What it is
Testicular self-examination (TSE) is a method of checking your own testicles for unusual lumps, swelling, or changes that could indicate conditions such as testicular cancer, infections, or cysts. Regular self-exams help men become familiar with the normal size, shape, and texture of their testicles, which allows for early detection of potential problems.
Key points:
- Non-invasive and can be performed at home.
- Recommended for all males, particularly between ages 15–45, when the risk of testicular cancer is highest.
- Complements clinical exams and imaging but does not replace professional evaluation.
- Encourages awareness of testicular health and prompt medical consultation if abnormalities are found.
Why it’s done
Testicular self-examination is performed for several reasons:
- Early detection of abnormalities: Enables timely identification of lumps, swelling, or hardening that may indicate cancer or other conditions.
- Awareness of normal anatomy: Helps individuals distinguish normal variations from unusual changes.
- Preventive health: Encourages proactive monitoring of reproductive and overall health.
- Support for clinical care: Findings provide valuable information to healthcare providers during routine check-ups.
Note: While TSE is valuable, it is not a substitute for clinical evaluation or imaging if changes are detected.
Alternatives
Other methods for monitoring testicular health include:
- Clinical testicular examination: Performed by a physician during routine health check-ups.
- Ultrasound imaging: Used for detailed evaluation of lumps or swelling.
- Blood tests: Measure tumor markers if cancer is suspected.
- Genetic or family risk assessment: For individuals with family history of testicular cancer.
Important: Combining TSE with professional screenings improves early detection and overall safety.
Preparation
Before performing a self-check, preparation ensures accuracy and comfort:
- Choose the right time: After a warm bath or shower, when the scrotal skin is relaxed.
- Environment: Ensure a private, comfortable space with good lighting.
- Understand normal anatomy: Know the size, shape, and texture of each testicle.
- Optional aids: Use a mirror for better visualization if needed.
Patient instructions:
- Stand in a relaxed position.
- Examine each testicle separately, noting any differences in size or consistency.
- Record findings if desired to track changes over time.
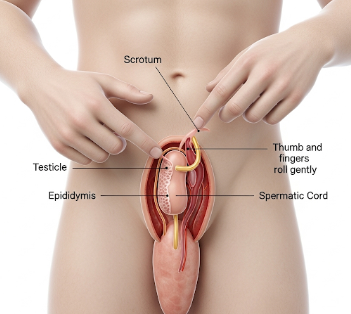
How it’s done
Testicular self-examination involves gentle palpation and inspection:
1. Inspection:
- Stand in front of a mirror and look for swelling, redness, or visible lumps.
- Check for asymmetry or changes in scrotal skin.
2. Manual Palpation:
- Use both hands, placing the index and middle fingers under the testicle and the thumbs on top.
- Gently roll the testicle between fingers, feeling for:
- Lumps or nodules
- Areas of firmness or irregularity
- Enlargement or swelling
- Repeat for the other testicle.
- Remember: it is normal for one testicle to be slightly larger or hang lower.
3. Epididymis check:
- The soft, coiled tube at the back of each testicle is normal and should not be confused with lumps.
Frequency:
- Monthly self-exams are recommended to maintain familiarity with normal anatomy.
Recovery and Benefits
Although TSE is not a treatment, the benefits include:
- Early awareness: Detects potential problems like testicular cancer at an earlier, more treatable stage.
- Empowerment: Encourages men to take responsibility for their reproductive health.
- Support for clinical care: Provides valuable information for physicians during exams.
- Peace of mind: Regular checks reassure men when no changes are present.
Tip: Any unusual findings should prompt timely consultation with a healthcare provider.
Complications
Testicular self-examination is safe, but some considerations include:
- False reassurance: Normal self-exams do not guarantee absence of disease.
- Anxiety: Discovering a lump can cause worry; professional evaluation is essential.
- Improper technique: May miss small or deep lumps if not performed correctly.
Prevention:
- Learn proper technique from a qualified healthcare provider.
- Combine TSE with regular clinical exams and imaging if indicated.
- Seek immediate medical attention for any new, persistent, or painful lumps.
Treatment Options in Korea
In Korea, testicular health monitoring is supported by public and private healthcare systems:
Key features:
- Clinical examinations are available in hospitals, urology clinics, and men’s health centers.
- Ultrasound and tumor marker testing are readily accessible if abnormalities are detected.
- Educational programs raise awareness about testicular self-exams and cancer prevention.
- Home self-examination is encouraged as a complementary preventive measure alongside professional screening.
- Korean hospitals follow international guidelines for early detection, diagnosis, and treatment of testicular conditions.
Summary: Learning how to check your testicles empowers men to detect changes early, supports preventive care, and complements professional screenings. Proper technique, monthly monitoring, and timely consultation with healthcare providers ensure optimal testicular health and early intervention if abnormalities arise.