What it is
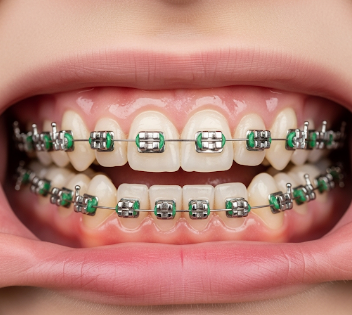
Orthodontics is a specialized branch of dentistry that focuses on the diagnosis, prevention, and correction of teeth and jaw misalignment. It addresses issues such as crooked teeth, malocclusion (bad bite), overcrowding, and jaw irregularities.
Key points:
- Involves the use of braces, aligners, retainers, and other appliances to correct alignment.
- Helps improve oral health, bite function, and facial aesthetics.
- Serves patients of all ages, including children, teenagers, and adults.
- Contributes to better oral hygiene, speech, and overall confidence.
Orthodontics not only enhances smiles and appearance but also prevents long-term dental complications like tooth decay, gum disease, and jaw pain.
Why it’s done
Orthodontic treatment is undertaken for several reasons:
- Aesthetic improvement: Aligns teeth for a balanced and attractive smile.
- Bite correction: Fixes overbite, underbite, crossbite, and open bite for proper jaw alignment.
- Functional improvement: Facilitates chewing, speaking, and overall oral function.
- Preventive care: Prevents tooth wear, gum disease, and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders.
- Early intervention: Corrects jaw growth and dental development issues in children, minimizing future complications.
Common conditions treated:
- Crowded or spaced teeth
- Misaligned jaws
- Protruding teeth
- Bite irregularities
- Congenital dental issues
Orthodontic treatment contributes to long-term oral health, overall well-being, and self-esteem.
Alternatives
While traditional orthodontics is the standard, there are other options:
- Clear aligners (Invisalign): Removable, transparent aligners for mild to moderate misalignment.
- Retainers: Used post-treatment to maintain teeth position.
- Surgical orthodontics: For severe jaw misalignment requiring both braces and surgery.
- Interceptive treatment: Early intervention in children to guide jaw growth and tooth eruption.
- Cosmetic dentistry: Veneers or bonding for minor aesthetic concerns, but does not correct underlying bite or alignment issues.
Important: Only orthodontic treatment guided by a specialist corrects structural misalignment and bite problems, while cosmetic procedures mainly improve appearance.
Preparation
Before beginning orthodontic treatment, certain preparations are necessary:
- Dental examination: Complete check-up, including X-rays, photographs, and dental impressions.
- Oral hygiene assessment: Teeth and gums should be healthy and free of decay or disease.
- Treatment planning: Orthodontist develops a personalized plan outlining the type of braces, duration, and expected outcomes.
- Patient education: Information on oral care, dietary restrictions, and treatment expectations.
Patient instructions:
- Maintain good oral hygiene before starting treatment.
- Avoid foods that damage braces (sticky, hard, or sugary foods).
- Discuss any medical conditions, allergies, or previous dental treatments with the orthodontist.
How it’s done
Orthodontic treatment involves several stages:
- Initial assessment and diagnostics:
- Clinical examination, X-rays, and 3D imaging to assess teeth, jaw alignment, and bite.
- Impressions or digital scans are taken for custom appliance design.
- Treatment planning:
- Decide on the type of braces or aligners (metal, ceramic, lingual, or clear aligners).
- Determine treatment duration, usually 12–36 months depending on complexity.
- Appliance placement:
- Braces are bonded to teeth with brackets and wires.
- Aligners are custom-made and removable, changed every 1–2 weeks.
- Regular adjustments ensure teeth move gradually into proper alignment.
- Monitoring and adjustments:
- Routine visits every 4–8 weeks for braces or aligners.
- Adjustments include wire tightening, bracket repositioning, or aligner progression.
- Monitoring ensures optimal tooth movement and oral health maintenance.
- Retention phase:
- After active treatment, retainers are provided to maintain teeth position.
- Can be fixed or removable, worn as prescribed by the orthodontist.
Duration: The complete process typically ranges from 1–3 years, depending on severity and patient compliance.
Recovery / Post-Treatment Considerations
After completing orthodontic treatment:
- Immediate recovery: Some soreness or discomfort is normal for a few days after adjustments.
- Oral care: Continue brushing, flossing, and using interdental brushes to prevent decay.
- Dietary adjustments: Avoid hard, sticky, or overly sugary foods that could compromise teeth alignment or retainers.
- Retention: Retainers must be worn consistently to prevent relapse.
Benefits:
- Improved aesthetic appearance and smile confidence.
- Corrected bite, chewing, and speaking function.
- Reduced risk of tooth decay, gum disease, and jaw problems.
- Enhanced long-term oral health and overall well-being.
Complications / Risks
Orthodontic treatment is generally safe, but minor risks include:
- Tooth decay or gum inflammation: If oral hygiene is inadequate.
- Tooth root resorption: Slight shortening of tooth roots in rare cases.
- Discomfort or soreness: Common after appliance adjustments.
- Allergic reactions: Rare reactions to metals or latex in appliances.
- Relapse: Teeth may shift if retainers are not worn as prescribed.
Prevention / Management:
- Maintain excellent oral hygiene and follow orthodontist instructions.
- Attend regular follow-up appointments.
- Report any pain, swelling, or appliance damage promptly.
Treatment Options in Korea
Orthodontic care is widely available in hospitals, specialized dental clinics, and private practices across Korea:
Key features:
- Treatment options for children, adolescents, and adults.
- Offers metal braces, ceramic braces, lingual braces, and clear aligners.
- Integrates with digital imaging, 3D modeling, and modern orthodontic technology.
- Supports complex cases requiring surgical orthodontics or multidisciplinary care.
- Many clinics provide consultation, treatment planning, financing options, and follow-up care.
Benefits in Korea:
- Ensures high-quality orthodontic care using advanced technology.
- Promotes long-term dental health, improved aesthetics, and functional bite.
- Supports early intervention for children, preventing more severe problems later.
- Provides multidisciplinary care for patients with congenital or acquired dental and jaw issues.
Additional Considerations for Patients
- Follow all oral hygiene instructions for the best results.
- Attend all scheduled appointments and adhere to treatment timelines.
- Wear retainers as prescribed to maintain teeth alignment.
- Communicate any discomfort, appliance breakage, or concerns with the orthodontist.
- Combine orthodontic treatment with regular dental check-ups for optimal oral health.
Summary: Orthodontics in Korea is a safe, effective, and advanced branch of dentistry focused on improving oral function, aesthetics, and long-term dental health. With modern appliances, expert care, and patient compliance, orthodontic treatment helps individuals achieve a healthy, attractive smile while enhancing functional bite and overall well-being.