What it is
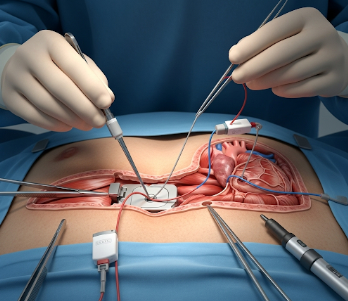
Pacemaker implantation is a surgical procedure in which a small electronic device, called a pacemaker, is placed under the skin—usually near the collarbone—to regulate abnormal heart rhythms. The device sends electrical impulses to the heart to maintain a normal heartbeat, especially in cases of bradycardia (slow heart rate) or heart block.
➡ Modern pacemakers:
- Small, battery-powered devices with leads connecting to the heart.
- Types include single-chamber, dual-chamber, or biventricular pacemakers, depending on which part of the heart needs stimulation.
➡ Home in Korea:
- Pacemaker implantation is a routine, highly advanced procedure in Korea.
- Patients benefit from state-of-the-art technology, strict safety protocols, and long-term follow-up programs.
Why it’s done
Pacemakers are prescribed when heart rhythm disorders cause insufficient blood flow, leading to symptoms or health risks.
➤ Common indications:
- Bradycardia (slow heart rate) → Fatigue, dizziness, fainting, shortness of breath.
- Heart block (AV block) → Disrupted electrical signals causing irregular or slow heartbeat.
- Atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular response → Pacemaker regulates heart rate.
- Heart failure → Biventricular pacemakers improve pumping efficiency.
- Syncope (fainting episodes) due to heart rhythm abnormalities → Prevents dangerous pauses in heartbeat.
➤ Key benefits:
- Restores normal heart rhythm
- Reduces fatigue, dizziness, fainting
- Improves quality of life and physical activity tolerance
- Prevents complications such as heart failure or stroke
Alternatives
While pacemakers are often the most effective solution, there are some alternatives or complementary strategies:
✔ Medications → Drugs to regulate heart rhythm or improve heart rate
✔ Lifestyle modifications → Healthy diet, stress management, limiting caffeine/alcohol
✔ Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) → Advanced pacemaker for heart failure
✔ Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) → Combines pacemaker function for patients at risk of dangerous arrhythmias
✔ Observation → Careful monitoring in mild, asymptomatic cases
Note: For symptomatic bradycardia or heart block, pacemaker implantation is usually the safest and standard treatment.
Preparation
Patients must follow several preparatory steps before implantation:
🔹 Medical evaluation
- ECG, echocardiogram, Holter monitoring
- Blood tests for overall health, kidney function, coagulation
- Review of medical history, allergies, and medications
🔹 Medication adjustments
- Blood thinners may be temporarily stopped to reduce bleeding risk
- Cardiovascular medications adjusted as needed
🔹 Hospital admission and fasting
- Fasting for several hours before surgery
- Admission on the day of surgery or the day before, depending on protocol
🔹 Consent and counseling
- Explanation of risks, benefits, and alternatives
- Opportunity to ask questions about device implantation and lifestyle changes
How it’s done
Pacemaker implantation is minimally invasive, performed under local anesthesia with sedation:
➡ Incision and pocket creation
- Small incision (~2–3 inches) near collarbone
- Pocket created under the skin for the device
➡ Lead insertion
- Leads inserted into a vein and guided to the heart using fluoroscopy
- Secured to the appropriate heart chamber(s) for optimal stimulation
➡ Device connection
- Leads connected to the pacemaker and device programmed to patient needs
➡ Closure and recovery
- Incision closed with sutures or surgical glue
- Sterile dressing applied and monitored in recovery
⏱ Procedure duration: Typically 1–2 hours, depending on complexity and pacemaker type
Recovery
Recovery after pacemaker implantation is generally quick, but proper care is essential:
- Hospital stay: 1–2 days for monitoring heart rhythm and incision healing
- Activity limitations: Avoid heavy lifting, overhead arm movements, or strenuous exercise for 4–6 weeks
- Wound care: Keep incision clean and dry; watch for infection signs
- Follow-up visits:
- Device checks using programmers or remote monitoring
- Regular cardiology appointments to adjust settings
➡ Lifestyle adjustments:
- Avoid strong magnetic fields or MRI machines unless pacemaker is MRI-compatible
- Always inform medical personnel about the device during other procedures
💡 Expected improvements:
- Reduced dizziness, fatigue, and fainting within days to weeks
- Full adjustment to the device may take several weeks
Complications
Although generally safe, potential risks include:
⚠ Infection → At incision site or around device
⚠ Bleeding or hematoma → Usually minor but monitored post-surgery
⚠ Lead displacement or malfunction → May require repositioning
⚠ Pneumothorax (collapsed lung) → Rare, accidental during lead insertion
⚠ Arrhythmias → Temporary irregular heartbeats immediately post-procedure
⚠ Device-related complications → Battery depletion or device failure
Regular follow-up and adherence to post-operative care minimize risks and ensure long-term device functionality.
Treatment Options in Korea
Pacemaker implantation is available in top hospitals and cardiac centers in Korea, providing advanced technology and expert care:
🏥 Hospitals and clinics:
- Seoul National University Hospital (SNUH) → Comprehensive cardiology, pacemaker implantation, and remote monitoring
- Asan Medical Center → Advanced cardiac electrophysiology, complex pacemaker and CRT devices
- Samsung Medical Center → Minimally invasive procedures, device programming, long-term patient support
- Other hospitals: Bundang, Severance, St. Mary’s
💰 Insurance coverage:
- National Health Insurance covers part of the cost for eligible patients
- Private insurance may cover device cost or hospitalization fees
🔹 Additional support:
- Cardiac rehabilitation programs post-implantation
- Patient education on device management and lifestyle adjustments
Conclusion
Pacemaker implantation in Korea is a safe and life-improving procedure for patients with slow or irregular heart rhythms. With modern technology, highly trained cardiologists, and structured follow-up programs, patients can experience:
- Significant improvement in symptoms
- Better quality of life
- Long-term cardiac health
Whether for bradycardia, heart block, or heart failure, pacemaker implantation provides a reliable solution for patients to maintain an active and healthy life with careful monitoring and professional support.