What it is
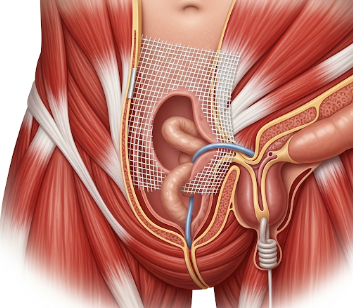
Inguinal hernia repair is a surgical procedure to correct an inguinal hernia, where part of the intestine or abdominal tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the lower abdominal wall, usually in the groin area. The surgery strengthens the abdominal wall and prevents complications such as obstruction or strangulation.
Key points:
- Most common type of hernia in men.
- Can be open or minimally invasive (laparoscopic).
- May use synthetic mesh to reinforce the abdominal wall.
- Performed to relieve pain, discomfort, and risk of complications.
Why it’s done
Inguinal hernia repair is recommended for:
- Pain or discomfort: Especially when bending, lifting, or coughing.
- Growing hernia: Enlargement over time may increase risk.
- Complications: Strangulation or obstruction of intestine requires urgent repair.
- Prevent future problems: Reduce the likelihood of chronic pain, bowel obstruction, or tissue damage.
Note: Even asymptomatic hernias are often repaired to prevent sudden complications.
Alternatives
Non-surgical options or temporary measures include:
- Watchful waiting: For small, asymptomatic hernias, with regular monitoring.
- Hernia truss or belt: Provides support but does not fix the underlying defect.
- Lifestyle modifications: Avoid heavy lifting, maintain healthy weight, and strengthen core muscles.
Important: Surgery is the definitive treatment. Non-surgical approaches only manage symptoms temporarily.
Preparation
Proper preparation ensures safe surgery and smooth recovery:
- Medical evaluation: Blood tests, ECG, imaging if necessary.
- Medication review: Stop blood thinners or adjust medications as advised.
- Fasting: Usually required for several hours before surgery.
- Informed consent: Discuss risks, benefits, surgical options, and recovery expectations.
- Preoperative hygiene: Shower and follow any hospital instructions.
Patient instructions:
- Arrange for postoperative transportation.
- Plan for time off work and limited physical activity.
- Wear comfortable clothing on the day of surgery.
How it’s done
Inguinal hernia repair can be performed using several approaches:
1. Open repair:
- Incision in the groin area.
- Herniated tissue is pushed back into the abdomen.
- Mesh reinforcement may be placed to strengthen the abdominal wall.
- Closed with sutures or staples.
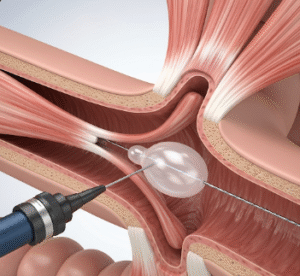
2. Laparoscopic repair:
- Several small abdominal incisions are made.
- A laparoscope and instruments are inserted to repair the hernia with mesh.
- Less postoperative pain and quicker recovery compared to open repair.
Anesthesia:
- General or regional anesthesia is used depending on approach and patient factors.
Duration:
- Open repair: ~30–60 minutes
- Laparoscopic repair: ~45–90 minutes
Recovery
Recovery depends on surgical method and individual health:
- Hospital stay: Often outpatient or 1-day admission.
- Initial recovery: Mild pain or swelling in the groin area; managed with pain medication.
- Activity: Light activity after a few days; avoid heavy lifting for 4–6 weeks.
- Follow-up: Doctor evaluates healing, suture removal if needed, and check for recurrence.
Benefits of recovery:
- Relief from pain and discomfort.
- Reduced risk of hernia complications.
- Improved mobility and quality of life.
Complications
Inguinal hernia repair is generally safe, but potential risks include:
- Infection: At incision or around the mesh.
- Recurrence: Hernia may return in rare cases.
- Chronic pain: Sometimes occurs due to nerve irritation.
- Bleeding or hematoma: Rare but possible.
- Anesthesia-related risks: Reactions to medications or sedation.
Prevention:
- Choose a qualified surgeon and accredited hospital.
- Follow postoperative instructions carefully.
- Monitor for signs of infection, severe pain, or swelling and seek prompt care.
Treatment Options in Korea
Inguinal hernia repair is widely available in Korea in both public and private healthcare settings:
Key features:
- Performed in general hospitals, surgical centers, and specialized hernia clinics.
- Both open and laparoscopic techniques are offered.
- Korean surgeons follow international guidelines for mesh use, anesthesia, and postoperative care.
- Minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery is commonly used for faster recovery and reduced pain.
- Postoperative care includes pain management, follow-up monitoring, and guidance on activity resumption.
Summary: Inguinal hernia repair in Korea is a safe and effective treatment for hernia-related discomfort, risk prevention, and improved quality of life. With skilled surgeons, modern techniques, and proper postoperative care, patients can return to normal activity quickly and safely.