What it is
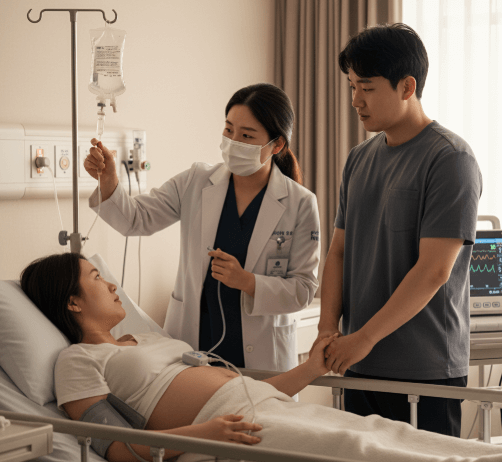
Labor induction is the process of stimulating uterine contractions before spontaneous labor begins, with the goal of achieving a vaginal birth. It is done when continuing the pregnancy poses risks to the mother or the baby, or when medical conditions require delivery at a certain time.
In Korea, labor induction is performed in advanced hospitals and maternity centers with modern monitoring equipment and skilled medical teams. The procedure can involve medications, mechanical methods, or a combination of both.
➡️ Key aspects of labor induction:
- Medications such as oxytocin or prostaglandins to stimulate contractions
- Mechanical methods like membrane sweeping or balloon catheters
- Close monitoring of both the mother and fetus throughout the process
- Goal: safe vaginal delivery without unnecessary complications
Why it’s done
Labor induction is recommended for several medical and non-medical reasons, always based on the health of the mother and baby.
✔️ Medical reasons:
- Pregnancy going beyond 41–42 weeks (post-term pregnancy)
- High blood pressure or preeclampsia in the mother
- Gestational diabetes requiring earlier delivery
- Premature rupture of membranes (water breaking without contractions)
- Concerns about fetal growth restriction or reduced amniotic fluid
✔️ Non-medical or elective reasons:
- Maternal request for convenience or anxiety about overdue pregnancy
- Distance from hospital, ensuring safe timing for delivery
✔️ Benefits of induction:
- Prevents stillbirth in overdue pregnancies
- Reduces risks associated with pregnancy-related complications
- Provides better control over timing of delivery in high-risk cases
Alternatives
Not every situation requires labor induction. Alternatives may be considered if mother and baby are stable.
🔹 Expectant management (watchful waiting):
- Allowing labor to begin naturally while carefully monitoring the baby’s well-being
- Frequent ultrasounds, non-stress tests (NST), and check-ups
🔹 Elective Cesarean Section (C-section):
- Considered if induction fails or if vaginal delivery is unsafe
- Useful in cases of placenta previa, abnormal fetal position, or multiple prior C-sections
🔹 Natural methods (less proven):
- Walking, nipple stimulation, or herbal teas sometimes believed to trigger contractions
- These are not medically reliable and are usually only considered complementary options
Preparation
Before induction, thorough preparation ensures safety and effectiveness.
➡️ Medical preparation:
- Cervical assessment using the Bishop score (evaluates dilation, effacement, consistency, and position of cervix)
- Maternal health evaluation for blood pressure, blood sugar, and overall condition
- Fetal monitoring through ultrasound and heart rate checks
➡️ Personal preparation:
- Packing hospital essentials (comfortable clothing, baby supplies, documents)
- Discussing pain management preferences (epidural, breathing techniques, natural support)
- Reviewing possible scenarios with the doctor, including the chance of cesarean section if induction fails
➡️ Mental preparation:
- Attending childbirth education sessions
- Understanding the step-by-step induction process to reduce anxiety
- Preparing emotionally for a potentially longer labor compared to spontaneous onset
How it’s done
Labor induction in Korea follows internationally recognized medical protocols, with individual customization depending on the patient’s condition.
✔️ Step 1 – Cervical ripening
- Prostaglandin medications (inserted vaginally) soften and dilate the cervix
- Mechanical methods like balloon catheters may be used to open the cervix gradually
✔️ Step 2 – Stimulating contractions
- Oxytocin (Pitocin) administered through an IV drip to strengthen contractions
- Dosage carefully adjusted to avoid overstimulation
✔️ Step 3 – Breaking the water (Amniotomy)
- Artificial rupture of membranes may be performed to enhance contractions
- Used only when the cervix is favorable and the baby’s head is well-engaged
✔️ Step 4 – Monitoring progress
- Continuous fetal heart rate monitoring
- Regular vaginal exams to assess dilation and descent of the baby
- Adjustments in medication or interventions based on progress
✔️ Step 5 – Delivery
- If induction is successful, labor continues to vaginal delivery
- If complications arise (fetal distress, stalled labor), cesarean section may be required
Recovery
Recovery after labor induction is similar to recovery from spontaneous vaginal delivery, but labor may feel more intense because contractions can start suddenly and strongly.
➡️ Immediate recovery:
- Fatigue due to longer or stronger contractions
- Possible soreness if mechanical devices were used
- Vaginal bleeding and uterine cramping for several days
➡️ Physical recovery:
- Return to normal activities in a few weeks
- Perineal care if there were tears or episiotomy
- Monitoring for signs of infection or heavy bleeding
➡️ Emotional recovery:
- Some mothers may feel disappointed if induction leads to a C-section
- Support from family and postpartum care centers can ease the adjustment
- Counseling available in Korean maternity facilities if emotional stress occurs
➡️ Recommendations for recovery:
- Adequate rest, hydration, and balanced diet
- Gentle pelvic floor exercises once approved
- Regular postpartum check-ups to monitor healing
Treatment option in Korea
Korea offers highly advanced facilities and personalized care for labor induction, ensuring both safety and comfort.
✔️ Hospital facilities:
- Modern maternity wards with state-of-the-art monitoring equipment
- Private labor and delivery rooms with family-friendly support
- Emergency C-section readiness if induction fails
✔️ Expert medical care:
- Skilled obstetricians and midwives with experience in both natural and induced labor
- Pain management options including epidural anesthesia, nitrous oxide, and relaxation techniques
- Strict protocols to prevent complications like uterine overstimulation or fetal distress
✔️ Postpartum support:
- Access to Sanhujoriwon (postpartum care centers) offering recovery programs, nutrition, and mental health support
- Lactation consultants to help mothers start breastfeeding after induced labor
- Holistic approach combining medical care with traditional Korean postpartum practices
✔️ Highlight: In Korea, labor induction is handled with precision, safety, and holistic aftercare, making it a reliable choice for mothers who need timely delivery while maintaining a focus on comfort and recovery.