What it is
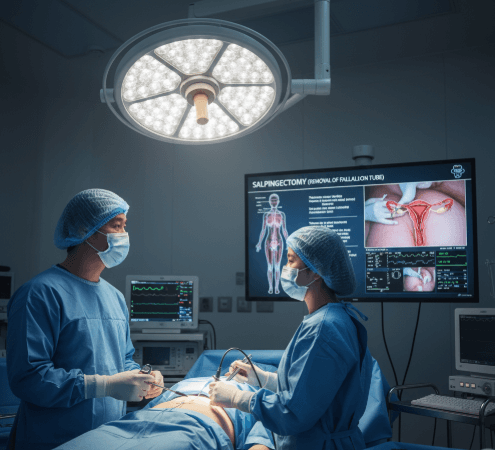
A salpingectomy is a surgical procedure to remove one or both fallopian tubes, the structures that connect the ovaries to the uterus. It may be performed alone or alongside other gynecological surgeries, depending on the condition.
In Korea, salpingectomy is commonly performed using laparoscopic and robotic-assisted techniques, which are minimally invasive and ensure quicker recovery. This procedure may be recommended for treating medical conditions, preventing disease, or as part of infertility treatment.
➡️ Key points about salpingectomy:
- Can be unilateral (one tube removed) or bilateral (both tubes removed)
- Preserves ovarian and uterine function unless removed for specific reasons
- May improve fertility chances in women with blocked or damaged tubes
Why it’s done
Salpingectomy is performed for several medical and preventive reasons.
✔️ Medical reasons include:
- Ectopic pregnancy: When a fertilized egg implants in the fallopian tube instead of the uterus
- Blocked or damaged fallopian tubes: Often caused by infections or pelvic inflammatory disease
- Hydrosalpinx: Fluid-filled tube interfering with fertility and IVF success rates
- Infections or abscesses causing chronic pain or complications
- Cancer prevention: Removal of fallopian tubes reduces ovarian cancer risk, especially in women with BRCA gene mutations
✔️ Benefits of salpingectomy:
- Prevents life-threatening complications of ectopic pregnancy
- Improves outcomes of assisted reproductive technologies (e.g., IVF)
- Reduces the risk of ovarian and fallopian tube cancers
- Relieves chronic pelvic pain and inflammation
Alternatives
Not every case requires a full salpingectomy. Depending on the condition, alternatives may be considered.
🔹 Salpingostomy (tube incision):
- Removes ectopic pregnancy while preserving the fallopian tube
- Not always effective for severely damaged tubes
🔹 Tuboplasty:
- Surgical repair of blocked fallopian tubes to restore fertility
- Less commonly performed due to lower success rates compared to IVF
🔹 Medication management:
- Methotrexate for early ectopic pregnancy (non-surgical option)
🔹 Watchful waiting:
- Small, asymptomatic conditions may only need monitoring with ultrasound
Preparation
Proper preparation helps ensure safety and better outcomes.
➡️ Medical preparation:
- Ultrasound or MRI to confirm diagnosis and assess tube condition
- Blood tests to check overall health and screen for infection
- Pregnancy test and hormone evaluations if related to fertility issues
- Preoperative consultation about fertility preservation options
➡️ Personal preparation:
- Fasting before surgery if general anesthesia will be used
- Packing hospital essentials (short stay of 1–3 days may be needed)
- Arranging family support during initial recovery
➡️ Mental preparation:
- Understanding fertility implications, especially if both tubes are removed
- Emotional readiness for the possibility of IVF as the only pregnancy option afterward
- Counseling sessions may be helpful for women anxious about surgery or fertility outcomes
How it’s done
Salpingectomy in Korea is usually performed using advanced minimally invasive approaches.
✔️ Surgical approaches:
➡️ Laparoscopic salpingectomy
- Small abdominal incisions made for inserting a camera and instruments
- Fallopian tube carefully removed with minimal disruption to surrounding organs
- Quick recovery and less scarring
➡️ Robotic-assisted salpingectomy
- Robotic arms controlled by the surgeon offer greater precision
- Recommended for complex cases or when cancer prevention is the goal
- Shorter recovery and minimal pain
➡️ Open abdominal salpingectomy
- Larger incision made in the abdomen
- Used for complicated cases such as widespread infection or large pelvic masses
- Longer recovery compared to laparoscopic methods
✔️ Step-by-step procedure:
- Anesthesia (general) administered
- Incisions made (laparoscopic/robotic) or one larger incision (open surgery)
- Fallopian tube detached from uterus and surrounding tissues
- Tube removed carefully to prevent damage to nearby organs
- Area checked for bleeding or infection risk
- Incisions closed with sutures or surgical glue
✔️ Duration:
- Typically 1–2 hours depending on complexity
- Hospital stay: same day or 1–3 days for laparoscopic/robotic, longer for open surgery
Recovery
Recovery varies depending on the surgical method but is generally fast with minimally invasive techniques.
➡️ Immediate recovery:
- Mild abdominal pain and fatigue after anesthesia
- Walking encouraged within hours to prevent blood clots
- Monitoring for infection, bleeding, or complications
➡️ Physical recovery:
- Return to light activities within 1–2 weeks for laparoscopic/robotic procedures
- 4–6 weeks for open abdominal surgery
- Avoid heavy lifting or strenuous activity until cleared by the doctor
➡️ Emotional recovery:
- Relief from pain or complications of damaged tubes
- Emotional adjustment if fertility is affected (especially bilateral removal)
- Counseling and fertility consultations available in Korean hospitals
➡️ Key recommendations:
- Adequate rest and balanced diet to aid healing
- Pain medication as prescribed
- Follow-up visits and imaging tests if necessary
- Consider fertility counseling and IVF planning if both tubes removed
Treatment option in Korea
Korea is a global leader in women’s health and fertility care, offering state-of-the-art salpingectomy procedures with excellent recovery support.
✔️ Hospital facilities:
- Equipped with advanced laparoscopic and robotic surgery systems
- Specialized fertility clinics for patients undergoing salpingectomy for infertility reasons
- Comprehensive cancer-prevention programs for high-risk women
✔️ Medical expertise:
- Skilled surgeons specializing in reproductive surgery and gynecologic oncology
- High success rates with minimal complications
- Personalized surgical approach based on fertility plans and medical conditions
✔️ Postoperative care:
- Close monitoring in modern recovery units
- Fertility counseling and IVF services for women who lose both fallopian tubes
- Access to integrative recovery care, including nutrition and traditional Korean therapies
✔️ Cultural aspect:
- Korean medical culture emphasizes fertility preservation whenever possible
- Families are often actively involved in supporting recovery and long-term health
➡️ Highlight: Salpingectomy in Korea combines advanced minimally invasive surgery, fertility-focused care, and holistic recovery support, making it one of the safest and most effective treatments for fallopian tube conditions worldwide.