What it is
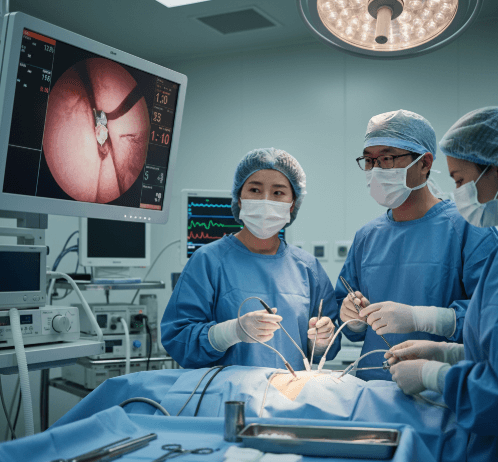
Pelvic laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that uses a thin, lighted instrument (laparoscope) inserted through small abdominal incisions to examine and treat conditions in the female pelvic organs, including the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and surrounding tissues.
In Korea, pelvic laparoscopy is widely performed in gynecology for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, offering shorter recovery times, minimal scarring, and highly precise surgical outcomes thanks to advanced laparoscopic and robotic-assisted technologies.
➡️ Key points about pelvic laparoscopy:
- Involves small incisions instead of large abdominal cuts
- Can be used to diagnose unexplained pelvic pain or infertility
- Also used to treat conditions like endometriosis, fibroids, cysts, or adhesions
Why it’s done
Pelvic laparoscopy is performed for both diagnosis and treatment of gynecological conditions.
✔️ Diagnostic reasons:
- Investigation of chronic pelvic pain
- Evaluation of infertility when imaging results are inconclusive
- Checking for endometriosis, adhesions, or pelvic masses
✔️ Therapeutic reasons:
- Removal of ovarian cysts, fibroids, or polyps
- Treatment of endometriosis and pelvic adhesions
- Performing tubal surgeries such as salpingectomy or tuboplasty
- Hysterectomy or myomectomy with minimally invasive access
✔️ Benefits of laparoscopy:
- Smaller incisions and reduced scarring
- Less pain and quicker recovery compared to open surgery
- Lower risk of infection and blood loss
- Outpatient or short hospital stay in most cases
Alternatives
While pelvic laparoscopy is highly effective, alternatives may be considered depending on the case.
🔹 Imaging-based evaluation:
- Ultrasound, MRI, or CT scan for diagnosis without surgery
- Less invasive but not always conclusive
🔹 Medical management:
- Medications for endometriosis or hormonal therapy for fibroids
- Symptom control but not a cure in many cases
🔹 Open abdominal surgery (laparotomy):
- Used when conditions are too complex for laparoscopy
- Larger incision, longer hospital stay, and slower recovery
Preparation
Preparation is crucial for safety and success.
➡️ Medical preparation:
- Preoperative imaging (ultrasound, MRI) to plan the procedure
- Blood tests and overall health evaluation
- Fasting for 6–8 hours before surgery if general anesthesia is used
- Discussion about medications, especially blood thinners or hormonal therapy
➡️ Personal preparation:
- Packing essentials for a short hospital stay
- Arranging transportation and home support for recovery days
- Preparing mentally for possible conversion to open surgery if needed
➡️ Mental preparation:
- Understanding the procedure’s benefits and risks
- Counseling for women concerned about fertility outcomes
- Reassurance about minimal scarring and faster recovery
How it’s done
Pelvic laparoscopy in Korea is carried out using state-of-the-art equipment and skilled surgical teams.
✔️ Step 1 – Anesthesia
- General anesthesia administered for comfort and pain-free experience
✔️ Step 2 – Creating access
- Small incision near the navel made
- Carbon dioxide gas pumped into the abdomen to lift abdominal wall and improve visibility
✔️ Step 3 – Inserting the laparoscope
- Thin tube with camera inserted to project images on a monitor
- Additional small incisions may be made for surgical instruments
✔️ Step 4 – Diagnosis or treatment
- Surgeons may examine pelvic organs for abnormalities
- Depending on findings, they may remove cysts, fibroids, adhesions, or treat endometriosis
- Tubes or ovaries may be repaired or removed if necessary
✔️ Step 5 – Completion
- Instruments removed, gas released
- Incisions closed with sutures or surgical glue
✔️ Duration:
- Typically 1–3 hours, depending on complexity
- Outpatient or 1–2 day hospital stay
Recovery
Recovery from pelvic laparoscopy is faster compared to open surgery.
➡️ Immediate recovery:
- Mild abdominal discomfort, bloating, or shoulder pain (from gas used)
- Drowsiness or fatigue from anesthesia
- Monitoring for bleeding or infection
➡️ Physical recovery:
- Return to light activities within 1–2 weeks
- Strenuous exercise or heavy lifting avoided for 3–4 weeks
- Most patients resume work within a few days for minor procedures
➡️ Emotional recovery:
- Relief from diagnosis or treatment of pelvic pain
- Positive impact on fertility in women with endometriosis or adhesions treated
- Counseling available for women recovering from reproductive surgeries
➡️ Key recommendations:
- Adequate rest and hydration
- Pain management with prescribed medication
- Light walking to improve circulation and prevent clots
- Follow-up visits for wound check and surgical outcomes
Treatment option in Korea
Korea is a top destination for pelvic laparoscopy due to advanced surgical expertise, modern hospital facilities, and holistic recovery care.
✔️ Hospital facilities:
- Equipped with high-definition laparoscopic and robotic systems
- Specialized women’s hospitals with fertility and oncology units
- Comprehensive imaging and diagnostic support
✔️ Medical expertise:
- Surgeons trained in minimally invasive and fertility-preserving procedures
- High success rates in treating endometriosis, fibroids, and infertility issues
- Personalized treatment tailored to each patient’s condition
✔️ Postoperative care:
- Access to specialized recovery programs, including Sanhujoriwon-style centers
- Nutritional and physical therapy support for faster healing
- Counseling and emotional support services for women undergoing reproductive surgeries
✔️ Cultural aspect:
- Korea emphasizes comfort, fertility preservation, and long-term women’s health
- Strong family involvement and recovery culture ensure mothers and women receive extended support after surgery
➡️ Highlight: Pelvic laparoscopy in Korea provides safe, minimally invasive solutions for diagnosis and treatment of gynecologic conditions, offering precision, fertility-focused care, and world-class recovery support.