What it is
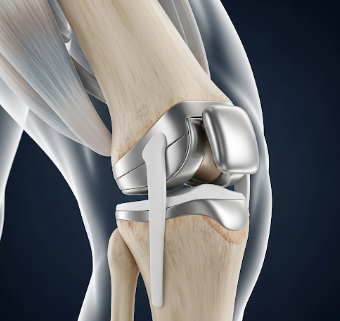
Knee replacement, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which a damaged or worn-out knee joint is replaced with an artificial joint (prosthesis). This surgery is typically performed to relieve pain, restore function, and improve mobility in patients with severe knee joint conditions.
Key points:
- Can be total or partial knee replacement depending on the extent of damage.
- The artificial joint is usually made of metal alloys, high-grade plastics, or ceramics.
- Commonly recommended for patients with osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or traumatic knee injury.
- Improves quality of life and daily activities by reducing pain and restoring joint function.
Why it’s done
Knee replacement is performed to address:
- Severe knee pain or stiffness: That limits daily activities like walking, climbing stairs, or standing.
- Osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis: Where cartilage degeneration causes joint pain and deformity.
- Post-traumatic damage: Following fractures or injuries that compromise knee function.
- Failed conservative treatments: When medications, physical therapy, or injections no longer relieve pain.
- Deformities: Correct misalignment such as bow legs or knock knees.
Note: Surgery is usually considered when non-surgical treatments have been ineffective and pain significantly impacts life.
Alternatives
Other options before considering surgery include:
- Physical therapy: Strengthening muscles around the knee to improve function.
- Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, or corticosteroid injections.
- Weight management: Reducing stress on the knee joint.
- Assistive devices: Braces, walking aids, or orthotics to support mobility.
- Hyaluronic acid injections: To improve joint lubrication and reduce pain.
Important: These alternatives manage symptoms but cannot repair severe joint damage. Knee replacement is the definitive solution for end-stage arthritis or joint destruction.
Preparation
Proper preparation improves surgical outcomes and recovery:
- Medical evaluation: Blood tests, ECG, X-rays, MRI, and anesthesia assessment.
- Medication review: Adjust or stop blood thinners or other medications as advised.
- Physical preparation: Preoperative exercises may strengthen leg muscles.
- Informed consent: Discuss risks, benefits, prosthesis type, and postoperative expectations.
- Lifestyle preparation: Arrange for postoperative support at home and temporary mobility aids.
Patient instructions:
- Shower before surgery using antiseptic soap.
- Avoid eating or drinking for 6–8 hours before surgery.
- Wear comfortable clothing and leave valuables at home.
How it’s done
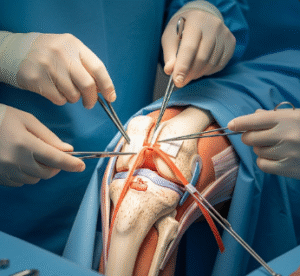
Knee replacement is performed under general or regional anesthesia and involves several steps:
- Incision: Surgeon makes an incision over the knee to expose the joint.
- Bone preparation: Damaged cartilage and bone are removed from the femur, tibia, and sometimes the patella.
- Prosthesis placement: The artificial components are fitted onto the prepared bones.
- Alignment and fixation: Components are aligned for optimal function and secured with cemented or cementless techniques.
- Closure: Incision is closed with sutures or staples, and a sterile dressing is applied.
Duration: Usually 1–2 hours, depending on complexity and whether it’s a total or partial replacement.
Recovery
Recovery after knee replacement involves:
- Hospital stay: Typically 2–5 days with monitoring for pain, swelling, and mobility.
- Pain management: Medications and cold therapy help control postoperative pain.
- Physical therapy: Begins within 24 hours after surgery to regain movement and strength.
- Mobility aids: Walking aids like crutches or walkers are used initially.
- Full recovery: Most patients regain functional mobility in 3–6 months, while some activities may take longer.
Benefits of recovery:
- Significant pain relief and improved joint function.
- Restoration of daily activity and quality of life.
- Reduced reliance on pain medications and mobility aids.
Complications / Risks
Knee replacement is generally safe but may include:
- Infection: Rare but serious; may require antibiotics or revision surgery.
- Blood clots: Risk of deep vein thrombosis; preventive measures include blood thinners and early mobilization.
- Prosthesis problems: Loosening, wear, or misalignment over time.
- Nerve or blood vessel injury: Rare but possible.
- Persistent pain or stiffness: Some patients experience lingering discomfort.
Prevention:
- Surgery performed by an experienced orthopedic surgeon.
- Follow rehabilitation and physiotherapy protocols carefully.
- Monitor for signs of infection or abnormal swelling.
Treatment Options in Korea
Knee replacement is widely available in Korean hospitals and orthopedic centers:
Key features:
- Hospitals offer state-of-the-art operating rooms and prosthetic options.
- Both total and partial knee replacement are available depending on patient needs.
- Rehabilitation programs include physiotherapy, occupational therapy, and pain management.
- Experienced orthopedic surgeons follow international guidelines for preoperative planning, surgery, and postoperative care.
- Suitable for patients seeking advanced surgical techniques, rapid recovery, and long-term mobility improvement.
Summary: Knee replacement in Korea is a safe and effective treatment for severe knee pain and joint dysfunction. With skilled surgeons, advanced prosthetics, and comprehensive rehabilitation, patients can regain mobility, reduce pain, and improve overall quality of life.