What it is
A lumbar puncture, also known as a spinal tap, is a medical procedure in which a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is collected from the spinal canal in the lower back. This fluid surrounds the brain and spinal cord, providing protection and carrying nutrients.
Key points:
- Helps diagnose infections, bleeding, and neurological disorders.
- Can measure CSF pressure and analyze its contents.
- Sometimes used for therapeutic purposes, such as injecting medications (chemotherapy or anesthetics) directly into the spinal canal.
- Minimally invasive but requires trained medical professionals for safety.
Why it’s done
Lumbar puncture is performed for:
- Diagnosing infections: Meningitis, encephalitis, or other central nervous system infections.
- Detecting bleeding: Subarachnoid hemorrhage or trauma-related bleeding.
- Neurological disorders: Multiple sclerosis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, or certain cancers.
- Measuring CSF pressure: To detect conditions like hydrocephalus or idiopathic intracranial hypertension.
- Administering medications: Intrathecal chemotherapy, antibiotics, or anesthesia.
Note: It is both a diagnostic and therapeutic tool, depending on the patient’s condition.
Alternatives
Alternatives or complementary diagnostic methods include:
- MRI or CT scans: To visualize brain or spinal abnormalities.
- Blood tests: May provide indirect evidence of infection or disease.
- Nerve conduction studies: For certain neurological disorders.
- Non-invasive intracranial pressure monitoring: For evaluating CSF pressure.
Important: While imaging can show structural problems, lumbar puncture provides direct chemical and cellular analysis of CSF, which is essential for accurate diagnosis.
Preparation
Preparation ensures safety and reduces complications:
- Medical history review: Assess bleeding disorders, medications (e.g., anticoagulants), or previous back surgeries.
- Fasting: Usually not required, unless sedation is planned.
- Consent: Discuss procedure, risks, benefits, and post-procedure expectations.
- Positioning: Patient may lie on their side or sit leaning forward to open the spaces between vertebrae.
- Allergy check: Verify no allergy to local anesthetic agents.
Patient instructions:
- Wear loose clothing for easy access to the lower back.
- Stay still during the procedure to avoid needle-related injury.
- Report history of bleeding or neurological symptoms beforehand.
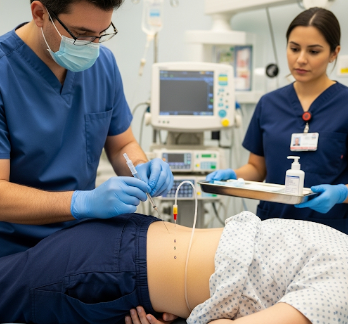
How it’s done
Lumbar puncture is performed by a trained physician in a sterile setting:
- Positioning: Patient lies on their side with knees pulled to the chest, or sits leaning forward.
- Cleaning and anesthesia: Area is disinfected, and local anesthetic is applied.
- Needle insertion: A thin spinal needle is inserted between lumbar vertebrae (usually L3-L4 or L4-L5) into the spinal canal.
- CSF collection: Cerebrospinal fluid is collected in sterile tubes for laboratory analysis.
- Needle removal and dressing: Needle is withdrawn, and a sterile dressing is applied.
Duration: Typically 15–30 minutes, including preparation and recovery.
Recovery / Post-Procedure Considerations
Recovery after a lumbar puncture is usually straightforward:
- Rest: Patients may be advised to lie flat for 1–2 hours to reduce the risk of headache.
- Hydration: Drinking fluids may help replace lost CSF and prevent headaches.
- Pain management: Mild back pain or soreness may occur at the puncture site.
- Activity: Normal activities can usually resume within 24 hours, avoiding strenuous exercise for a day or two.
- Follow-up: Results may take hours to days, depending on the tests ordered.
Benefits:
- Provides critical diagnostic information for infections, neurological disorders, and bleeding.
- Enables direct medication delivery into the CSF for therapeutic purposes.
- Helps guide treatment plans and prognosis.
Complications / Risks
Lumbar puncture is generally safe but may include:
- Post-lumbar puncture headache: Most common; usually resolves with rest, hydration, or caffeine.
- Back pain or stiffness: Mild and temporary.
- Bleeding or hematoma: Rare, more likely in patients on blood thinners.
- Infection: Rare; sterile technique minimizes risk.
- Nerve injury: Very rare; may cause temporary numbness or tingling.
- CSF leakage: Extremely rare, sometimes requiring medical intervention.
Prevention:
- Performed by experienced clinicians using proper sterile techniques.
- Monitor patients for headaches, numbness, or fever post-procedure.
- Follow all post-procedure instructions carefully.
Treatment Options in Korea
Lumbar puncture is widely available in hospitals, neurology centers, and specialized diagnostic facilities across Korea:
Key features:
- Conducted by experienced neurologists, anesthesiologists, or trained physicians.
- Sterile technique and modern equipment ensure patient safety and accurate sample collection.
- Used for diagnosis, monitoring, and intrathecal treatments.
- Follow-up care includes post-procedure observation and laboratory interpretation.
- Suitable for patients of all ages requiring neurological assessment or treatment.
Summary: Lumbar puncture in Korea is a safe and essential diagnostic and therapeutic procedure. It provides critical information about the central nervous system, guides treatment decisions, and, when indicated, delivers medications directly into the spinal canal for effective therapy.