What it is
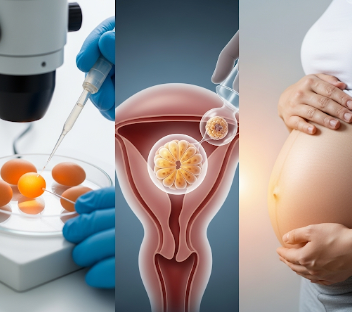
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is an assisted reproductive technology (ART) in which eggs are retrieved from a woman’s ovaries and fertilized with sperm in a laboratory. The resulting embryos are then transferred into the woman’s uterus to achieve pregnancy.
Key points:
- Often referred to as “test-tube baby” technology.
- Suitable for couples with fertility challenges such as blocked fallopian tubes, male infertility, or unexplained infertility.
- IVF can involve fresh or frozen embryos.
- May be combined with additional techniques such as ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm injection) or PGD (preimplantation genetic diagnosis).
Why it’s done
IVF is recommended for:
- Blocked or damaged fallopian tubes: Prevents natural fertilization.
- Male infertility: Low sperm count or poor sperm motility; often combined with ICSI.
- Ovulation disorders: Women who do not ovulate regularly or respond poorly to fertility medications.
- Unexplained infertility: When standard fertility evaluation does not reveal a cause.
- Genetic disorders: Couples at risk of passing on inherited diseases; IVF allows for genetic testing of embryos.
- Previous failed fertility treatments: When other assisted reproductive methods are unsuccessful.
Note: IVF is considered when other less invasive fertility treatments have failed or are unsuitable.
Alternatives
Other options for fertility management include:
- Timed intercourse: Natural conception with ovulation monitoring.
- Ovulation induction: Use of medications to stimulate egg release.
- Intrauterine insemination (IUI): Placement of sperm directly into the uterus.
- Donor eggs or sperm: For individuals or couples with reproductive challenges.
- Surrogacy: In cases where the uterus cannot carry a pregnancy.
Important: IVF is more invasive and costly than IUI or ovulation induction but offers higher success rates in specific infertility scenarios.
Preparation
Successful IVF requires careful preparation:
- Fertility evaluation: Blood tests, ultrasound, and semen analysis for both partners.
- Ovarian stimulation: Medications are prescribed to produce multiple mature eggs.
- Monitoring: Frequent ultrasound scans and hormone checks during stimulation.
- Sperm preparation: Collection and analysis to select high-quality sperm for fertilization.
- Informed consent: Discuss procedure, risks, success rates, costs, and emotional considerations.
Patient instructions:
- Abstain from sexual intercourse or alcohol during stimulation if advised.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle, balanced diet, and moderate exercise.
- Follow medication schedules strictly for optimal results.
How it’s done
IVF involves multiple sequential steps:
- Ovarian stimulation: Fertility drugs stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs.
- Egg retrieval: Eggs are collected using a transvaginal ultrasound-guided needle under sedation.
- Sperm collection: Sperm is collected from the partner or donor.
- Fertilization: Eggs and sperm are combined in a lab (or via ICSI) to create embryos.
- Embryo culture: Embryos are monitored for growth and quality over 3–5 days.
- Embryo transfer: One or more embryos are placed into the uterus using a thin catheter.
- Pregnancy testing: A blood test is conducted 10–14 days after transfer to confirm implantation.
Duration: Each IVF cycle typically lasts 4–6 weeks from ovarian stimulation to embryo transfer.
Recovery / Post-Procedure Considerations
Recovery after IVF is usually straightforward:
- Activity: Light rest after egg retrieval; resume normal activities after a few days.
- Medication adherence: Hormonal support (progesterone) may continue until pregnancy is confirmed.
- Pregnancy monitoring: Blood tests and early ultrasounds track embryo implantation and fetal development.
- Emotional support: Counseling or support groups may help manage stress or anxiety associated with IVF.
Benefits of successful IVF:
- Enables pregnancy for couples or individuals with fertility challenges.
- Offers options for genetic screening and family planning.
- Can use frozen embryos for future attempts, increasing long-term success.
Complications / Risks
IVF is generally safe but may include:
- Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS): Overreaction to fertility medications.
- Multiple pregnancy: Increased chance if multiple embryos are transferred.
- Procedure-related risks: Bleeding, infection, or discomfort during egg retrieval.
- Emotional stress: Anxiety, depression, or stress due to uncertainty or cycle failure.
- Ectopic pregnancy: Rare, when embryo implants outside the uterus.
Prevention:
- Regular monitoring during ovarian stimulation.
- Limit the number of embryos transferred.
- Follow medical instructions carefully and attend follow-ups.
Treatment Options in Korea
IVF is widely available in Korean fertility clinics and hospitals:
Key features:
- Performed in state-of-the-art reproductive centers with advanced technology.
- Supports fresh and frozen embryo cycles, ICSI, donor eggs/sperm, and genetic testing.
- Experienced fertility specialists guide personalized protocols for each patient.
- Psychological counseling and support services are offered throughout treatment.
- Success rates in Korea are comparable to international standards, benefiting from advanced laboratory facilities and clinical expertise.
Summary: IVF in Korea is a safe, highly effective assisted reproductive technology that provides hope for individuals and couples facing infertility. With modern protocols, experienced specialists, and comprehensive support, IVF offers the opportunity to achieve pregnancy even in complex fertility scenarios.