What it is
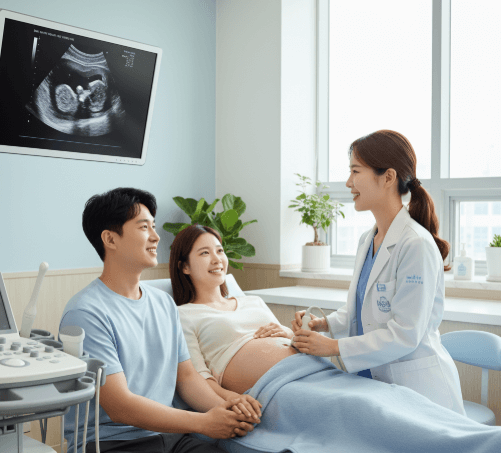
Prenatal check-ups are regular medical visits that expectant mothers attend throughout pregnancy. These visits allow doctors to monitor the health of both the mother and the baby while also detecting potential complications early.
👩⚕️ Key aspects of prenatal check-ups:
- 🩺 Physical examinations – checking blood pressure, weight, and overall health
- 🧪 Laboratory tests – blood, urine, and genetic screenings
- 🖥️ Ultrasounds – monitoring fetal growth and development
- 💬 Counseling – guidance on nutrition, lifestyle, and emotional well-being
Prenatal care in Korea is highly structured, often following strict schedules recommended by the Korean Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Why it’s done
The primary purpose of prenatal check-ups is to ensure a safe pregnancy and delivery.
🔹 Benefits of regular prenatal visits:
➡️ Early detection of complications such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, or anemia
➡️ Monitoring fetal growth to ensure healthy development
➡️ Guidance for mothers on safe diet, exercise, and mental health support
➡️ Reduced risk of preterm birth through preventive care
➡️ Building trust with healthcare providers for a smoother delivery experience
In Korea, prenatal care is also tied to government health programs, ensuring that mothers receive standardized and affordable services.
Alternatives
While prenatal check-ups are considered essential, some women explore alternative or complementary approaches.
🔸 Alternatives or complements include:
- 🌿 Midwife-led care – especially for low-risk pregnancies
- 🧘 Natural or holistic approaches – yoga, meditation, and herbal support (with doctor approval)
- 🌍 Telemedicine consultations – growing in popularity, particularly for women in rural areas
- 👩👩👧 Doula support – offering emotional and practical care throughout pregnancy
⚠️ Important note: Alternatives should not replace professional prenatal check-ups, especially in Korea where hospital-based care is strongly recommended.
Preparation
Preparing for prenatal check-ups ensures that mothers get the most out of each visit.
✔️ Steps to prepare:
➡️ Keep a record of symptoms (morning sickness, unusual pain, mood changes)
➡️ Write down questions for the doctor (about diet, exercise, medications)
➡️ Carry medical documents (previous reports, test results, vaccination history)
➡️ Bring your partner or family member for emotional support
➡️ Make sure to fast or adjust diet if certain blood tests are scheduled
In Korea, many hospitals provide digital pregnancy apps that track appointments, weight, and baby growth, helping mothers stay organized.
How it’s done
Prenatal check-ups in Korea follow a standard schedule, typically once a month until 28 weeks, twice a month until 36 weeks, and weekly after 36 weeks.
🩺 Typical check-up procedure includes:
- ✅ Vital signs check – blood pressure, weight, heart rate
- ✅ Urine and blood tests – to check for infections, anemia, or gestational diabetes
- ✅ Ultrasound scans – to observe fetal growth, placenta position, and amniotic fluid levels
- ✅ Physical examination – checking uterus size and baby’s heartbeat
- ✅ Vaccinations and supplements – iron, folic acid, and recommended shots
- ✅ Discussion of birth plan – delivery options, pain relief methods, and hospital arrangements
💡 Unique aspect in Korea: Many hospitals offer 3D/4D ultrasound imaging, allowing parents to see clear images of their baby. Some clinics also provide video recordings as keepsakes.
Recovery
Recovery in the context of prenatal care refers to managing health after each check-up and adapting to new advice from the doctor.
🟢 Tips for smooth recovery between visits:
- 🥗 Follow nutrition guidelines (iron-rich foods, folic acid, calcium)
- 💤 Rest adequately – Korean doctors often emphasize balanced rest and moderate exercise
- 💊 Take prescribed supplements regularly
- 📖 Attend prenatal classes offered in many Korean hospitals
- 💬 Communicate concerns quickly if new symptoms arise (e.g., severe swelling, bleeding, or reduced fetal movement)
In Korea, many women also join postnatal preparation programs during late pregnancy, which help with recovery planning after birth.
Treatment options in Korea
South Korea is known for its world-class maternal healthcare system. Expectant mothers have access to advanced technology, skilled doctors, and supportive programs.
🇰🇷 Key treatment options for prenatal check-ups in Korea:
➡️ Public hospitals – affordable and government-supported prenatal packages
➡️ Private clinics – more personalized care, shorter wait times, and luxury facilities
➡️ University hospitals – ideal for high-risk pregnancies with specialized care
➡️ Maternity centers – offering combined prenatal, delivery, and postnatal care
🌟 Highlights of prenatal care in Korea:
- ✅ Government subsidies: The National Health Insurance Service provides financial support for prenatal visits
- ✅ Comprehensive check-up packages: From routine blood work to advanced genetic testing
- ✅ High safety standards: Low maternal and infant mortality rates compared to global averages
- ✅ Multilingual services: Many hospitals in Seoul and major cities cater to international patients
- ✅ Holistic care: Including prenatal yoga, mental health counseling, and diet consultations
✅ Final Note:
Prenatal check-ups in Korea are more than routine doctor visits—they are a comprehensive support system ensuring the health, safety, and comfort of both mother and baby. With advanced medical technology, structured schedules, and supportive government programs, Korea stands out as a top destination for expectant mothers seeking reliable and high-quality care.