What it is
Lung cancer screening is a preventive medical process used to detect lung cancer at an early stage, before symptoms appear. Early detection increases the likelihood of successful treatment and improved survival rates.
Key points:
- Involves imaging tests, most commonly low-dose computed tomography (LDCT).
- Targets high-risk individuals, such as long-term smokers or those with a family history of lung cancer.
- Helps identify small nodules or tumors that may not cause symptoms.
- Can lead to earlier intervention and better outcomes compared to symptom-based diagnosis.
Why it’s done
Lung cancer screening is recommended for individuals at higher risk to:
- Detect cancer early: Early-stage lung cancer can be treated more effectively.
- Reduce mortality risk: Screening has been shown to lower lung cancer death rates in high-risk populations.
- Identify other lung conditions: Such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or infections.
- Guide lifestyle changes: Encourages smoking cessation and regular medical follow-up.
Note: Screening is most beneficial for adults aged 50–80 with significant smoking history or other risk factors.
Alternatives
Other approaches to lung health monitoring include:
- Chest X-rays: Less sensitive than LDCT for early-stage cancer.
- Sputum cytology: Examines mucus for abnormal cells; less commonly used.
- Regular clinical check-ups: Physical examination and discussion of respiratory symptoms.
- Smoking cessation programs: Reduce future risk but do not replace imaging screening.
Important: Low-dose CT is currently the most effective and recommended screening method for high-risk individuals.
Preparation
Preparation for lung cancer screening is generally straightforward:
- Medical history: Provide information about smoking history, family history, and prior lung conditions.
- Clothing: Wear comfortable, metal-free clothing for easy scanning.
- Fasting: Not required for standard low-dose CT scans.
- Avoid jewelry or metal objects: Remove items that may interfere with imaging.
- Inform staff of pregnancy: Although unlikely, pregnant women should avoid CT scans unless essential.
Patient instructions:
- Arrive on time for the scheduled scan.
- Bring previous imaging results if available.
- Follow any instructions given by the radiology staff.
How it’s done
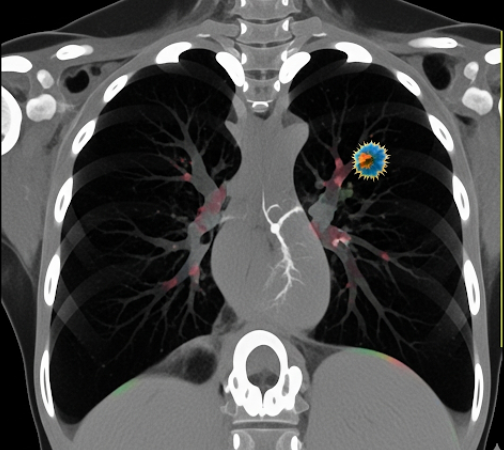
The screening process typically involves low-dose CT scanning:
- Positioning: Patient lies on the CT table.
- Scanning: A low-dose X-ray CT scan is performed, taking images of the lungs in thin slices.
- Duration: The scan usually takes 5–10 minutes.
- Image analysis: Radiologists examine the images for nodules, masses, or other abnormalities.
- Follow-up: If abnormalities are detected, further tests such as biopsy, PET scans, or repeat imaging may be recommended.
Note: The radiation dose in low-dose CT is significantly lower than conventional CT scans, minimizing risk.
Recovery / Post-Screening Considerations
Lung cancer screening is non-invasive with minimal recovery required:
- Patients can resume normal activities immediately.
- Mild anxiety may occur while waiting for results.
- Follow-up tests may be required if nodules are detected.
- Lifestyle advice, including smoking cessation and regular check-ups, is provided.
Benefits:
- Early detection of lung cancer and other lung abnormalities.
- Enables timely treatment and improved prognosis.
- Supports preventive healthcare and long-term lung health.
Complications / Risks
Screening is generally safe, but potential risks include:
- Radiation exposure: Minimal with low-dose CT but cumulative exposure may be considered.
- False positives: May lead to unnecessary follow-up tests or procedures.
- False negatives: Rare; small tumors may be missed.
- Anxiety or stress: Waiting for results can cause temporary psychological distress.
Prevention / Mitigation:
- Performed according to international guidelines for high-risk patients.
- Radiologists follow strict protocols to minimize unnecessary radiation.
- Counseling is provided to explain results and next steps.
Treatment Options in Korea
Lung cancer screening is widely available in Korean hospitals and specialized diagnostic centers:
Key features:
- Low-dose CT scans performed in advanced radiology departments.
- Screening programs target high-risk populations, including long-term smokers and individuals with family history.
- Experienced radiologists provide accurate interpretation and follow-up guidance.
- Facilities offer comprehensive follow-up care, including biopsies, PET-CT, or early-stage surgical interventions if needed.
- Promotes preventive care and improved lung cancer outcomes through early detection.
Summary: Lung cancer screening in Korea is a safe, effective, and preventive healthcare strategy. With early detection using low-dose CT scans and expert follow-up care, patients can benefit from improved treatment outcomes, reduced mortality, and enhanced long-term lung health.