- The deformity affects confidence, daily function, and quality of life.
- They want natural-looking breasts with stability in all movements.
Good candidates include:
- Patients with implants placed under the chest muscle (submuscular or dual-plane).
- Individuals in good overall health seeking revision.
- Those dissatisfied with movement-related deformities after augmentation or reconstruction.
Alternatives
- External support bras: May minimize appearance temporarily but do not correct the issue.
- Fat grafting alone: Improves contour but often insufficient without pocket change.
- Observation: For mild deformities that are not bothersome.
Preparation
Before animation deformity correction in Korea, patients will:
- Undergo consultation with 3D imaging, ultrasound, or MRI to evaluate implant position and muscle movement.
- Stop smoking and alcohol 2–4 weeks prior to surgery.
- Avoid blood-thinning medications and certain supplements.
- Decide whether to keep existing implants, replace them, or switch to fat transfer.
How It’s Done
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is required.
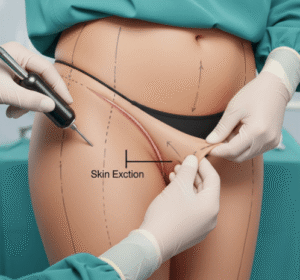
- Pocket adjustment: Implants are repositioned from submuscular to prepectoral placement (above the muscle).
- ADM reinforcement: Acellular dermal matrix or mesh may be used to support the implant.
- Muscle modification: The pectoralis muscle may be released to reduce implant movement.
- Fat grafting: Often added to improve natural contour and camouflage implant edges.
- Duration: 2–4 hours, depending on complexity.
Recovery
- First week: Swelling, bruising, and mild discomfort are common.
- Hospital stay: Outpatient or 1 night if combined with major revision.
- Return to activities: Light duties in 1–2 weeks; strenuous exercise avoided for 4–6 weeks.
- Final results: Breasts appear natural and stable during movement within 2–3 months.
Possible Complications
- Implant malposition or asymmetry after revision.
- Infection or delayed wound healing.
- Visible scarring, though minimized with Korean techniques.
- Recurrence of minor deformity in rare cases.
- Capsular contracture or implant-related complications.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Korean surgeons use 3D motion analysis, ultrasound, and MRI to study implant displacement during chest muscle movement.
Medical Treatments
- Supportive bras or lifestyle adjustments for mild cases (not permanent solutions).
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Implant pocket change from submuscular to prepectoral.
- ADM or mesh reinforcement for implant stabilization.
- Muscle release or modification to prevent abnormal movement.
- Hybrid augmentation with fat grafting for natural correction.
Rehabilitation and Support
- Scar care with silicone gels or fractional laser.
- Physiotherapy may be recommended for muscle relaxation.
- Long-term follow-ups to monitor implant stability.
- International patients benefit from Korea’s expertise in complex breast revision surgery, advanced ADM techniques, and tailored aftercare.